PHP for Loop
Description
The PHP for loop allows the user to put all the loop-related statements (i.e. INITIALIZER; CONDITION; INCREMENTOR or DECREMENTOR) in one place. The structure is similar to C language.
Syntax
for ( initialize counter ; test counter ; increment counter)
{
execute the statement;
}
- initialize counter : Initialize the loop counter value.
- test counter : Verify the loop counter whether the condition is true.
- increment counter : Increasing the loop counter value.
- execute the statement : Execute php statements.
Alternatively, you can write for loop statement using the following syntax also.
for (expr1; expr2; expr3): statement ... endfor;
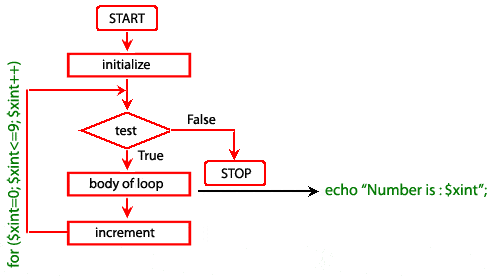
Pictorial representation of for loop
Example:
The following example displays the numbers between 0 to 5.
<?php
for ($xint=0; $xint<=5; $xint++)
{
echo "Number is : $xint <br />";
}
?>
Output:
Number is : 0 Number is : 1 Number is : 2 Number is : 3 Number is : 4 Number is : 5
View the example in the browser
You can execute for in the following ways also.
<?php
for ($xint = 1; ; $xint++) {
if ($i >= 5) {
break;
}
echo $xint;
}
?>
<?php
$xint = 1;
for (; ; )
{
if ($xint >= 5)
{
break;
}
echo $xint;
$xint++;
}
?>
Example: Counting number of times a word present in a sentence.
<?php
$text="The quick brown Fox jumps over the lazy Dog";
$words = explode(" ", $text); // explode function looks for " " and creates an array, where each word is an element of the array
$now = count($words);
$j = 0;
for($i=0; $i<$now; $i++)
{
if ($words[$i] == "the" or $words[$i] == "The")
{
$j = $j+1;
}
}
echo $j;
?>
Output:
2
View the example in the browser
Previous: do-while statement
Next: foreach statement
