Python PyQt5 drawing application
Write a Python program to build a PyQt5 application that allows users to draw shapes and freehand lines on a canvas.
From doc.qt.io:
QApplication Class: The QApplication class manages the GUI application's control flow and main settings.
QMainWindow Class: The QMainWindow class provides a main application window.
QWidget Class: The QWidget class is the base class of all user interface objects.
QPainter Class: The QPainter class performs low-level painting on widgets and other paint devices.
QPen Class: The QPen class defines how a QPainter should draw lines and outlines of shapes.
Qt module: PyQt5 is a set of Python bindings for the Qt application framework. It allows us to use Qt, a popular C++ framework, to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) in Python.
QPoint Class: The QPoint class defines a point in the plane using integer precision.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import sys
from PyQt5.QtWidgets import QApplication, QMainWindow, QWidget
from PyQt5.QtGui import QPainter, QPen
from PyQt5.QtCore import Qt, QPoint
class DrawingApp(QMainWindow):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.setWindowTitle("Drawing Application")
self.setGeometry(100, 100, 800, 600)
self.canvas = CanvasWidget(self)
self.setCentralWidget(self.canvas)
class CanvasWidget(QWidget):
def __init__(self, parent=None):
super().__init__(parent)
self.parent = parent
self.setGeometry(0, 0, 800, 600)
self.drawing = False
self.last_point = QPoint()
self.current_point = QPoint()
self.shapes = []
def mousePressEvent(self, event):
if event.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
self.drawing = True
self.last_point = event.pos()
self.current_point = event.pos()
def mouseMoveEvent(self, event):
if self.drawing:
self.current_point = event.pos()
self.update()
def mouseReleaseEvent(self, event):
if event.button() == Qt.LeftButton:
self.drawing = False
shape = (self.last_point, self.current_point)
self.shapes.append(shape)
self.update()
def paintEvent(self, event):
painter = QPainter(self)
pen = QPen()
pen.setWidth(2)
pen.setColor(Qt.black)
painter.setPen(pen)
for shape in self.shapes:
painter.drawLine(shape[0], shape[1])
if self.drawing:
painter.drawLine(self.last_point, self.current_point)
def main():
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = DrawingApp()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec_())
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- Import the necessary PyQt5 modules.
- "mousePressEvent" starts drawing when the left mouse button is clicked, and "mouseReleaseEvent" stops drawing when the button is released.
- "mouseMoveEvent" updates the current line endpoint while drawing.
- Maintain a list of line shapes in the self.shapes list.
- In the "paintEvent()" method, we use a QPainter to draw the shapes and lines on the canvas.
- The main function sets up the application and runs it.
Output:
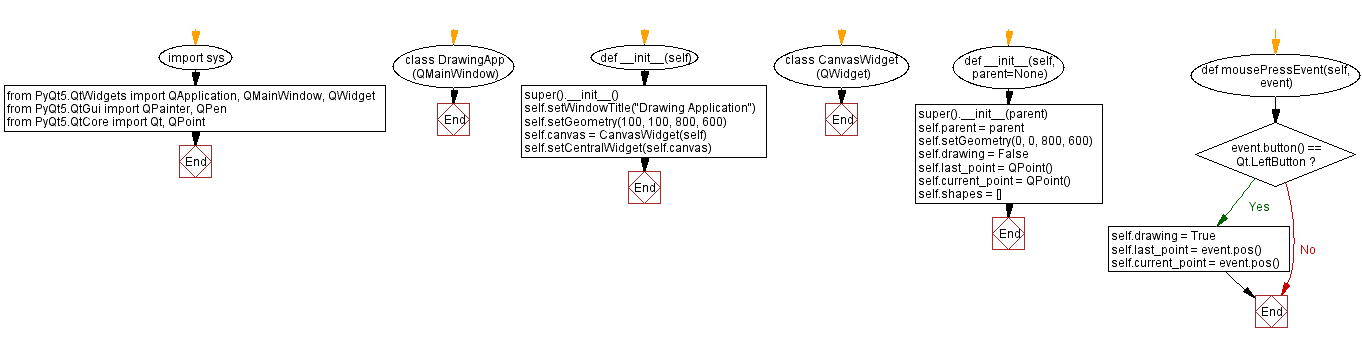
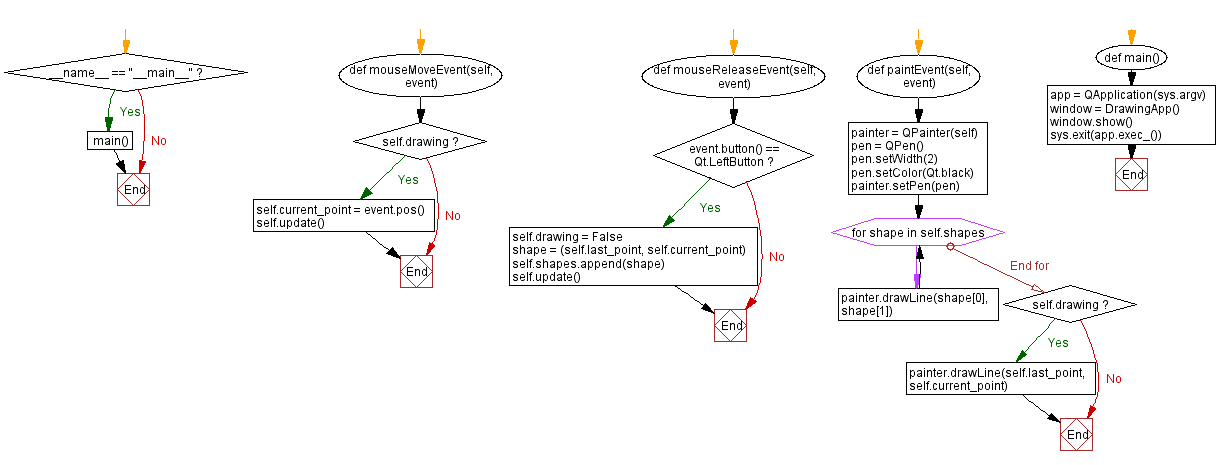
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor:
Previous: Python PyQt mouse tracking example.
Next: Python PyQt5 image annotation application.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.