Creating a Python decorator to log function arguments and return value
1. Create a Decorator to Log Function Arguments and Return Value
Write a Python program to create a decorator that logs the arguments and return value of a function.
The decorator in this code logs the function name, arguments, and return value whenever the decorated function is called.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
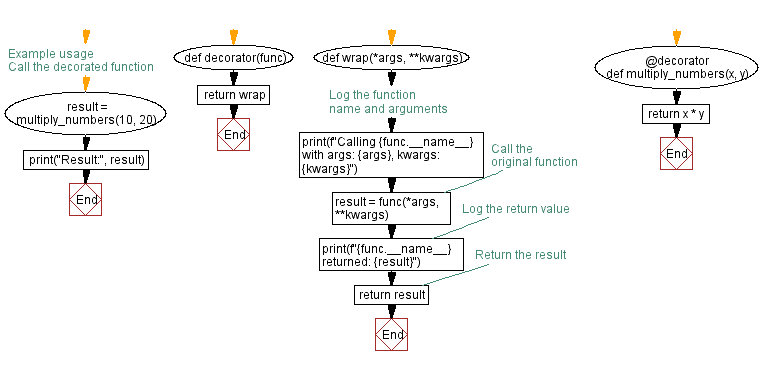
def decorator(func):
def wrap(*args, **kwargs):
# Log the function name and arguments
print(f"Calling {func.__name__} with args: {args}, kwargs: {kwargs}")
# Call the original function
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
# Log the return value
print(f"{func.__name__} returned: {result}")
# Return the result
return result
return wrap
# Example usage
@decorator
def multiply_numbers(x, y):
return x * y
# Call the decorated function
result = multiply_numbers(10, 20)
print("Result:", result)
Sample Output:
Calling multiply_numbers with args: (10, 20), kwargs: {}
multiply_numbers returned: 200
Result: 200
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
- The "decorator()" function is defined with a single parameter func, representing the function to be decorated.
- Inside the decorator function, another function called "wrap()" is defined. This "wrap()" function serves as a wrapper function that adds extra functionality to the original function.
- The "wrap()" function accepts any number of positional and keyword arguments (*args and **kwargs), allowing it to handle functions with varying arguments.
- The wrapper function first logs the function name and its arguments using formatted string literals (f"...").
- The original function is then called using func(*args, **kwargs), and the result is stored in the result variable.
- The wrapper function logs the return value after calling the original function.
- Finally, the wrapper function returns the result.
The "@decorator" syntax is used to apply the "decorator" to the "multiply_numbers()" function, indicating that it should be decorated with the functionality provided by the "decorator()" function.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python decorator that logs the function name, its input parameters, and output to the console using print().
- Write a Python decorator that writes the function’s arguments and return value to a file each time the function is called.
- Write a Python decorator that stores the log of a function call in a global list for later analysis.
- Write a Python decorator that conditionally logs calls based on a debug flag passed as an argument to the decorator.
Go to:
Previous: Python Decorator Exercises Home.
Next: Creating a Python decorator to measure function execution time.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
