MySQL COUNT() function
COUNT() function
MySQL COUNT() function returns a count of a number of non-NULL values of a given expression. It's a fundamental and versatile function that provides valuable insights into your data.
If it does not find any matching row, it returns 0.
This function is useful in -
- The COUNT() function can be used to validate that certain data meets certain criteria or conditions.
- COUNT() helps in generating accurate and informative reports.
- The COUNT() function is often used in conjunction with SUM(), AVG(), and MAX() that allows to perform complex analyses and calculations on your data.
- When dealing with large datasets, it's more efficient to retrieve just the count of rows rather than fetching all the rows themselves.
- COUNT() provides valuable data for analysis and decision-making.
- You can track changes in data over time by using COUNT() in combination with timestamps or date ranges.
Syntax
COUNT(expr);
Where expr is an expression.
MySQL Version: 8.0
Contents:
Example : MySQL COUNT() function
The following MySQL statement will return the number of rows in author table.
Sample table: author
+--------+----------------------+-----------+----------------+ | aut_id | aut_name | country | home_city | +--------+----------------------+-----------+----------------+ | AUT001 | William Norton | UK | Cambridge | | AUT002 | William Maugham | Canada | Toronto | | AUT003 | William Anthony | UK | Leeds | | AUT004 | S.B.Swaminathan | India | Bangalore | | AUT005 | Thomas Morgan | Germany | Arnsberg | | AUT006 | Thomas Merton | USA | New York | | AUT007 | Piers Gibson | UK | London | | AUT008 | Nikolai Dewey | USA | Atlanta | | AUT009 | Marquis de Ellis | Brazil | Rio De Janerio | ........... | AUT015 | Butler Andre | USA | Florida | +--------+----------------------+-----------+----------------+
Code:
-- This SQL query counts the number of rows in the author table.
SELECT COUNT(*) -- Selects the count of all rows from the author table
FROM author; -- Specifies the table from which to retrieve data (author table)
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the author table.
- It counts the total number of rows in the author table.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query uses the COUNT(*) function to count all rows in the specified table.
- Since * is used as an argument to COUNT, it counts all rows regardless of the values in any specific column.
- Finally, the query returns the count of rows from the author table.
Output:
mysql> SELECT COUNT(*)
-> FROM author;
+----------+
| COUNT(*) |
+----------+
| 15 |
+----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example : MySQL COUNT() with logical operator
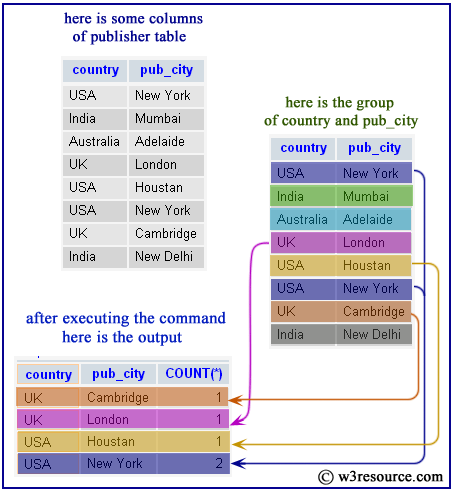
The following MySQL statement returns the number of publishers for USA and UK. The WHERE clause filters the rows for the country USA and UK. Grouping is performed on country and pub-city columns by GROUP BY and then COUNT() counts a number of publishers for each groups.
Sample table: publisher
+--------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+----------------+--------------+------------+ | pub_id | pub_name | pub_city | country | country_office | no_of_branch | estd | +--------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+----------------+--------------+------------+ | P001 | Jex Max Publication | New York | USA | New York | 15 | 1969-12-25 | | P002 | BPP Publication | Mumbai | India | New Delhi | 10 | 1985-10-01 | | P003 | New Harrold Publication | Adelaide | Australia | Sydney | 6 | 1975-09-05 | | P004 | Ultra Press Inc. | London | UK | London | 8 | 1948-07-10 | | P005 | Mountain Publication | Houstan | USA | Sun Diego | 25 | 1975-01-01 | | P006 | Summer Night Publication | New York | USA | Atlanta | 10 | 1990-12-10 | | P007 | Pieterson Grp. of Publishers | Cambridge | UK | London | 6 | 1950-07-15 | | P008 | Novel Publisher Ltd. | New Delhi | India | Bangalore | 10 | 2000-01-01 | +--------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+----------------+--------------+------------+
Code:
-- This SQL query counts the number of publishers in each city for the countries USA and UK.
SELECT country, pub_city, COUNT(*) -- Selects the country, publisher city, and counts the number of publishers in each city
FROM publisher -- Specifies the table from which to retrieve data (publisher table)
WHERE country='USA' OR country='UK' -- Filters the data to include only publishers from the countries USA and UK
GROUP BY country, pub_city; -- Groups the results by country and publisher city, so that the count is calculated for each combination of country and city
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the publisher table.
- It counts the number of publishers in each city for the countries USA and UK.
- The WHERE clause filters the data to include only publishers from the countries USA and UK.
- The GROUP BY clause ensures that the results are grouped by country and publisher city, allowing for separate counts to be calculated for each combination of country and city.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query selects the country, publisher city, and counts the number of publishers in each city.
- It filters the data to include only publishers from the countries USA and UK using the WHERE clause.
- The results are then grouped by country and publisher city using GROUP BY country, pub_city, ensuring that the count is calculated for each combination of country and city.
- Finally, the query returns the country, publisher city, and the count of publishers for each combination of country and city.
