JavaScript: Compute the factors of a positive integer
JavaScript Function: Exercise-13 with Solution
Compute Factors
Write a JavaScript function to compute the factors of a positive integer.
Sample Solution-1:
JavaScript Code:
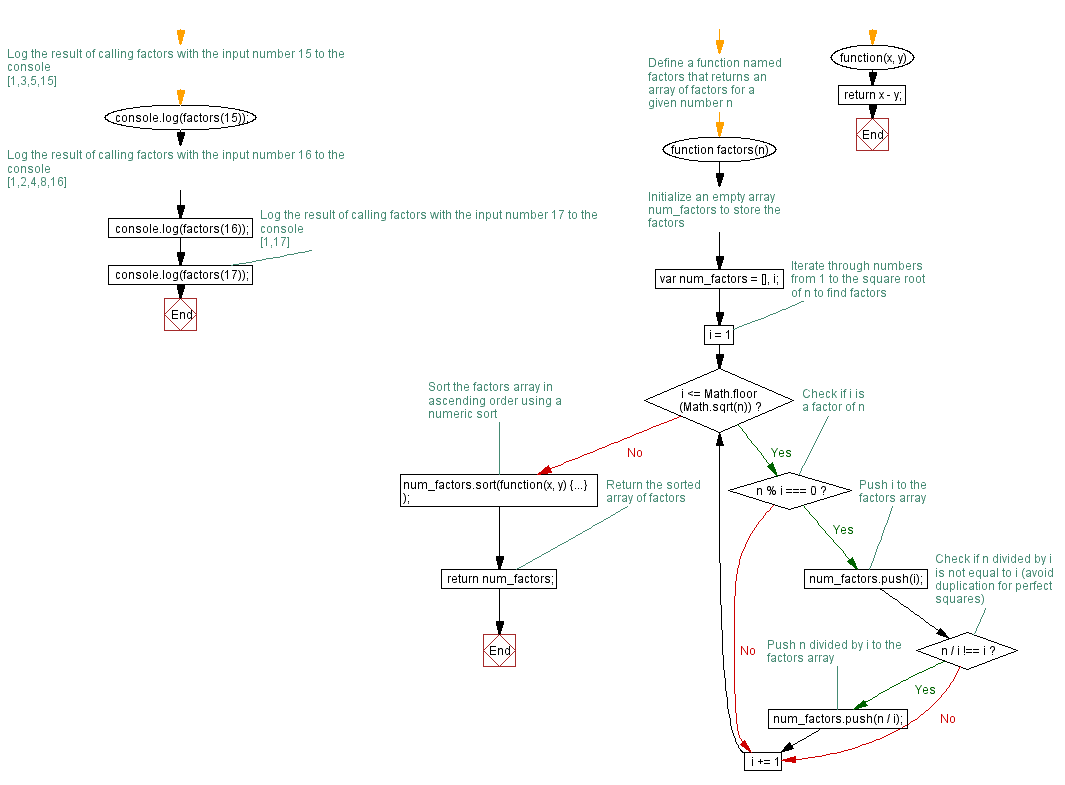
// Define a function named factors that returns an array of factors for a given number n
function factors(n) {
// Initialize an empty array num_factors to store the factors
var num_factors = [], i;
// Iterate through numbers from 1 to the square root of n to find factors
for (i = 1; i <= Math.floor(Math.sqrt(n)); i += 1) {
// Check if i is a factor of n
if (n % i === 0) {
// Push i to the factors array
num_factors.push(i);
// Check if n divided by i is not equal to i (avoid duplication for perfect squares)
if (n / i !== i)
// Push n divided by i to the factors array
num_factors.push(n / i);
}
}
// Sort the factors array in ascending order using a numeric sort
num_factors.sort(function(x, y) {
return x - y;
});
// Return the sorted array of factors
return num_factors;
}
// Log the result of calling factors with the input number 15 to the console
console.log(factors(15)); // [1,3,5,15]
// Log the result of calling factors with the input number 16 to the console
console.log(factors(16)); // [1,2,4,8,16]
// Log the result of calling factors with the input number 17 to the console
console.log(factors(17)); // [1,17]
Output:
[1,3,5,15] [1,2,4,8,16] [1,17]
Flowchart:
Live Demo:
See the Pen JavaScript - Compute the factors of a positive integers-function-ex- 13 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
Sample Solution-2:
JavaScript Code:
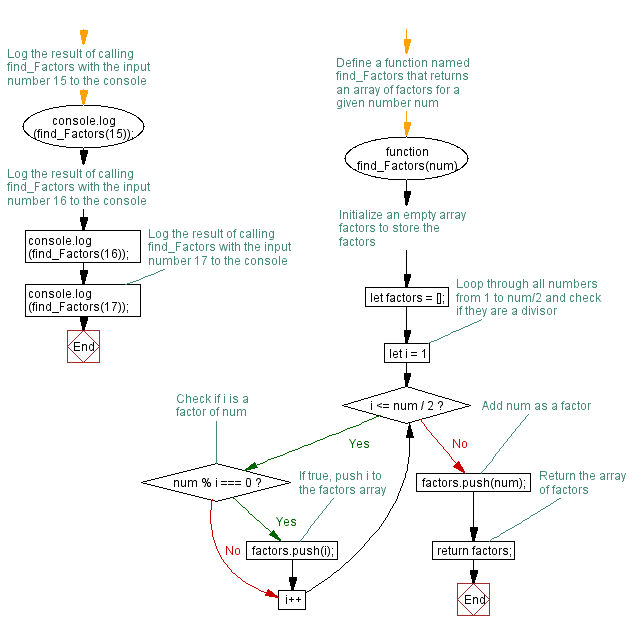
// Define a function named find_Factors that returns an array of factors for a given number num
function find_Factors(num) {
// Initialize an empty array factors to store the factors
let factors = [];
// Loop through all numbers from 1 to num/2 and check if they are a divisor
for (let i = 1; i <= num / 2; i++) {
// Check if i is a factor of num
if (num % i === 0) {
// If true, push i to the factors array
factors.push(i);
}
}
// Add num as a factor
factors.push(num);
// Return the array of factors
return factors;
}
// Log the result of calling find_Factors with the input number 15 to the console
console.log(find_Factors(15));
// Log the result of calling find_Factors with the input number 16 to the console
console.log(find_Factors(16));
// Log the result of calling find_Factors with the input number 17 to the console
console.log(find_Factors(17));
Output:
[1,3,5,15] [1,2,4,8,16] [1,17]
Explanation:
The above function takes a positive integer num as input and loops through all numbers from 1 to num/2 to check if they are divisors of the input number. If a number is a divisor, it is added to an array of factors. Lastly, the function returns an array of factors which includes the input number itself.
Flowchart:
Live Demo:
See the Pen javascript-function-exercise-13-1 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a JavaScript function that computes all factors of a positive integer using a traditional for loop.
- Write a JavaScript function that computes and returns the factors of a number in sorted order.
- Write a JavaScript function that computes the factors of a number using a recursive approach.
- Write a JavaScript function that computes the factors of a number and filters out those that are prime.
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
Previous: Write a JavaScript function which says whether a number is perfect.
Next: Write a JavaScript function to convert an amount to coins.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
