C++ File handling: Split a large text file
10. Split a Large Text File into Smaller Files
Write a C++ program to split a large text file into smaller files of equal size.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <iostream> // Including the input/output stream library
#include <fstream> // Including the file stream library
#include <string> // Including the string handling library
#include <vector> // Including the vector container
// Function to split a file into smaller chunks
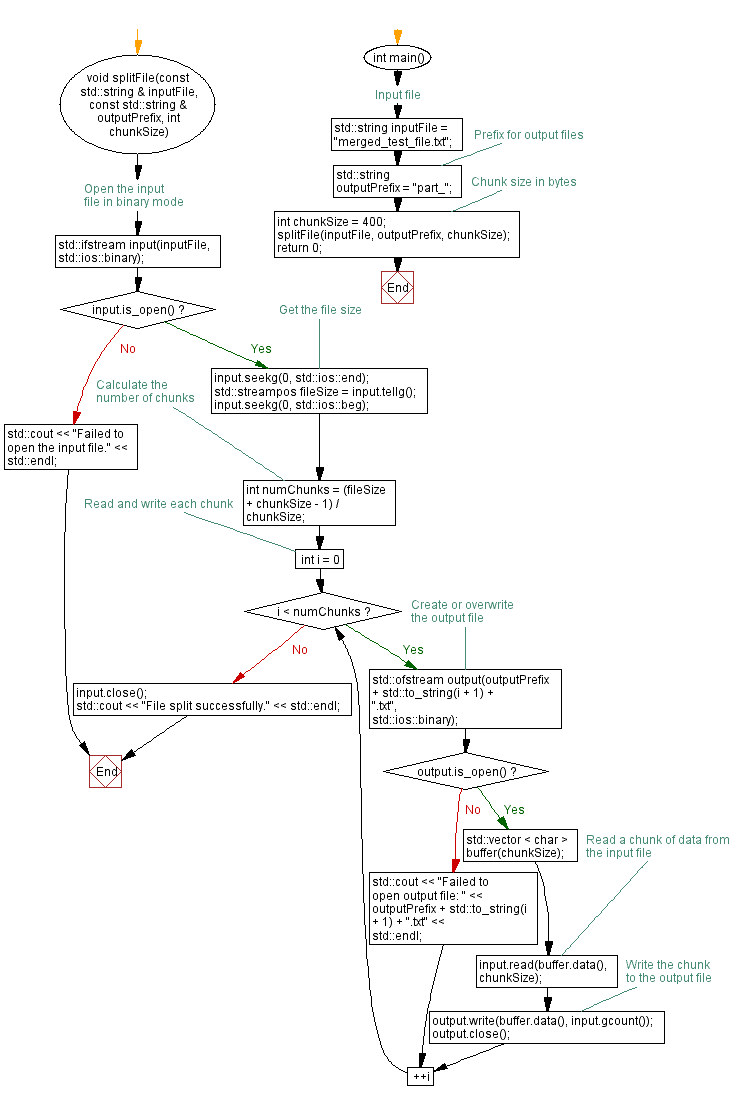
void splitFile(const std::string & inputFile, const std::string & outputPrefix, int chunkSize) {
// Open the input file in binary mode
std::ifstream input(inputFile, std::ios::binary); // Open the input file in binary mode
if (input.is_open()) { // Check if the input file was successfully opened
// Get the file size
input.seekg(0, std::ios::end); // Move the file pointer to the end of the file
std::streampos fileSize = input.tellg(); // Get the current position of the file pointer, indicating the file size
input.seekg(0, std::ios::beg); // Move the file pointer back to the beginning of the file
// Calculate the number of chunks
int numChunks = (fileSize + chunkSize - 1) / chunkSize; // Calculate the number of chunks based on file size and chunk size
// Read and write each chunk
for (int i = 0; i < numChunks; ++i) { // Iterate through each chunk
// Create or overwrite the output file with an incremental suffix
std::ofstream output(outputPrefix + std::to_string(i + 1) + ".txt", std::ios::binary); // Create or overwrite the output file
if (output.is_open()) { // Check if the output file was successfully opened
std::vector<char> buffer(chunkSize); // Create a buffer to hold the chunk data
// Read a chunk of data from the input file
input.read(buffer.data(), chunkSize); // Read chunkSize number of bytes into the buffer
// Write the chunk to the output file
output.write(buffer.data(), input.gcount()); // Write the read data from the buffer to the output file
output.close(); // Close the output file
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to open output file: " << outputPrefix + std::to_string(i + 1) + ".txt" << std::endl; // Display an error message if output file opening failed
}
}
input.close(); // Close the input file
std::cout << "File split successfully." << std::endl; // Display a success message after splitting
} else {
std::cout << "Failed to open the input file." << std::endl; // Display an error message if input file opening failed
}
}
int main() {
std::string inputFile = "merged_test_file.txt"; // Input file
std::string outputPrefix = "part_"; // Prefix for output files
int chunkSize = 400; // Chunk size in bytes
splitFile(inputFile, outputPrefix, chunkSize); // Call the function to split the file
return 0; // Return 0 to indicate successful execution
}
Sample Output:
File split successfully
Explanation:
In the above exercise,
- The function splitFile() takes three parameters: inputFile (the name of the input file to be split), outputPrefix (the prefix for the output files), and chunkSize (the size of each chunk in bytes).
- The program opens the input file using std::ifstream in binary mode. It then determines the size of the input file using the seekg() and tellg() functions.
- Next, it calculates the number of chunks required to split the file based on the specified chunk size.
- The program iterates over each chunk, creates or overwrites the corresponding output file using std::ofstream, and reads a chunk of data from the input file using a std::vector<char> buffer.
- Each chunk is then written to the output file using the write function.
- After all the chunks have been written, the input and output files are closed, and a success message is displayed.
Note:
Content of "merged_test_file.txt"
Many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Embarcadero, Oracle, and IBM.
C++ is a high-level, general-purpose programming language created by Danish computer scientist Bjarne Stroustrup.
It is almost always implemented in a compiled language.
Modern C++ currently has object-oriented, generic, and functional features, in addition to facilities for low-level memory manipulation.
First released in 1985 as an extension of the C programming language, it has since expanded significantly over time.
Content of the split files
part_1.txt
Many vendors provide C++ compilers, including the Free Software Foundation, LLVM, Microsoft, Intel, Embarcadero, Oracle, and IBM.
C++ is a high-level, general-purpose programming language created by Danish computer scientist Bjarne Stroustrup.
It is almost always implemented in a compiled language.
Modern C++ currently has object-oriented, generic, and functional features, in addition to facil.
part_2.txt
ities for low-level memory manipulation.
First released in 1985 as an extension of the C programming language, it has since expanded significantly over time.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to split a large text file into n smaller files with approximately equal number of lines.
- Write a C++ program that reads a large file and divides it into multiple files based on a user-specified number of lines per file.
- Write a C++ program to partition a text file into smaller chunks and save each chunk as a separate file with sequential naming.
- Write a C++ program to split a text file into several parts and ensure that each part is correctly numbered in its filename.
Go to:
PREV : Merge Multiple Text Files into One.
NEXT : Search for a Specific String in a Text File and Display Line Numbers.
CPP Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
