Creating a Python decorator to measure function execution time
2. Create a Decorator to Measure Function Execution Time
Write a Python program to create a decorator function to measure the execution time of a function.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
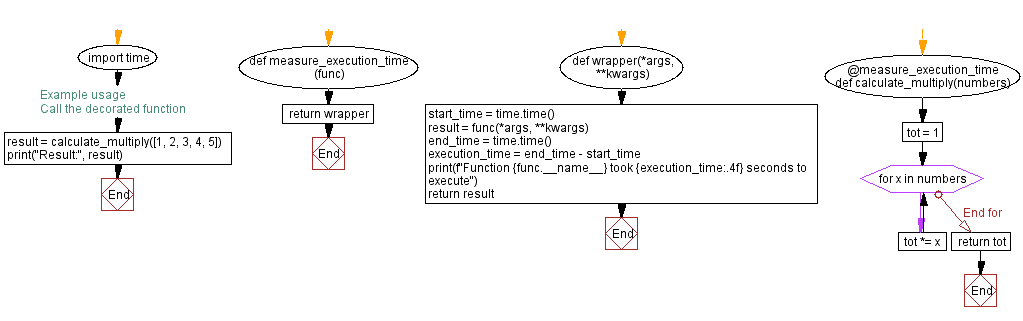
import time
def measure_execution_time(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start_time = time.time()
result = func(*args, **kwargs)
end_time = time.time()
execution_time = end_time - start_time
print(f"Function {func.__name__} took {execution_time:.4f} seconds to execute")
return result
return wrapper
# Example usage
@measure_execution_time
def calculate_multiply(numbers):
tot = 1
for x in numbers:
tot *= x
return tot
# Call the decorated function
result = calculate_multiply([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
print("Result:", result)
Sample Output:
Function calculate_multiply took 0.0000 seconds to execute Result: 120
Explanation:
In the above exercise -
- The execution_time variable is calculated by subtracting start_time from end_time, representing the elapsed time.
- The execution time is printed to the console, indicating which function was measured and how long it took. This is done using the format string f"Function {func.__name__} took {execution_time:.4f} seconds to execute". The .4f format specifier ensures four decimal places for execution time.
- Finally, the original function result is returned.
The @execution_time syntax is used to apply the execution_time decorator to the calculate_multiply function. This indicates that it should be decorated with the functionality provided by the execution_time function.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python decorator that computes and prints the execution time of a function using the time.time() method.
- Write a Python decorator that returns a tuple of (result, execution_time) when a function is called.
- Write a Python decorator that logs the execution time only if it exceeds a specified threshold.
- Write a Python decorator that uses functools.wraps to preserve function metadata while timing its execution.
Go to:
Previous: Creating a Python decorator to log function arguments and return value.
Next: Creating a Python decorator to convert function return value.
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