Output:
mysql> SELECT country,pub_city,COUNT(*)
-> FROM publisher
-> WHERE country='USA' OR country='UK' GROUP BY country, pub_city;
+---------+-----------+----------+
| country | pub_city | COUNT(*) |
+---------+-----------+----------+
| UK | Cambridge | 1 |
| UK | London | 1 |
| USA | Houstan | 1 |
| USA | New York | 2 |
+---------+-----------+----------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Pictorial Presentation
MySQL COUNT() using multiple tables
The following MySQL statement retrieves those rows from publisher table whose 'pub_id' in publisher table match the 'pub_id' in 'book_mast' table.
A grouping operation is performed on pub_id column of publisher table by GROUP BY and then number of times pub_id exists in publisher table is counted by COUNT().
Sample table: book_mast
+---------+-------------------------------------+-------------+---------+--------+--------+------------+----------+---------+------------+ | book_id | book_name | isbn_no | cate_id | aut_id | pub_id | dt_of_pub | pub_lang | no_page | book_price | +---------+-------------------------------------+-------------+---------+--------+--------+------------+----------+---------+------------+ | BK001 | Introduction to Electrodynamics | 0000979001 | CA001 | AUT001 | P003 | 2001-05-08 | English | 201 | 85.00 | | BK002 | Understanding of Steel Construction | 0000979002 | CA002 | AUT002 | P001 | 2003-07-15 | English | 300 | 105.50 | | BK003 | Guide to Networking | 0000979003 | CA003 | AUT003 | P002 | 2002-09-10 | Hindi | 510 | 200.00 | | BK004 | Transfer of Heat and Mass | 0000979004 | CA002 | AUT004 | P004 | 2004-02-16 | English | 600 | 250.00 | | BK005 | Conceptual Physics | 0000979005 | CA001 | AUT005 | P006 | 2003-07-16 | NULL | 345 | 145.00 | | BK006 | Fundamentals of Heat | 0000979006 | CA001 | AUT006 | P005 | 2003-08-10 | German | 247 | 112.00 | | BK007 | Advanced 3d Graphics | 0000979007 | CA003 | AUT007 | P002 | 2004-02-16 | Hindi | 165 | 56.00 | | BK008 | Human Anatomy | 0000979008 | CA005 | AUT008 | P006 | 2001-05-17 | German | 88 | 50.50 | | BK009 | Mental Health Nursing | 0000979009 | CA005 | AUT009 | P007 | 2004-02-10 | English | 350 | 145.00 | | BK010 | Fundamentals of Thermodynamics | 0000979010 | CA002 | AUT010 | P007 | 2002-10-14 | English | 400 | 225.00 | ... ... ... +---------+-------------------------------------+-------------+---------+--------+--------+------------+----------+---------+------------+
Sample table: publisher
+--------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+----------------+--------------+------------+ | pub_id | pub_name | pub_city | country | country_office | no_of_branch | estd | +--------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+----------------+--------------+------------+ | P001 | Jex Max Publication | New York | USA | New York | 15 | 1969-12-25 | | P002 | BPP Publication | Mumbai | India | New Delhi | 10 | 1985-10-01 | | P003 | New Harrold Publication | Adelaide | Australia | Sydney | 6 | 1975-09-05 | | P004 | Ultra Press Inc. | London | UK | London | 8 | 1948-07-10 | | P005 | Mountain Publication | Houstan | USA | Sun Diego | 25 | 1975-01-01 | | P006 | Summer Night Publication | New York | USA | Atlanta | 10 | 1990-12-10 | | P007 | Pieterson Grp. of Publishers | Cambridge | UK | London | 6 | 1950-07-15 | | P008 | Novel Publisher Ltd. | New Delhi | India | Bangalore | 10 | 2000-01-01 | +--------+------------------------------+-----------+-----------+----------------+--------------+------------+
Code:
-- This SQL query counts the number of books published by each publisher and retrieves the publisher names.
SELECT publisher.pub_name, COUNT(*) -- Selects the publisher name and counts the number of books published by each publisher
FROM publisher, book_mast -- Specifies the tables from which to retrieve data (publisher and book_mast tables)
WHERE publisher.pub_id = book_mast.pub_id -- Specifies the condition to join the tables based on publisher ID
GROUP BY publisher.pub_id; -- Groups the results by publisher ID, so that the count is calculated for each publisher
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the publisher and book_mast tables.
- It counts the number of books published by each publisher and retrieves the publisher names.
- The tables are joined based on the common column pub_id.
- The GROUP BY clause ensures that the results are grouped by publisher ID, allowing for separate counts to be calculated for each publisher.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query selects the publisher name (publisher.pub_name) and counts the number of books published by each publisher.
- It specifies the condition to join the publisher and book_mast tables based on the publisher ID (publisher.pub_id = book_mast.pub_id).
- The results are then grouped by publisher ID using GROUP BY publisher.pub_id, ensuring that the count is calculated for each publisher.
- Finally, the query returns the publisher name and the count of books published by each publisher.
Output:
mysql> SELECT publisher.pub_name,COUNT(*)
-> FROM publisher,book_mast
-> WHERE publisher.pub_id=book_mast.pub_id
-> GROUP BY publisher.pub_id;
+------------------------------+----------+
| pub_name | COUNT(*) |
+------------------------------+----------+
| Jex Max Publication | 2 |
| BPP Publication | 2 |
| New Harrold Publication | 2 |
| Ultra Press Inc. | 2 |
| Mountain Publication | 2 |
| Summer Night Publication | 2 |
| Pieterson Grp. of Publishers | 2 |
| Novel Publisher Ltd. | 2 |
+------------------------------+----------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
PREV :
BIT_XOR()
NEXT :
COUNT() with group by