PHP do while Loop Statement
Description
There is a small difference between the while and do while loops. The difference is the place where the condition is tested. As we already seen in a while loop that condition is tested at the beginning, i.e. before execution any of the statement within the while loop.
In the case of do while loop the condition is tested after having executed the statements within the loop. This means that do-while would execute its statements at least once, even if the condition fails for the first time itself.
Syntax:
do
{
execute the statements;
}
while (condition is true)
Example -1:
The following example print "Increment Number" with $x1 value as well as "Hello world" five times.
<?php
$x1=1;
do {
echo "Increment Number : $x1 <br />";
echo "Hello World <br />";
$x1=$x1+1;
}while ($x1<=5)
?>
Output:
Increment Number : 1 Hello World Increment Number : 2 Hello World Increment Number : 3 Hello World Increment Number : 4 Hello World Increment Number : 5 Hello World
View the example in the browser
Pictorial representation of do while loop
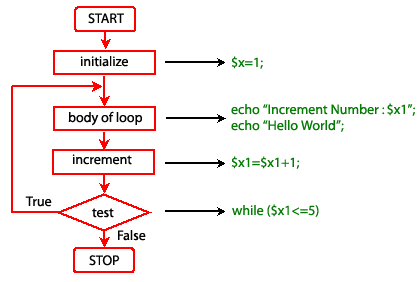
Example -2:
In the following example, the loop will run one time exactly since after the first iteration, when truth expression is checked, it evaluates to FALSE (as $X is not bigger than 5) and the loop execution ends.
<?php
$x1=0;
do {
echo "Increment Number : $x1 <br />";
echo "Hello World <br />";
$x1=$x1+1;
}while ($x1>5)
?>
Output:
Increment Number : 0 Hello World
View the example in the browser See also
Previous: while statement
Next: for statement
