Create a dashboard with Python and Tkinter
Write a Python program that implements a dashboard interface with multiple widgets, such as graphs and statistics. Use the Grid geometry manager to create a responsive layout.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk
import random
class DashboardApp:
def __init__(self, parent):
self.parent = parent
self.parent.title("Dashboard")
# Create a Frame to hold the dashboard widgets
self.dashboard_frame = ttk.Frame(parent)
self.dashboard_frame.grid(sticky="nsew")
# Create and place widgets on the dashboard using the Grid geometry manager
self.create_widgets()
def create_widgets(self):
# Create and place labels
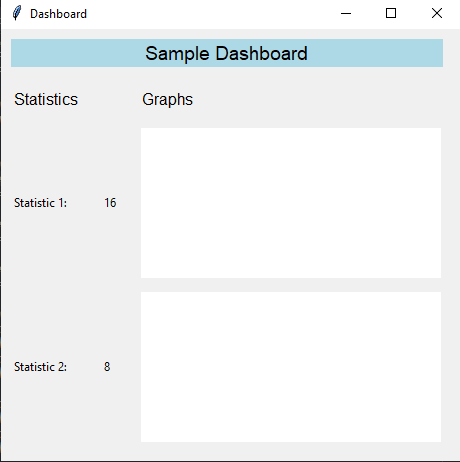
label1 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text="Sample Dashboard", bg="lightblue", font=("Helvetica", 14))
label1.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=10, pady=10, sticky="nsew")
label2 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text="Statistics", font=("Helvetica", 12))
label2.grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10, pady=10, sticky="w")
label3 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text="Graphs", font=("Helvetica", 12))
label3.grid(row=1, column=2, padx=10, pady=10, sticky="w")
# Create and place statistics widgets (placeholders)
stat_label1 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text="Statistic 1:")
stat_label1.grid(row=2, column=0, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="w")
stat_value1 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text=str(random.randint(1, 100)))
stat_value1.grid(row=2, column=1, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="w")
stat_label2 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text="Statistic 2:")
stat_label2.grid(row=3, column=0, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="w")
stat_value2 = tk.Label(self.dashboard_frame, text=str(random.randint(1, 100)))
stat_value2.grid(row=3, column=1, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="w")
# Create and place graph widgets (placeholders)
# You can use Matplotlib or other libraries for more advanced graphs
graph1 = tk.Canvas(self.dashboard_frame, bg="white", width=300, height=150)
graph1.grid(row=2, column=2, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="nsew")
graph2 = tk.Canvas(self.dashboard_frame, bg="white", width=300, height=150)
graph2.grid(row=3, column=2, padx=10, pady=5, sticky="nsew")
# Configure grid layout weights to make the dashboard responsive
self.dashboard_frame.columnconfigure(0, weight=1)
self.dashboard_frame.columnconfigure(1, weight=1)
self.dashboard_frame.columnconfigure(2, weight=1)
self.dashboard_frame.rowconfigure(2, weight=1)
self.dashboard_frame.rowconfigure(3, weight=1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
parent = tk.Tk()
app = DashboardApp(parent)
parent.mainloop()
Explanation:
In the exercise above -
- We create a "DashboardApp" class to encapsulate the dashboard application.
- Grid geometry manager creates and places labels, statistics placeholders, and graph placeholders.
- Grid layouts are configured with weights to make the dashboard responsive to window resizing.
- Placeholder values for statistics and graphs are generated randomly. For more advanced graphing capabilities, you can replace these placeholders with real data and use libraries like Matplotlib.
Sample Output:
Flowchart:
Go to:
Previous: Create a contact information form with Python Tkinter.
Next: Create a Python Tkinter auditorium reservation system.
Python Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.