Python: Display some information about the OS where the script is running
OS Information Display
Write a Python program to display some information about the OS where the script is running.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Import the 'platform' module and alias it as 'pl'.
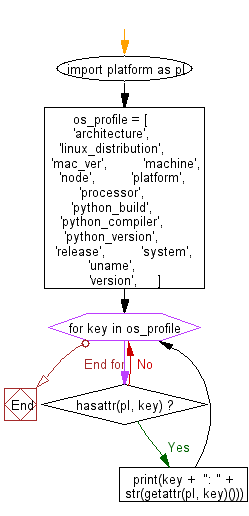
import platform as pl
# List of attributes to retrieve from the 'platform' module.
os_profile = [
'architecture',
'linux_distribution',
'mac_ver',
'machine',
'node',
'platform',
'processor',
'python_build',
'python_compiler',
'python_version',
'release',
'system',
'uname',
'version',
]
# Iterate through the list of attributes.
for key in os_profile:
# Check if the attribute exists in the 'platform' module.
if hasattr(pl, key):
# Print the attribute name and its corresponding value.
print(key + ": " + str(getattr(pl, key)()))
Sample Output:
architecture: ('64bit', 'ELF')
linux_distribution: ('Ubuntu', '16.04', 'xenial')
mac_ver: ('', ('', '', ''), '')
machine: x86_64
node: 9a911676793b
platform: Linux-4.4.0-57-generic-x86_64-with-Ubuntu-16.04-xenial
processor: x86_64
python_build: ('default', 'Nov 17 2016 17:05:23')
python_compiler: GCC 5.4.0 20160609
python_version: 3.5.2
release: 4.4.0-57-generic
system: Linux
uname: uname_result(system='Linux', node='9a911676793b', release='4.4.0-57-generic', version='#78-Ubuntu SMP Fri Dec 9 23:50:32 UTC 2016', machine='x86_64', processor='x86_64')
version: #78-Ubuntu SMP Fri Dec 9 23:50:32 UTC 2016
Explanation:
The above Python code uses the "platform" module to gather and print various system-related information. It specifies a list of attributes related to the operating system and Python environment. It then iterates through this list, checks if each attribute is available in the "platform" module, and prints the attribute name along with its corresponding value if it exists. The information printed includes details about the system architecture, distribution, version, Python build, and more.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to display detailed operating system information including version, architecture, and uptime.
- Write a Python program to list all environment variables available on the operating system.
- Write a Python program to retrieve and display disk usage statistics from the host operating system.
- Write a Python program to monitor and display current CPU and memory usage information of the system.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to get a list of locally installed Python modules.
Next: Write a Python program to check the sum of three elements (each from an array) from three arrays is equal to a target value. Print all those three-element combinations.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
