Java Abstract Classes - Abstract Animal Class with Lion, Tiger, and Deer Subclasses
Write a Java program to create an abstract class Animal with abstract methods eat() and sleep(). Create subclasses Lion, Tiger, and Deer that extend the Animal class and implement the eat() and sleep() methods differently based on their specific behavior.
In this program, the Animal class is an abstract class that defines the abstract methods eat() and sleep(). The Lion, Tiger, and Deer classes extend the Animal class and provide their own implementations for the eat() and sleep() methods based on their specific behavior. The Main class demonstrates the usage of these classes by creating objects of each subclass and invoking the eat() and sleep() methods accordingly.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
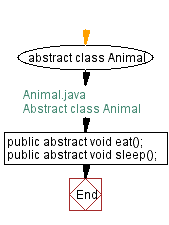
// Animal.java
// Abstract class Animal
// Define abstract class Animal
abstract class Animal {
// Declare abstract method eat
public abstract void eat();
// Declare abstract method sleep
public abstract void sleep();
}
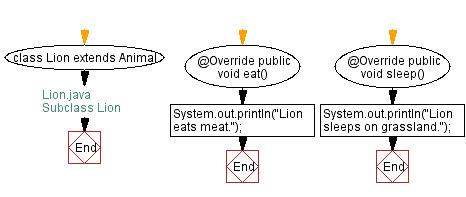
// Lion.java
// Subclass Lion
// Define class Lion that extends Animal
class Lion extends Animal {
// Override the eat method from Animal
@Override
public void eat() {
// Print what the lion eats
System.out.println("Lion eats meat.");
}
// Override the sleep method from Animal
@Override
public void sleep() {
// Print where the lion sleeps
System.out.println("Lion sleeps on grassland.");
}
}
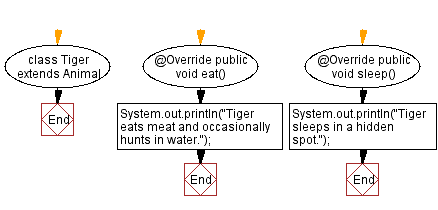
// Tiger.java
// Subclass Tiger
// Define class Tiger that extends Animal
class Tiger extends Animal {
// Override the eat method from Animal
@Override
public void eat() {
// Print what the tiger eats
System.out.println("Tiger eats meat and occasionally hunts in water.");
}
// Override the sleep method from Animal
@Override
public void sleep() {
// Print where the tiger sleeps
System.out.println("Tiger sleeps in a hidden spot.");
}
}
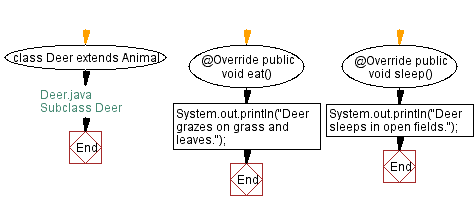
// Deer.java
// Subclass Deer
// Define class Deer that extends Animal
class Deer extends Animal {
// Override the eat method from Animal
@Override
public void eat() {
// Print what the deer eats
System.out.println("Deer grazes on grass and leaves.");
}
// Override the sleep method from Animal
@Override
public void sleep() {
// Print where the deer sleeps
System.out.println("Deer sleeps in open fields.");
}
}
// Main.java
// Subclass Main
// Define public class Main
public class Main {
// Define the main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a new Lion object
Lion lion = new Lion();
// Call the eat method on the Lion object
lion.eat();
// Call the sleep method on the Lion object
lion.sleep();
// Print an empty line for separation
System.out.println();
// Create a new Tiger object
Tiger tiger = new Tiger();
// Call the eat method on the Tiger object
tiger.eat();
// Call the sleep method on the Tiger object
tiger.sleep();
// Print an empty line for separation
System.out.println();
// Create a new Deer object
Deer deer = new Deer();
// Call the eat method on the Deer object
deer.eat();
// Call the sleep method on the Deer object
deer.sleep();
}
}
Output:
Lion eats meat. Lion sleeps on grassland. Tiger eats meat and occasionally hunts in water. Tiger sleeps in a hidden spot. Deer grazes on grass and leaves. Deer sleeps in open fields.
Explanation:
In this program, the Animal class is an abstract class that defines the abstract methods eat() and sleep(). The Lion, Tiger, and Deer classes extend the Animal class and provide their own implementations for the eat() and sleep() methods based on their specific behavior. The Main class demonstrates the usage of these classes by creating objects of each subclass and invoking the eat() and sleep() methods accordingly.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Lion" subclass includes a method to simulate a roar.
- Write a Java program where the "Deer" subclass adds a method to simulate grazing behavior.
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class has a method to track migration patterns.
- Write a Java program where the "Tiger" subclass includes a method to simulate swimming behavior.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Abstract Bank Account Class with Savings and Current Accounts.
NEXT : Abstract Employee class with Manager and Programmer subclasses.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
