Java Test Case: Exception Testing
2. Assert Exception Thrown on Invalid Input
Write a Java test case to verify that a specific exception is thrown when a method is called with invalid input.
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
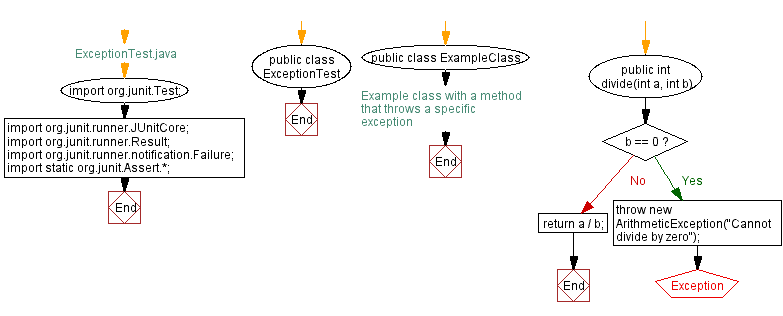
// ExceptionTest.java
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.JUnitCore;
import org.junit.runner.Result;
import org.junit.runner.notification.Failure;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class ExceptionTest {
// Example class with a method that throws a specific exception
public class ExampleClass {
public int divide(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) {
throw new ArithmeticException("Cannot divide by zero");
}
return a / b;
}
}
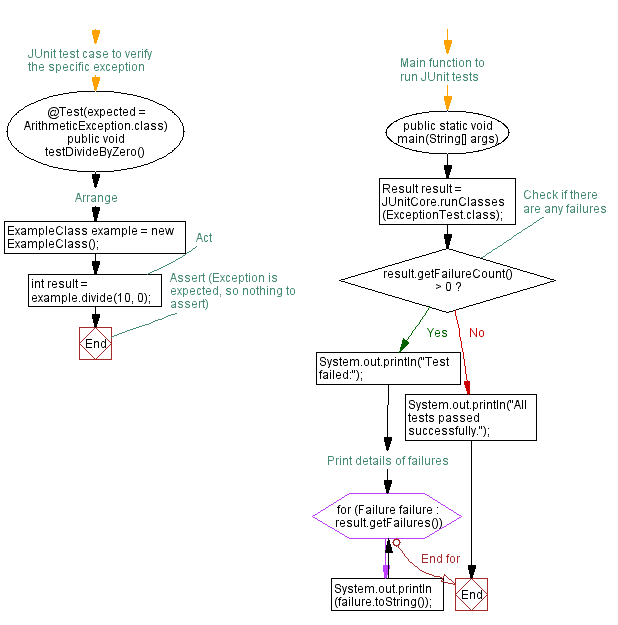
// JUnit test case to verify the specific exception
@Test(expected = ArithmeticException.class)
public void testDivideByZero() {
// Arrange
ExampleClass example = new ExampleClass();
// Act
int result = example.divide(10, 0);
// Assert (Exception is expected, so nothing to assert)
}
// Main function to run JUnit tests
public static void main(String[] args) {
Result result = JUnitCore.runClasses(ExceptionTest.class);
// Check if there are any failures
if (result.getFailureCount() > 0) {
System.out.println("Test failed:");
// Print details of failures
for (Failure failure : result.getFailures()) {
System.out.println(failure.toString());
}
} else {
System.out.println("All tests passed successfully.");
}
}
}
Sample Output:
All tests passed successfully.
Explanation:
In the exercise above,
- The "ExampleClass" has a "divide()" method that throws an "ArithmeticException" if the divisor is zero.
- The "testDivideByZero" JUnit test case uses the @Test annotation with the expected attribute to specify that an "ArithmeticException" is expected to be thrown during the execution of the test.
- The main() function uses JUnitCore.runClasses(ExceptionTest.class) to run the tests. If any test case fails, it prints details about the failure; otherwise, it prints a success message.
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to create a test case that verifies a NullPointerException is thrown when a method receives a null argument.
- Write a Java program to implement a test case that checks for an IllegalArgumentException when input parameters are out of bounds.
- Write a Java program to create a test case that asserts a custom exception is thrown for invalid business logic inputs.
- Write a Java program to design a test case that confirms a division by zero operation throws an ArithmeticException.
Go to:
PREV : Assert Method Returns Expected Value.
NEXT : JUnit Setup and Teardown Test.
Java Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
