Oracle ATAN2() function
Description
The ATAN2() function is used to calculate the arc tangent of two numbers for a point on a Cartesian plane. The first number in the argument can be in an unbounded range and returns a value in the range of -pi to pi, depending on the signs of num1 and num2 specified in the argument, expressed in radians.
The function takes any numeric or nonnumeric data type (can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type) as an argument.
If any argument is BINARY_FLOAT or BINARY_DOUBLE, then the function returns BINARY_DOUBLE. Otherwise, the function returns NUMBER.
Uses of Oracle ATAN2() Function
- Trigonometric Calculations: Determine the angle between the positive x-axis and the point (num2, num1) on the Cartesian plane.
- Mathematical Modeling: Essential in models requiring accurate angle calculations from coordinates.
- Engineering Applications: Used in engineering to compute angles in navigation and robotics.
- Graphics Programming: Applied in computer graphics to determine rotation angles.
- Data Analysis: Useful in analyzing data involving directional components or angular measurements.
- Scientific Research: Employed in scientific studies requiring precise angular calculations for points on a plane.
Syntax:
ATAN2(num1, num2);
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| num1 | A number. |
| num2 | A number. |
Pictorial Presentation of ATAN2() function
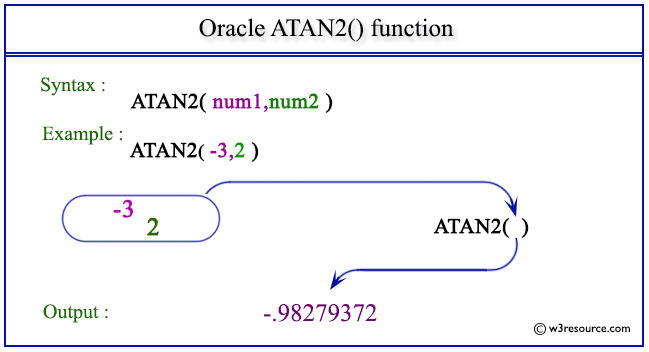
Example1:
The statement below will return the arc tangent in radians of -3 and 2 for a point in a Cartesian plane.
SELECT ATAN2(-3,2) FROM dual;
Here is the result
ATAN2(-3,2) ----------- -.98279372
Example2
The statement below will return the arc tangent of .5 and .3 for a point in a Cartesian plane.
SELECT ATAN2(.5,.3) FROM dual;
Here is the result
ATAN2(.5,.3) ------------ 1.03037683
