Oracle CONCAT function
Description
The Oracle CONCAT() function returns the result (a string) of concatenating two string values. This function is equivalent to using the concatenation operator (||). It takes two string arguments and produces a single string as the output.
Uses of Oracle CONCAT Function
- Combining Two Strings: Joins two strings into a single string, useful for constructing dynamic strings.
- Creating Full Names: Combines first and last names or other parts of names to form a full name.
- Generating Dynamic SQL: Constructs dynamic SQL queries or commands by concatenating strings.
- Formatting Output: Helps in formatting output by combining static text with dynamic content.
- Handling LOB and National Data Types: Manages concatenation involving large objects (LOBs) and national character sets, returning the appropriate data type to avoid loss of information.
Syntax:
CONCAT(char1, char2)
Parameters :
| Name | Description | Data Types |
|---|---|---|
| char1, char2 | A string value to concatenate to the other values. | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
Return Value Type :
CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB
If there are two different data types in concatenations Oracle Database returns the data type that results in a lossless conversion.
Therefore, if one of the arguments is a LOB, then the returned value is a LOB. If one of the arguments is a national data type, then the returned value is a national data type.
Here are some examples:
- CONCAT(CLOB, NCLOB) returns NCLOB
- CONCAT(NCLOB, NCHAR) returns NCLOB
- CONCAT(NCLOB, CHAR) returns NCLOB
- CONCAT(NCHAR, CLOB) returns NCLOB
Applies to
Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g, Oracle 9i, Oracle 8i
Pictorial Presentation
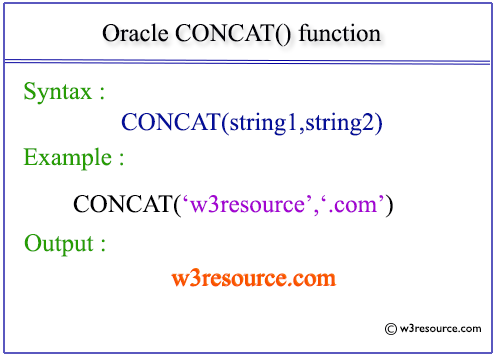
Example: Oracle CONCAT function
SQL> SELECT CONCAT ('w3resource', '.com') AS DomainName from dual;
Sample Output:
DOMAINNAME -------------- w3resource.com
Example: Using CONCAT with NULL values
SQL> CREATE TABLE temp1 (
2 student_firstname varchar(200) NOT NULL,
3 student_lastname varchar(200));
Table created.
SQL> INSERT INTO temp1 VALUES('Steven','King');
1 row created.
SQL> INSERT INTO temp1 VALUES('Neena','');
1 row created.
SQL> INSERT INTO temp1 VALUES('Lex','De Haan');
1 row created.
SQL>
SQL> SELECT CONCAT( student_firstname, student_lastname) FROM temp1;
Sample Output:
CONCAT(STUDENT_FIRSTNAME,STUDENT_LASTNAME) ----------------------------------------- StevenKing Neena LexDe Haan
