C Exercises: Compute the sum of values in a given array of integers except the number 17
52. Sum Array Excluding 17
Write a C program to compute the sum of values in a given array of integers except the number 17. Return 0 if the given array has no integers.
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Function prototype for 'test'
int test(int nums[], int arr_size);
int main(void){
// Declaration and initialization of an integer array 'array1'
int array1[] = {1, 2, 5, 7, 9, 10, 12, 17};
// Calculating the size of the array 'array1'
int arr_size = sizeof(array1)/sizeof(array1[0]);
// Printing a message indicating the purpose of the program
printf("Sum of values in the array of integers except the number 17: ");
// Printing the result of the 'test' function for the array 'array1'
printf("%d",test(array1, arr_size));
}
// Definition of the 'test' function
int test(int nums[], int arr_size)
{
// Declaration of a variable 'sum' to accumulate the sum of values
int sum = 0;
// Looping through the elements of the array
for (int i = 0; i < arr_size; i++)
{
// Checking if the current element is not equal to 17
if (nums[i] != 17)
{
// Adding the value to 'sum' if it's not equal to 17
sum += nums[i];
}
else
{
// Skipping the element if it is equal to 17
i++;
}
}
// Returning the accumulated sum
return sum;
}
Sample Output:
Sum of values in the array of integers except the number 17: 46
Pictorial Presentation:
Flowchart:
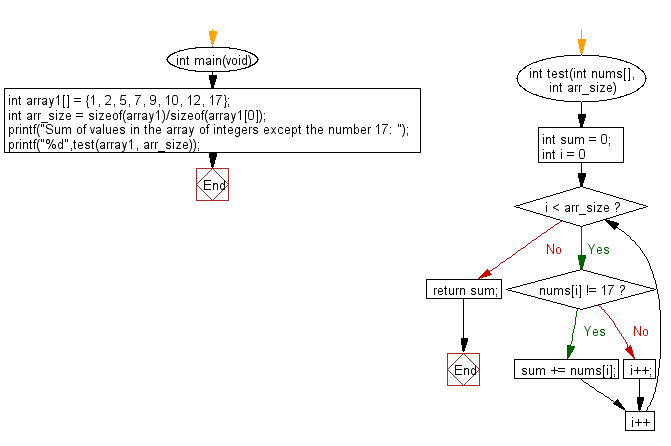
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to compute the sum of an array excluding negative numbers.
- Write a C program to sum elements of an array, ignoring any numbers divisible by 3.
- Write a C program to compute the sum of an array while excluding the maximum value.
- Write a C program to calculate the sum of an array excluding duplicate numbers.
Go to:
PREV : Count Even Elements in Array.
NEXT : Sum Array Excluding Pattern Starting with 5.
C Programming Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
