Java Polymorphism Programming - Animal Class with Bird and Cat Subclasses for Specific Sounds
Write a Java program to create a base class Animal (Animal Family) with a method called Sound(). Create two subclasses Bird and Cat. Override the Sound() method in each subclass to make a specific sound for each animal.
In the given exercise, here is a simple diagram illustrating polymorphism implementation:
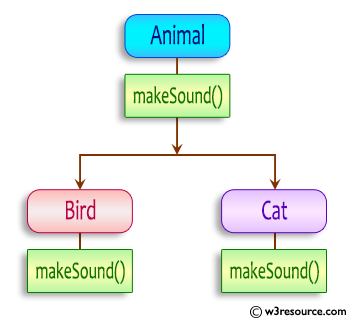
In the above diagram, we have a base class Animal with the makeSound() method. It serves as the superclass for two subclasses, Bird and Cat. Both subclasses override the makeSound() method to provide their own sound implementations.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
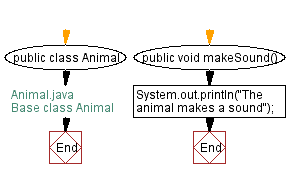
// Animal.java
// Base class Animal
// Declare the Animal class
public class Animal {
// Method to print the sound the animal makes
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("The animal makes a sound");
}
}
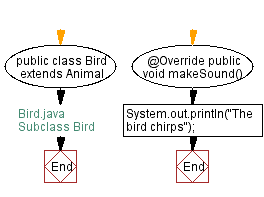
// Bird.java
// Subclass Bird
// Declare the Bird class that extends the Animal class
public class Bird extends Animal {
// Override the makeSound method to provide a specific implementation for Bird
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("The bird chirps");
}
}
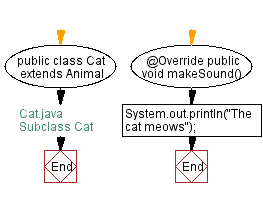
// Cat.java
// Subclass Cat
// Declare the Cat class that extends the Animal class
public class Cat extends Animal {
// Override the makeSound method to provide a specific implementation for Cat
@Override
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("The cat meows");
}
}
// Main.java
// Main class
// Declare the Main class
public class Main {
// Main method: entry point of the program
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance of Animal
Animal animal = new Animal();
// Create an instance of Bird
Bird bird = new Bird();
// Create an instance of Cat
Cat cat = new Cat();
// Call the makeSound method on the Animal instance
animal.makeSound(); // Output: The animal makes a sound
// Call the makeSound method on the Bird instance
bird.makeSound(); // Output: The bird chirps
// Call the makeSound method on the Cat instance
cat.makeSound(); // Output: The cat meows
}
}
Output:
The animal makes a sound The bird chirps The cat meows
Flowchart:
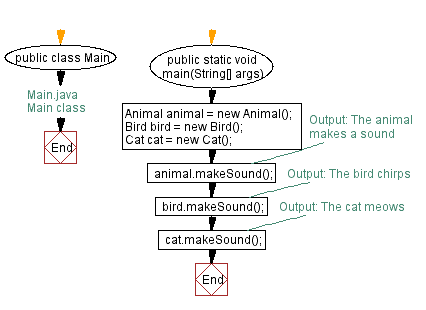
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class includes a move() method describing how each animal moves.
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class supports a lifespan attribute with different values for each subclass.
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class includes a method to check if the animal is domesticated.
- Write a Java program where the "Animal" class implements a feeding behavior method.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Java Polymorphism Exercises Home.
NEXT : Vehicle Class with Car and Bicycle Subclasses for Speed Control.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
