Oracle MOD() function
Description
The Oracle MOD() is used to return the remainder of a dividend divided by a divisor. This function also works on fractional values and returns the exact remainder. The function returns dividend when the value of divisor is 0.
The function takes any numeric or nonnumeric data type (can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type) as an argument.
If the argument is BINARY_FLOAT, then the function returns BINARY_DOUBLE. Otherwise, the function returns the same numeric data type as the argument
Uses of Oracle MOD() Function
- Finding the remainder: Returns the remainder of a division operation.
- Handling fractional values: Works with fractional values to return the exact remainder.
- Zero divisor handling: Returns the dividend when the divisor is 0.
- Mathematical calculations: Useful in various mathematical and statistical computations.
- Modulus operations: Commonly used in modulus operations within algorithms and data processing tasks.
Syntax:
MOD(N,M)
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | Dividend. |
| M | Divisor. |
Pictorial Presentation of MOD() function
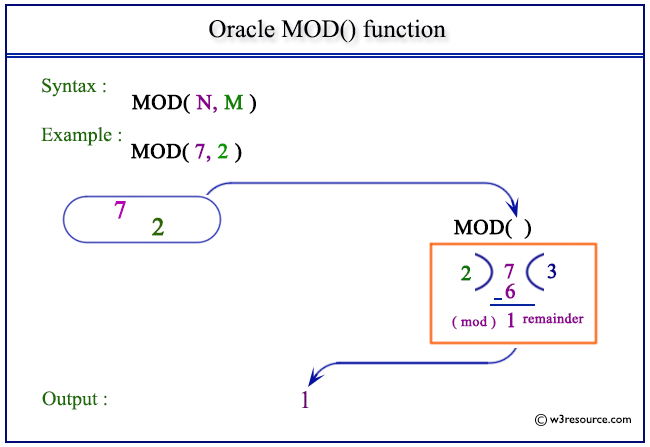
Example-1:
The statement below returns the remainder of17 divided by 2.
SELECT MOD(7,2) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
MOD(7,2)
----------
1
Example-2:
The statement below returns the remainder of 7 divided by -2.
SELECT MOD(7,-2) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
MOD(7,-2)
----------
1
Example-3:
The statement below returns the remainder of -7 divided by 2.
SELECT MOD(-7, 2);
Here is the result.
MOD(-7,2)
----------
-1
Example-4:
The statement below returns the remainder of -7 divided by -2.
SELECT MOD(-7, -2);
Here is the result.
MOD(-7,-2)
----------
-1
