Python: Check if a given list is strictly increasing or not
Check Strictly Increasing List
Write a Python program to check if a given list increases strictly. Moreover, if removing only one element from the list results in a strictly increasing list, we still consider the list true.
Visual Presentation:

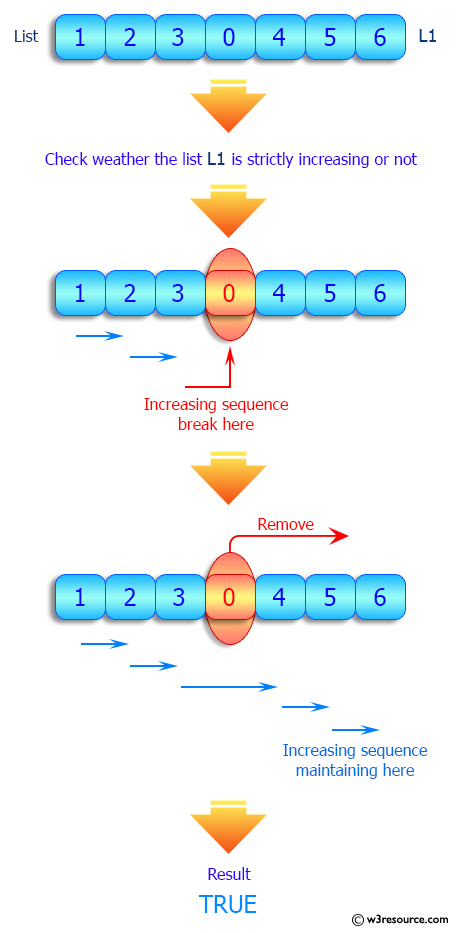
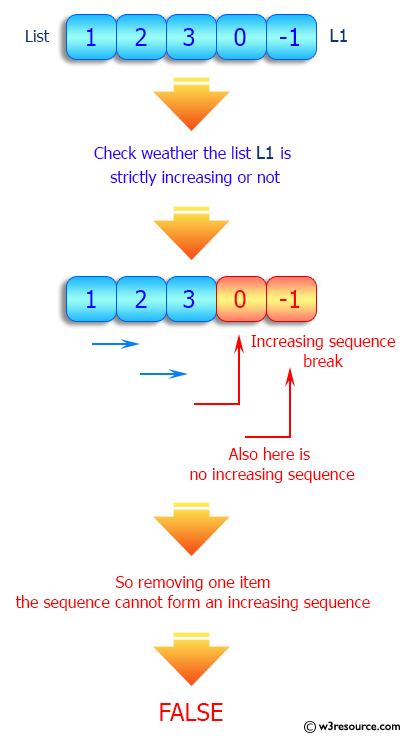
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
# Source: https://bit.ly/3qZqcwm
# Define a function called 'almost_increasing_sequence' that checks if a given sequence is an almost increasing sequence.
def almost_increasing_sequence(sequence):
# Check if the length of the sequence is less than 3, and if so, return True.
if len(sequence) < 3:
return True
# Extract the first two elements 'a' and 'b' from the sequence using extended unpacking.
a, b, *sequence = sequence
# Initialize a variable 'skipped' to keep track of the number of skipped elements.
skipped = 0
# Iterate through the remaining elements 'c' in the sequence.
for c in sequence:
if a < b < c: # Check if the current subsequence is in increasing order (e.g., 1 < 2 < 3).
a, b = b, c # Update 'a' and 'b' for the next comparison and continue.
continue
elif b < c: # Check if the current subsequence has two increasing elements and one out of order (e.g., 1 < 2, but 2 < 0).
a, b = b, c # Update 'a' and 'b' for the next comparison.
elif a < c: # Check if the current subsequence has one increasing element and two out of order (e.g., 1 < 0, but 0 < 3).
a, b = a, c # Update 'a' for the next comparison.
skipped += 1 # Increment the 'skipped' count to track the number of skipped elements.
if skipped == 2: # If two or more elements have been skipped, return False.
return False
return a < b # Check if the final 'a' and 'b' form an increasing subsequence.
# Test cases to check the behavior of the 'almost_increasing_sequence' function.
print(almost_increasing_sequence([]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 3]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([3, 1, 2]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 3, 0, 4, 5, 6]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 3, 0]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 0, 3]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([10, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 10, 3, 4]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 3, 12, 4, 5]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([3, 2, 1]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 0, -1]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([5, 6, 1, 2]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([1, 2, 3, 0, -1]))
print(almost_increasing_sequence([10, 11, 12, 2, 3, 4, 5]))
Sample Output:
True True True True True True True True True True True False False False False False
Flowchart:
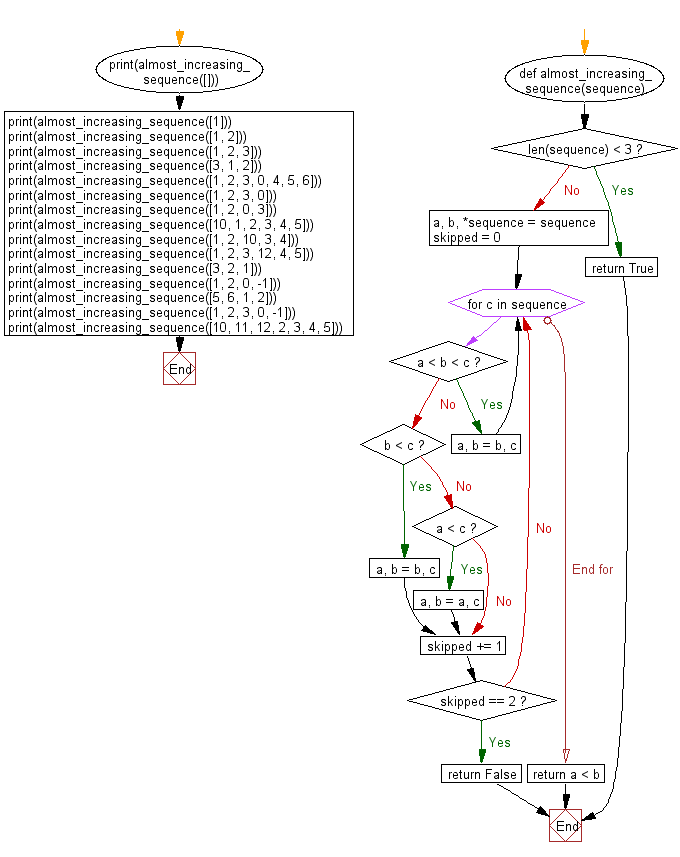
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to determine if a list can be made strictly increasing by removing at most one element and return the index of the removed element, if any.
- Write a Python program to check if the subsequence of even-indexed elements in a list is strictly increasing.
- Write a Python program to verify whether modifying a single element in a list can yield a strictly increasing sequence.
- Write a Python program to check if a list becomes strictly increasing after removing the first occurrence of a duplicate element.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to remove first specified number of elements from a given list satisfying a condition.
Next: Write a Python program to find the last occurrence of a specified item in a given list.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
