Java: Compute the sum of first n given prime numbers
Sum of First n Prime Numbers
Write a Java program to compute the sum of the first n prime numbers.
Input:
n ( n ≤ 10000). Input 0 to exit the program.
Visual Presentation:
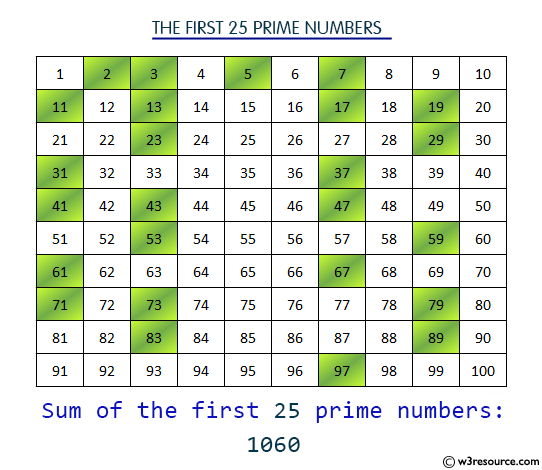
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Importing necessary classes for input/output operations and mathematical functions
import java.util.*;
// Main class named "Main"
public class Main {
// Main method to execute the program, throws IOException
public static void main(String[] args) throws java.io.IOException {
// Creating Scanner object to read input from the user
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// Initializing variables to count prime numbers and calculate their sum
int count = 0;
int sum = 0;
// Prompting the user to input a number (n<=10000) to compute the sum
System.out.println("Input a number (n<=10000) to compute the sum:");
// Reading the input number
int n = scan.nextInt();
// Looping through numbers to find prime numbers and calculate their sum
for (int i = 2;; i++) {
if (prime(i)) {
count++;
sum += i;
// Breaking the loop when the required number of prime numbers is reached
if (count == n) break;
}
}
// Outputting the sum of the first n prime numbers
System.out.println("Sum of first " + n + " prime numbers:");
System.out.println(sum);
}
// Method to check if a number is prime
public static boolean prime(int n) {
// If n is 1, it is not prime
if (n == 1) return false;
// Checking for factors up to the square root of n
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(n); i++)
if (n % i == 0) return false;
// If no factors are found, n is prime
return true;
}
}
Sample Output:
Input a number (n<=10000) to compute the sum: 100 Sum of first 100 prime numbers: 24133
Flowchart:
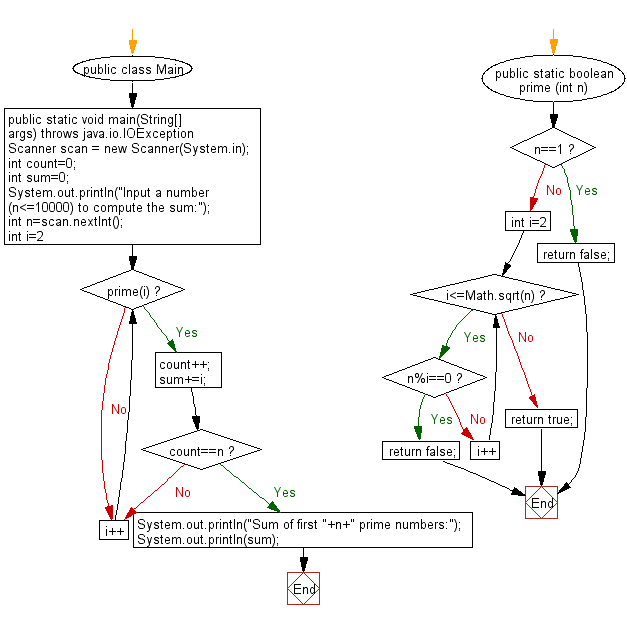
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to compute the sum of the first n prime numbers using a segmented sieve algorithm.
- Write a Java program to compute the sum of prime numbers until the cumulative sum exceeds a specified limit.
- Write a Java program to find the sum and average of the first n prime numbers.
- Write a Java program to compute the sum of the first n prime numbers and display the result in a formatted table.
Go to:
PREV : Difference Between Largest and Smallest Integer.
NEXT : Goldbach Combinations of Even Number.
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
