Java Polymorphism - Employee Class with Manager and Programmer Subclasses for Salary Calculation
Write a Java program to create a class Employee with a method called calculateSalary(). Create two subclasses Manager and Programmer. In each subclass, override the calculateSalary() method to calculate and return the salary based on their specific roles.
In the given exercise, here is a simple diagram illustrating polymorphism implementation:
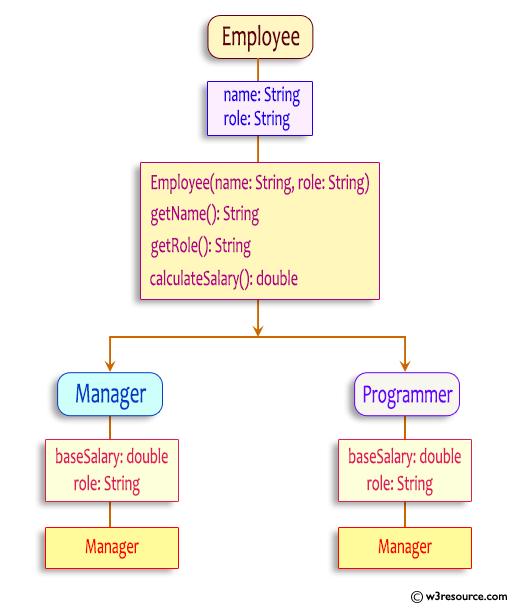
In the above diagram, the Employee class is the base class, and it has two subclasses, Manager and Programmer. The Employee class has private instance variables name and role, along with getter methods for retrieving their values. It also has a method calculateSalary() which returns a double.
The diagram demonstrates the inheritance relationship between the classes and how the calculateSalary() method is polymorphically overridden in the subclasses.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
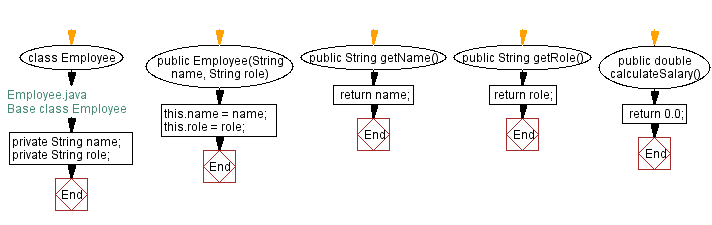
// Employee.java
// Base class Employee
// Define the Employee class
class Employee {
// Declare private String variables name and role
private String name;
private String role;
// Constructor for Employee class that takes name and role as parameters
public Employee(String name, String role) {
// Assign the parameter name to the instance variable name
this.name = name;
// Assign the parameter role to the instance variable role
this.role = role;
}
// Public method to get the name of the employee
public String getName() {
// Return the name of the employee
return name;
}
// Public method to get the role of the employee
public String getRole() {
// Return the role of the employee
return role;
}
// Public method to calculate the salary of the employee
public double calculateSalary() {
// Return 0.0 as the default salary
return 0.0;
}
}
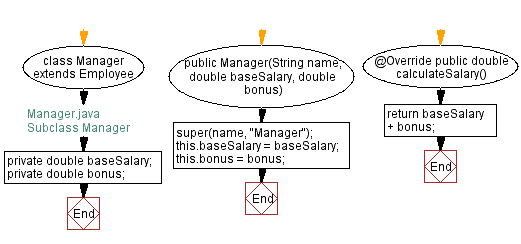
// Manager.java
// Subclass Manager
// Define the Manager class as a subclass of Employee
class Manager extends Employee {
// Declare private double variables baseSalary and bonus
private double baseSalary;
private double bonus;
// Constructor for Manager class that takes name, baseSalary, and bonus as parameters
public Manager(String name, double baseSalary, double bonus) {
// Call the constructor of the superclass Employee with name and role "Manager"
super(name, "Manager");
// Assign the parameter baseSalary to the instance variable baseSalary
this.baseSalary = baseSalary;
// Assign the parameter bonus to the instance variable bonus
this.bonus = bonus;
}
// Override the calculateSalary method from the Employee class
@Override
public double calculateSalary() {
// Calculate and return the salary of the manager by adding baseSalary and bonus
return baseSalary + bonus;
}
}
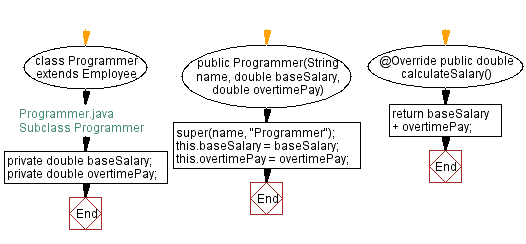
// Programmer.java
// Subclass Programmer
// Define the Programmer class as a subclass of Employee
class Programmer extends Employee {
// Declare private double variables baseSalary and overtimePay
private double baseSalary;
private double overtimePay;
// Constructor for Programmer class that takes name, baseSalary, and overtimePay as parameters
public Programmer(String name, double baseSalary, double overtimePay) {
// Call the constructor of the superclass Employee with name and role "Programmer"
super(name, "Programmer");
// Assign the parameter baseSalary to the instance variable baseSalary
this.baseSalary = baseSalary;
// Assign the parameter overtimePay to the instance variable overtimePay
this.overtimePay = overtimePay;
}
// Override the calculateSalary method from the Employee class
@Override
public double calculateSalary() {
// Calculate and return the salary of the programmer by adding baseSalary and overtimePay
return baseSalary + overtimePay;
}
}
// Main.java
// Main class
// Define the Main class
public class Main {
// Main method that serves as the entry point for the application
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a Manager object with name "Lilo Heidi", baseSalary 7500.0, and bonus 1500.0
Employee emp1 = new Manager("Lilo Heidi", 7500.0, 1500.0);
// Create a Programmer object with name "Margrit Cathrin", baseSalary 5000.0, and overtimePay 600.0
Employee emp2 = new Programmer("Margrit Cathrin", 5000.0, 600.0);
// Print the name, role, and salary of the Manager object
System.out.println("Manager: " + emp1.getName() + "\nRole: " + emp1.getRole() + "\nSalary: $" + emp1.calculateSalary());
// Print the name, role, and salary of the Programmer object
System.out.println("\nProgrammer: " + emp2.getName() + "\nRole: " + emp2.getRole() + "\nSalary: $" + emp2.calculateSalary());
}
}
Output:
Manager: Lilo Heidi Role: Manager Salary: $9000.0 Programmer: Margrit Cathrin Role: Programmer Salary: $5600.0
Flowchart:
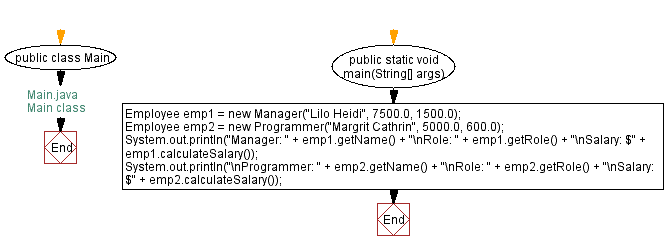
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" class implements a bonus calculation method.
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" class supports a method to determine the promotion eligibility.
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" class tracks attendance and deducts salary accordingly.
- Write a Java program where the "Employee" class calculates overtime pay based on hours worked.
Go to:
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
PREV : Employee Class with Manager and Programmer Subclasses for Salary Calculation.
NEXT : Sports Class with Football, Basketball, and Rugby Subclasses for Playing Statements.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
