Java: Sort a given binary array in linear times
56. Sort a binary array in linear time
Write a Java program to sort a binary array in linear time.
From Wikipedia,
Linear time: An algorithm is said to take linear time, or O(n) time, if its time complexity is O(n). Informally, this means that the running time increases at most linearly with the size of the input. More precisely, this means that there is a constant c such that the running time is at most cn for every input of size n. For example, a procedure that adds up all elements of a list requires time proportional to the length of the list, if the adding time is constant, or, at least, bounded by a constant.
Linear time is the best possible time complexity in situations where the algorithm has to sequentially read its entire input. Therefore, much research has been invested into discovering algorithms exhibiting linear time or, at least, nearly linear time. This research includes both software and hardware methods. There are several hardware technologies which exploit parallelism to provide this. An example is content-addressable memory. This concept of linear time is used in string matching algorithms such as the Boyer–Moore algorithm and Ukkonen's algorithm.
Example:
Input :
b_nums[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }
Output:
After sorting: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Import the necessary Java class for working with arrays.
import java.util.Arrays;
// Define a class named 'solution'.
class solution
{
// A method to sort binary numbers in an array.
public static void sort_binary_nums(int[] b_nums)
{
int k = 0;
// Iterate through the array to move all 0s to the front.
for (int i = 0; i < b_nums.length; i++)
{
if (b_nums[i] == 0) {
b_nums[k++] = 0;
}
}
// Fill the remaining positions with 1s to sort the binary array.
for (int i = k; i < b_nums.length; i++) {
b_nums[k++] = 1;
}
}
public static void main (String[] args)
{
// Define an array 'b_nums' containing binary numbers.
int b_nums[] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 };
System.out.println("Original array: " + Arrays.toString(b_nums));
// Sort the binary numbers in the array.
sort_binary_nums(b_nums);
System.out.println("After sorting: " + Arrays.toString(b_nums));
}
}
Sample Output:
Original array: [0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0] After sorting: [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
Flowchart:
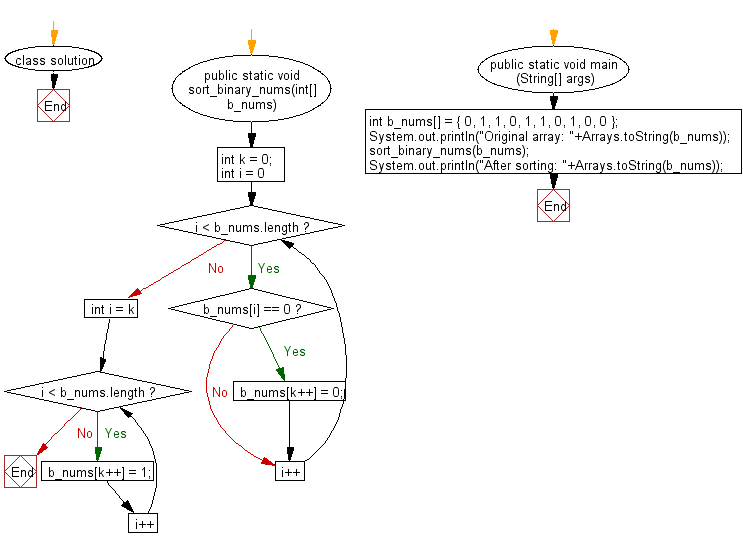
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to sort an array of 0s, 1s, and 2s in linear time.
- Write a Java program to sort a binary array using the two-pointer approach.
- Write a Java program to find the minimum number of swaps required to sort a binary array.
- Write a Java program to find the length of the longest contiguous subarray containing only 1s.
Go to:
PREV : Print all sub-arrays with sum zero in an array.
NEXT : Check if sub-array is formed by consecutive integers.
Java Code Editor:
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
