Java: Quick sort Algorithm
1. Quick Sort Implementation
Write a Java program to sort an array of given integers using the Quick sort algorithm.
Quick sort is a comparison sort, meaning it can sort items of any type for which a "less-than" relation (formally, a total order) is defined.
Pictorial presentation - Quick Sort algorithm :
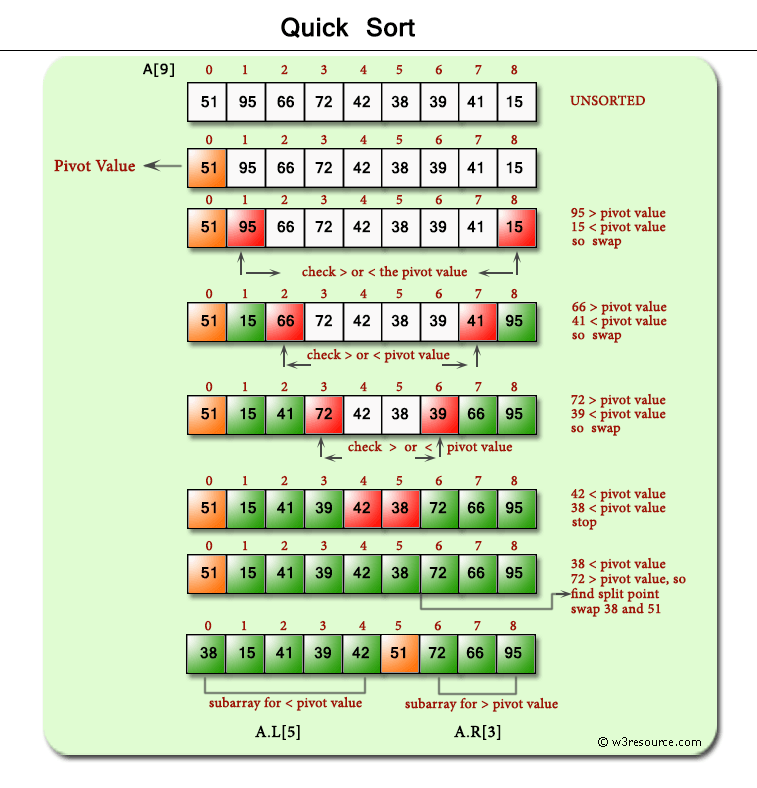
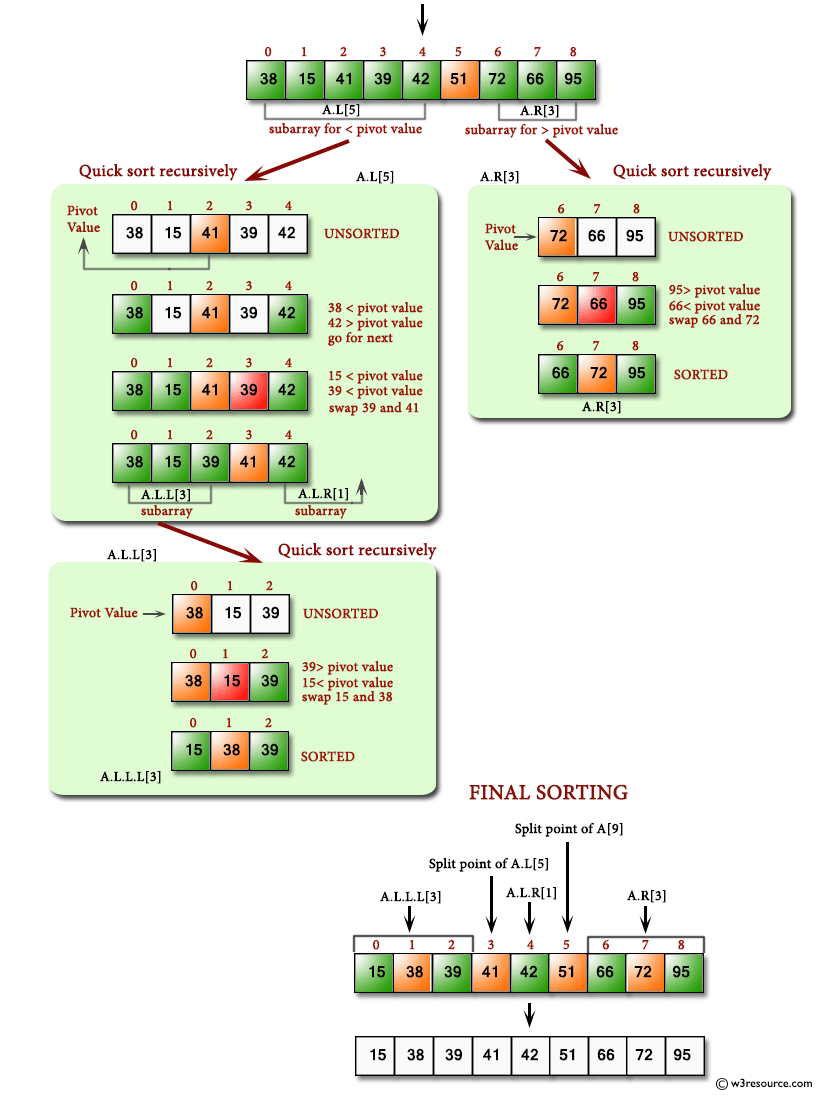
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSort {
private int temp_array[];
private int len;
public void sort(int[] nums) {
if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) {
return;
}
this.temp_array = nums;
len = nums.length;
quickSort(0, len - 1);
}
private void quickSort(int low_index, int high_index) {
int i = low_index;
int j = high_index;
// calculate pivot number
int pivot = temp_array[low_index+(high_index-low_index)/2];
// Divide into two arrays
while (i <= j) {
while (temp_array[i] < pivot) {
i++;
}
while (temp_array[j] > pivot) {
j--;
}
if (i <= j) {
exchangeNumbers(i, j);
//move index to next position on both sides
i++;
j--;
}
}
// call quickSort() method recursively
if (low_index < j)
quickSort(low_index, j);
if (i < high_index)
quickSort(i, high_index);
}
private void exchangeNumbers(int i, int j) {
