MySQL SUM() function
SUM() function
MySQL SUM() function returns the sum of an expression. SUM() function returns NULL when the return set has no rows. It's a fundamental aggregate function that provides valuable insights into data analysis and numerical calculations.
This function is useful in -
- This is essential for understanding the cumulative value of a dataset.
- SUM() is used to aggregate data, making it easier to present the combined value of multiple records.
- For inventory tracking, the SUM() function calculates the total quantity of products in stock or sold.
- SUM() helps in validating calculations by comparing the expected sum with the calculated sum to identify discrepancies.
- In performance analysis, SUM() assists in evaluating cumulative metrics, such as total sales over a period.
- When generating summary reports, the SUM() function is employed to show the total value of specific attributes.
- In resource management, SUM() helps calculate the total utilization or consumption of resources.
Syntax:
SUM([DISTINCT] expr)
Where expr is an expression.
The DISTINCT keyword can be used to sum only the distinct values of expr.
MySQL Version: 8.0
Contents:
Example: MySQL SUM() function
The following MySQL statement returns the sum of 'total_cost' from purchase table.
Sample table: purchase
Code:
-- This query calculates the sum of the 'total_cost' column in the 'purchase' table.
SELECT SUM(total_cost)
-- This statement selects the sum of the 'total_cost' column.
FROM purchase;
-- This part of the query specifies the table from which data is being retrieved, which is 'purchase'.
Explanation:
- The purpose of this SQL query is to compute the total sum of the 'total_cost' values in the 'purchase' table.
- SELECT SUM(total_cost): This part of the query selects the sum of the 'total_cost' column. The SUM function adds up all the values in the specified column.
- FROM purchase: This part specifies the table from which the data is being selected, which is the 'purchase' table.
- The query will return a single value, which is the total sum of the 'total_cost' values in the 'purchase' table. This value represents the overall cost incurred across all purchases recorded in the dataset.
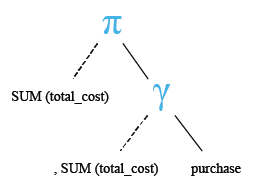
Relational Algebra Expression:
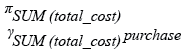
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
mysql> SELECT SUM(total_cost)
-> FROM purchase;
+-----------------+
| SUM(total_cost) |
+-----------------+
| 3590.00 |
+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: MySQL SUM() function with where clause
MySQL SUM() function with WHERE retrieves the sum of a given expression which is filtered against a condition placed after WHERE. The following MySQL statement returns the sum of 'total_cost' from purchase table for the category ('cate_id') given with WHERE clause.
Sample table: purchase
Code:
-- This query calculates the sum of the 'total_cost' column in the 'purchase' table for purchases belonging to the category 'CA001'.
SELECT SUM(total_cost)
-- This statement selects the sum of the 'total_cost' column.
FROM purchase
-- This part of the query specifies the table from which data is being retrieved, which is 'purchase'.
WHERE cate_id='CA001';
-- This clause filters the rows to include only those where the 'cate_id' column has the value 'CA001'.
Explanation:
- The purpose of this SQL query is to compute the total sum of the 'total_cost' values in the 'purchase' table, specifically for purchases belonging to the category 'CA001'.
- SELECT SUM(total_cost): This part of the query selects the sum of the 'total_cost' column. The SUM function adds up all the values in the specified column.
- FROM purchase: This part specifies the table from which the data is being selected, which is the 'purchase' table.
- WHERE cate_id='CA001': This clause filters the rows to include only those where the 'cate_id' column has the value 'CA001'. This ensures that only purchases belonging to the specified category are considered for the sum calculation.
- The query will return a single value, which is the total sum of the 'total_cost' values in the 'purchase' table for purchases belonging to the category 'CA001'. This value represents the overall cost incurred for purchases in that specific category.
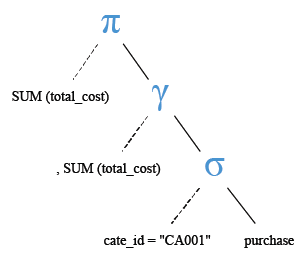
Relational Algebra Expression:
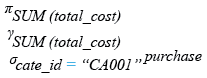
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
mysql> SELECT SUM(total_cost)
-> FROM purchase
-> WHERE cate_id='CA001';
+-----------------+
| SUM(total_cost) |
+-----------------+
| 1725.00 |
+-----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: MySQL SUM() function using multiple columns
MySQL SUM() function retrieves the sum value of an expression which is made up of more than one columns. The above MySQL statement returns the sum of multiplication of 'receive_qty' and 'purch_price' from purchase table for each group of category ('cate_id') .
Sample table: purchase
Code:
-- This query calculates the total cost (receive_qty * purch_price) for each category (cate_id) in the 'purchase' table.
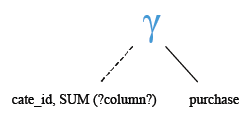
SELECT cate_id,
SUM(receive_qty * purch_price)
-- This statement selects the category ID (cate_id) and calculates the sum of receive_qty * purch_price for each category.
FROM purchase
-- This part of the query specifies the table from which data is being retrieved, which is 'purchase'.
GROUP BY cate_id;
-- This clause groups the results by the 'cate_id' column, so that the total cost can be calculated for each category separately.
Explanation:
- The purpose of this SQL query is to compute the total cost (quantity received multiplied by purchase price) for each category in the 'purchase' table.
