C Exercises: Find the Armstrong number for a given range of number
30. Armstrong Numbers in a Range
Write a C program to find the Armstrong number for a given range of number.
An Armstrong number (or narcissistic number) is a number that is equal to the sum of its own digits each raised to the power of the number of digits. The program should prompt the user for the lower and upper limits of the range. It should iterate through each number in that range, checking if it meets the Armstrong number condition, and print out any Armstrong numbers found.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
/*
When the sum of the cube of the individual digits of a number
is equal to that number, the number is called Armstrong number.
For example 153. Sum of its divisor is 13 + 53 + 33 = 1 + 125 + 27 = 153
*/
#include <stdio.h> // Include the standard input/output header file.
void main(){
int num, r, sum, temp; // Declare variables for the input number, remainder, sum, and a temporary variable.
int stno, enno; // Declare variables for the starting and ending range.
printf("Input starting number of range: "); // Prompt the user to input the starting range.
scanf("%d", &stno); // Read the starting range from the user.
printf("Input ending number of range : "); // Prompt the user to input the ending range.
scanf("%d", &enno); // Read the ending range from the user.
printf("Armstrong numbers in given range are: "); // Print a message indicating that Armstrong numbers will be displayed.
for(num = stno; num <= enno; num++){ // Start a loop to iterate through the numbers in the specified range.
temp = num; // Set 'temp' to the current number for manipulation.
sum = 0; // Initialize 'sum' to zero.
while(temp != 0){ // Start a loop to extract digits from 'temp'.
r = temp % 10; // Get the last digit of 'temp'.
temp = temp / 10; // Remove the last digit from 'temp'.
sum = sum + (r * r * r); // Calculate the sum of cubes of each digit.
}
if(sum == num) // If the sum of cubes of digits is equal to the original number.
printf("%d ", num); // Print the number, as it's an Armstrong number.
}
printf("\n"); // Print a newline to separate the output.
}
Output:
Input starting number of range: 1 Input ending number of range : 1000 Armstrong numbers in given range are: 1 153 370 371 407
Flowchart:
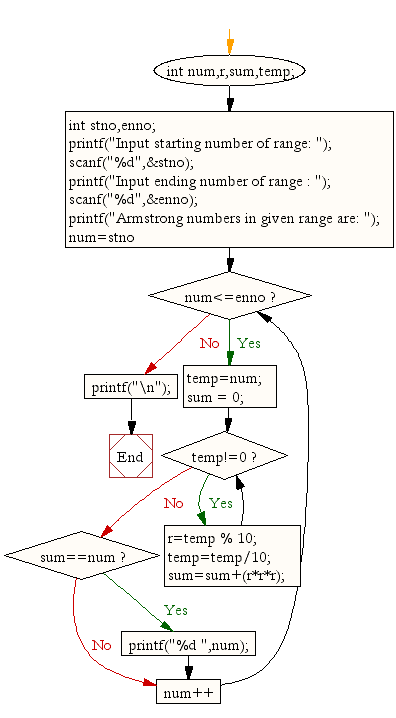
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C program to find all Armstrong numbers within a specified range using iterative loops.
- Write a C program to list Armstrong numbers in a range and count the total number found.
- Write a C program to identify Armstrong numbers within a range using a recursive power function.
- Write a C program to output Armstrong numbers in a range along with the digit count for each.
Go to:
PREV : Armstrong Number Check.
NEXT : Diamond Pattern Display.
C Programming Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