int temp = temp_array[i];
temp_array[i] = temp_array[j];
temp_array[j] = temp;
}
// Method to test above
public static void main(String args[])
{
QuickSort ob = new QuickSort();
int nums[] = {7, -5, 3, 2, 1, 0, 45};
System.out.println("Original Array:");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
ob.sort(nums);
System.out.println("Sorted Array");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums));
}
}
Sample Output:
Original Array: [7, -5, 3, 2, 1, 0, 45] Sorted Array [-5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 45]
Flowchart:
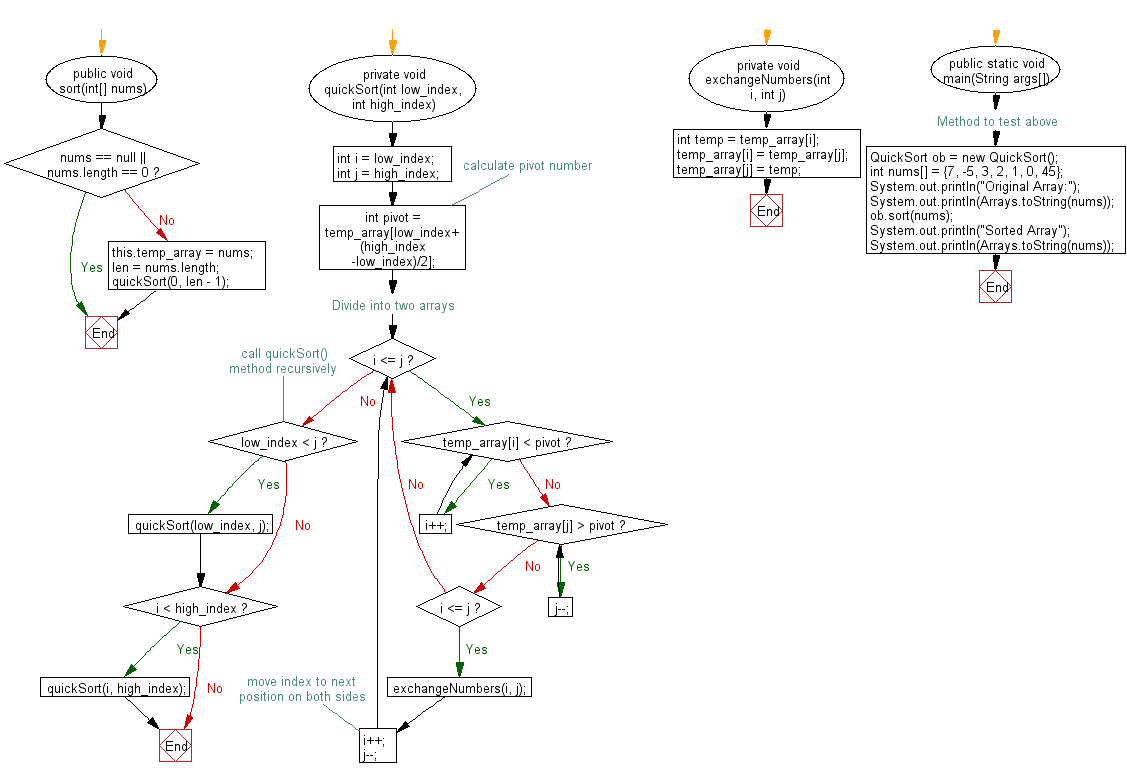
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to implement quick sort recursively with a randomized pivot selection to avoid worst-case performance.
- Write a Java program to perform quick sort on an array of objects using a custom comparator for descending order.
- Write a Java program to modify quick sort to sort only a portion of the array between given indices.
- Write a Java program to implement quick sort that switches to insertion sort when the subarray size falls below a threshold.
Go to:
PREV : Java Sorting Exercises.
NEXT : Bubble Sort Implementation.
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