- SELECT cate_id, SUM(receive_qty * purch_price): This part of the query selects two columns: 'cate_id', and the sum of receive_qty * purch_price for each category. The multiplication of receive_qty and purch_price gives the total cost for each purchase, and then SUM aggregates these costs for each category.
- FROM purchase: This part specifies the table from which the data is being selected, which is the 'purchase' table.
- GROUP BY cate_id: This clause groups the results by the 'cate_id' column. It ensures that the total cost is calculated for each unique category separately.
- The query will return a list of category IDs along with the total cost incurred for each category in the 'purchase' table. This provides insights into the overall expenditure for each product category.
Relational Algebra Expression:
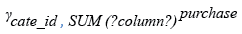
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
mysql> SELECT cate_id,
-> SUM(receive_qty*purch_price)
-> FROM purchase
-> GROUP BY cate_id;
+---------+------------------------------+
| cate_id | SUM(receive_qty*purch_price) |
+---------+------------------------------+
| CA001 | 1725.00 |
| CA002 | 965.00 |
| CA003 | 900.00 |
+---------+------------------------------+
3 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Example: MySQL SUM() function with COUNT() function and variables
The following MySQL statement will return the sum of the ‘mysum’, a temporary variable which counts number of books containing more than 200 pages from 'book_mast' table.
Sample table: book_mast
Code:
-- This query calculates the sum of the alias 'mysum' from the subquery.
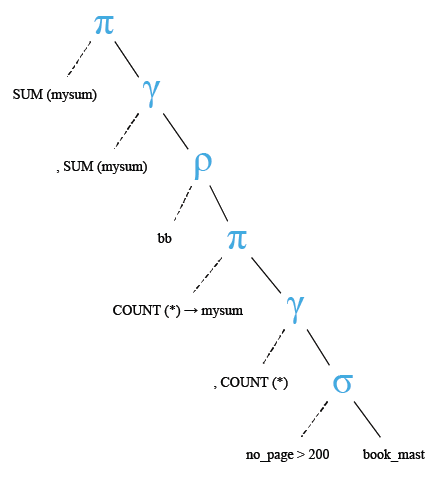
SELECT SUM(mysum)
-- This statement selects the sum of the alias 'mysum'.
FROM(
-- This subquery counts the number of rows where the 'no_page' column is greater than 200 and aliases the count as 'mysum'.
SELECT COUNT(*) AS mysum
-- This part of the subquery counts the number of rows in the 'book_mast' table.
FROM book_mast
-- This part of the subquery specifies the table from which data is being retrieved, which is 'book_mast'.
WHERE no_page > 200
-- This part of the subquery filters the rows to include only those where the 'no_page' column has a value greater than 200.
) AS bb;
-- This aliases the subquery as 'bb' and closes it. It allows the outer query to reference the result of the subquery.
Explanation:
- The purpose of this SQL query is to calculate the sum of the count of rows where the 'no_page' column is greater than 200 in the 'book_mast' table.
- The inner subquery first calculates the count of rows where the 'no_page' column is greater than 200 and aliases it as 'mysum'.
- The outer query then calculates the sum of the alias 'mysum', effectively giving the total count of rows where 'no_page' is greater than 200 across all rows in the 'book_mast' table.
- The alias 'bb' is used to reference the result of the subquery within the outer query.
- The query will return a single value, which is the sum of the count of rows where 'no_page' is greater than 200 in the 'book_mast' table. This provides insights into the total number of books with more than 200 pages in the dataset.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
mysql> SELECT SUM(mysum)
-> FROM(
-> SELECT COUNT(*) AS mysum
-> FROM book_mast
-> WHERE no_page>200) AS bb;
+------------+
| SUM(mysum) |
+------------+
| 12 |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
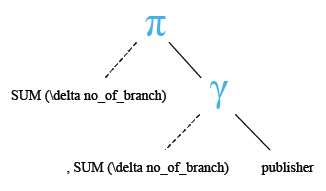
Example: MySQL SUM() function with DISTINCT clause
MySQL SUM() function retrieves the sum of a unique value of an expression if it is accompanied by DISTINCT clause. The following MySQL statement returns the sum of a number of branches ('no_of_branch') from publisher table, where, if more than one publisher has the same number of branches, that number (i.e. number of branches) is taken once only.
Sample table: publisher
Code:
-- This query calculates the sum of distinct values in the 'no_of_branch' column from the 'publisher' table.
SELECT SUM(DISTINCT no_of_branch)
-- This statement selects the sum of distinct values in the 'no_of_branch' column.
FROM publisher;
-- This part of the query specifies the table from which data is being retrieved, which is 'publisher'.
Explanation:
- The purpose of this SQL query is to calculate the sum of distinct values in the 'no_of_branch' column from the 'publisher' table.
- SELECT SUM(DISTINCT no_of_branch): This part of the query selects the sum of distinct values in the 'no_of_branch' column. The DISTINCT keyword ensures that only unique values are considered in the summation.
- FROM publisher: This part specifies the table from which the data is being selected, which is the 'publisher' table.
- The query will return a single value, which is the sum of distinct values in the 'no_of_branch' column of the 'publisher' table. This value represents the total count of unique branches across all publishers in the dataset.
Relational Algebra Expression:
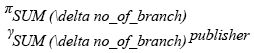
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
mysql> SELECT SUM(DISTINCT no_of_branch)
-> FROM publisher;
+----------------------------+
| SUM(DISTINCT no_of_branch) |
+----------------------------+
| 64 |
+----------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Previous:
STDDEV()
Next:
SUM() with group by
