Python: Calculate the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle
Triangle Hypotenuse Calculator
Write a Python program to calculate the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle.
From Wikipedia,
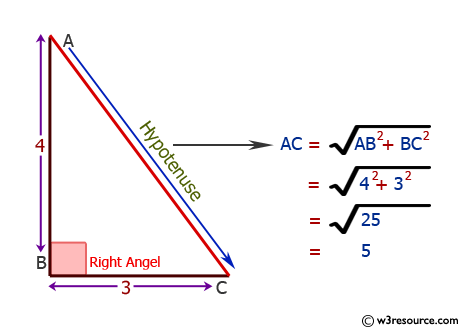
A right triangle or right-angled triangle, or more formally an orthogonal triangle, is a triangle in which one angle is a right angle. The relation between the sides and angles of a right triangle is the basis for trigonometry. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse.
If the lengths of all three sides of a right triangle are integers, the triangle is said to be a Pythagorean triangle and its side lengths are collectively known as a Pythagorean triple.
Pictorial Presentation:
Sample Solution-1:
Python Code :
# Import the sqrt function from the math module to calculate the square root.
from math import sqrt
# Prompt the user to input the lengths of the shorter triangle sides.
print("Input lengths of shorter triangle sides:")
# Read and convert the input for side 'a' to a floating-point number.
a = float(input("a: "))
# Read and convert the input for side 'b' to a floating-point number.
b = float(input("b: "))
# Calculate the length of the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem.
c = sqrt(a**2 + b**2)
# Print the calculated length of the hypotenuse.
print("The length of the hypotenuse is:", c)
Sample Output:
Input lengths of shorter triangle sides: a: 3 b: 4 The length of the hypotenuse is: 5.0
Explanation:
from math import sqrt: The sqrt() function is imported from the math module to allow the calculation of the square root of a value.
a = float(input("a: "))
b = float(input("b: "))
In the above code -
The input() function is used to prompt the user to enter the lengths of the shorter sides of a right triangle, and the float() function is used to convert the input to floating-point values, which are stored in the variables a and b.
c = sqrt(a**2 + b**2): The length of the hypotenuse is then calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse (c) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (a and b). The square root of this sum is taken using the sqrt() function, and the result is stored in the variable c.
Finally, the print() function prints a message to the console in the format "The length of the hypotenuse is: c", where c is the calculated length of the hypotenuse.
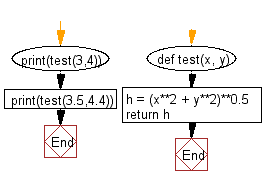
Sample Solution-2:
Python Code:
# Define a function named 'test' that takes two parameters 'x' and 'y'.
def test(x, y):
# Calculate the length of the hypotenuse (h) using the Pythagorean theorem.
h = (x**2 + y**2)**0.5
# Return the calculated hypotenuse.
return h
# Call the 'test' function with different values and print the results.
print(test(3, 4)) # Calculate the hypotenuse for a right triangle with sides 3 and 4.
print(test(3.5, 4.4)) # Calculate the hypotenuse for a right triangle with sides 3.5 and 4.4.
Sample Output:
5.0 5.622277118748239
Explanation:
In the above code -
The test() function takes two arguments, x and y, which represent the lengths of the legs of a right triangle. The length of the hypotenuse is calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, which states that the square of the length of the hypotenuse (h) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides (x and y). The square root of this sum is taken using the exponentiation operator (**) with a value of 0.5, and the result is stored in the variable h. The function returns the value of h.
The code then calls the test() function with two sets of arguments, (3, 4) and (3.5, 4.4), and prints the results to the console using the print() function.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to calculate the length of the other two sides of a right-angled triangle given the hypotenuse and one side.
- Write a Python program to determine if three given side lengths form a right-angled triangle.
- Write a Python program to compute the hypotenuse using an alternative formula that avoids floating-point precision issues.
- Write a Python program to find the missing side of a right-angled triangle given the other two sides.
Go to:
Previous: Write a Python program to convert height (in feet and inches) to centimeters.
Next: Write a Python program to convert the distance (in feet) to inches, yards, and miles.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
