Java: Implement a stack using a linked list
29. Implement a stack using a linked list.
Write a Java program to implement a stack using a linked list.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
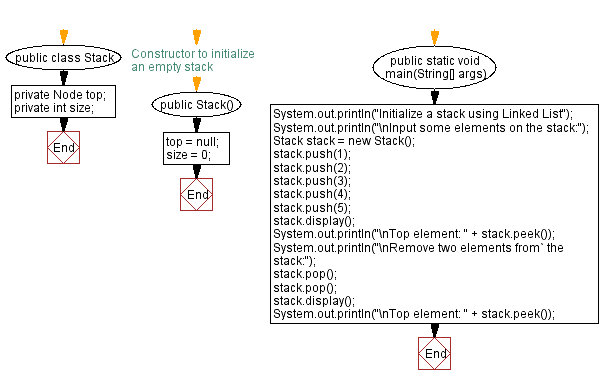
public class Stack {
private Node top;
private int size;
// Constructor to initialize an empty stack
public Stack() {
top = null;
size = 0;
}
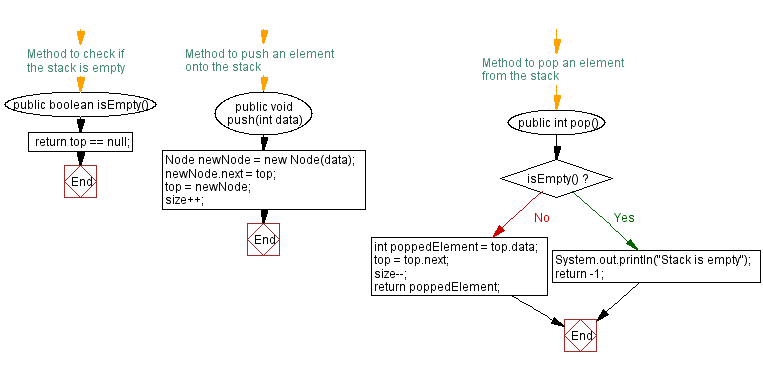
// Method to check if the stack is empty
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == null;
}
// Method to push an element onto the stack
public void push(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = top;
top = newNode;
size++;
}
// Method to pop an element from the stack
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
int poppedElement = top.data;
top = top.next;
size--;
return poppedElement;
}
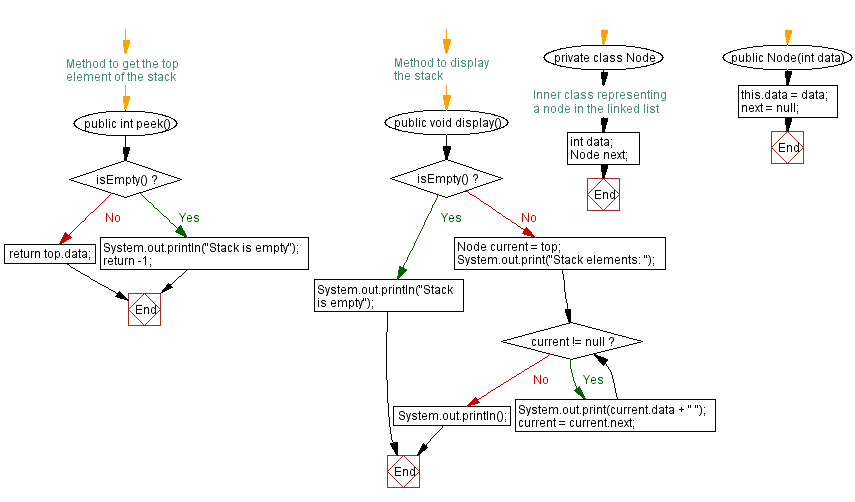
// Method to get the top element of the stack
public int peek() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
return -1;
}
return top.data;
}
// Method to display the stack
public void display() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Stack is empty");
} else {
Node current = top;
System.out.print("Stack elements: ");
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Inner class representing a node in the linked list
private class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
next = null;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Initialize a stack using Linked List");
System.out.println("\nInput some elements on the stack:");
Stack stack = new Stack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.push(4);
stack.push(5);
stack.display();
System.out.println("\nTop element: " + stack.peek());
System.out.println("\nRemove two elements from the stack:");
stack.pop();
stack.pop();
stack.display();
System.out.println("\nTop element: " + stack.peek());
}
}
Sample Output:
Initialize a stack using Linked List Input some elements on the stack: Stack elements: 5 4 3 2 1 Top element: 5 Remove two elements from the stack: Stack elements: 3 2 1 Top element: 3
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to implement a stack using a singly linked list and include methods for push, pop, and peek.
- Write a Java program to create a generic stack using a linked list and implement a method to reverse its elements.
- Write a Java program to implement a stack with a linked list that also tracks its size without using a counter variable.
- Write a Java program to design a stack using a doubly linked list that supports bidirectional traversal.
Go to:
PREV : Create a new stack by removing elements that don't satisfy a condition.
Live Demo:
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
