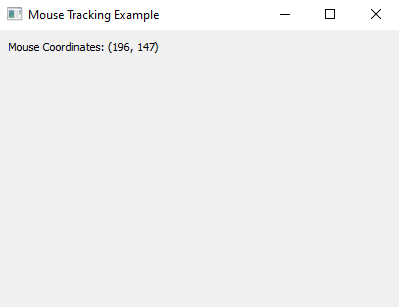
Python PyQt mouse tracking example
Write a Python program that creates a window using PyQt. The window will display the mouse coordinates, and update in real-time as you move the mouse cursor within the window.
From doc.qt.io:
QApplication Class: The QApplication class manages the GUI application's control flow and main settings.
QMainWindow Class: The QMainWindow class provides a main application window.
QLabel Class: The QLabel widget provides a text or image display.
Qt module: PyQt5 is a set of Python bindings for the Qt application framework. It allows us to use Qt, a popular C++ framework, to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in Python.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
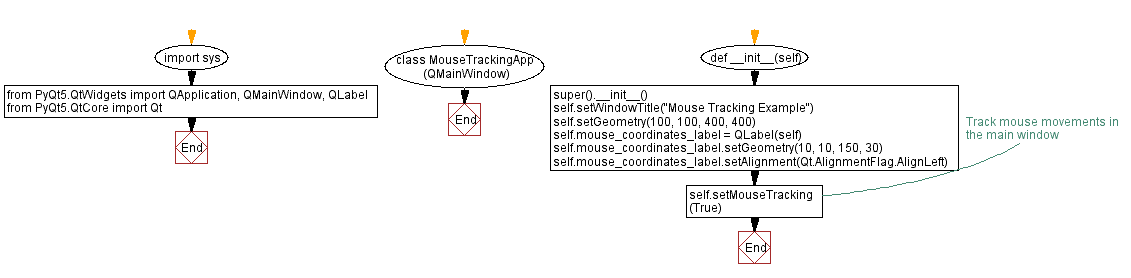
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QLabel
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt
class MouseTrackingApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Mouse Tracking Example")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 400, 400)
self.mouse_coordinates_label = QLabel(self)
self.mouse_coordinates_label.setGeometry(10, 10, 150, 30)
self.mouse_coordinates_label.setAlignment(Qt.AlignmentFlag.AlignLeft)
# Track mouse movements in the main window
self.setMouseTracking(True)
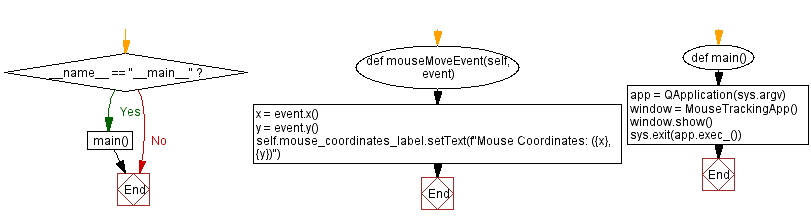
def mouseMoveEvent(self, event):
x = event.x()
y = event.y()
self.mouse_coordinates_label.setText(f"Mouse Coordinates: ({x}, {y})")
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = MouseTrackingApp()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the necessary PyQt5 modules.
- Create a "MouseTrackingApp" class that inherits from "QMainWindow".
- Inside the "MouseTrackingApp" class, we set up a 'QLabel' (self.mouse_coordinates_label) to display the mouse coordinates. We position this label in the top-left corner of the window and align the text to the left.
- Enable mouse tracking for the main window using self.setMouseTracking(True). This allows the window to continuously receive mouse 'move' events.
- Override the mouseMoveEvent method to capture mouse movement. Inside this method, we extract the x and y coordinates from the event object and update the label text to display the current mouse coordinates.
- Finally, we create an instance of MouseTrackingApp and run the PyQt5 application.
Output:
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor:
Previous: Python PyQt drag and drop labels example.
Next: Python PyQt5 drawing application.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.