Python Cyber Security - Program for simulating dictionary attack on password
9. Dictionary Attack Simulation
Write a Python program that simulates a dictionary attack on a password by trying out a list of commonly used passwords and their variations.
Note: This is a simple example and for educational purposes only and is not intended to be used for illegal purposes. In real-world scenarios, password attacks should only be carried out with explicit permission from the system owner being attacked.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
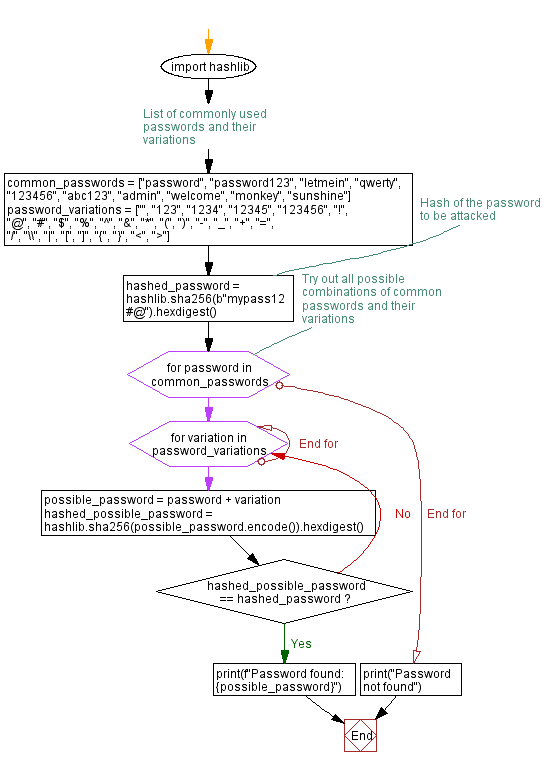
import hashlib
# List of commonly used passwords and their variations
common_passwords = ["password", "password123", "letmein", "qwerty", "123456", "abc123", "admin", "welcome", "monkey", "sunshine"]
password_variations = ["", "123", "1234", "12345", "123456", "!", "@", "#", "$", "%", "^", "&", "*", "(", ")", "-", "_", "+", "=", "/", "\\", "|", "[", "]", "{", "}", "<", ">"]
# Hash of the password to be attacked
hashed_password = hashlib.sha256(b"mypass12#@").hexdigest()
# Try out all possible combinations of common passwords and their variations
for password in common_passwords:
for variation in password_variations:
possible_password = password + variation
hashed_possible_password = hashlib.sha256(possible_password.encode()).hexdigest()
if hashed_possible_password == hashed_password:
print(f"Password found: {possible_password}")
break
else:
continue
break
else:
print("Password not found")
Sample Output:
Password not found
Explanation:
In the above exercise, we first define a list of commonly used passwords and their variations. We then define the hash of the password we want to attack (in this example, "mypass12#@" is hashed using SHA-256).
We then use a nested loop to try out all possible combinations of common passwords and their variations. For each combination, we hash the password using SHA-256 and check if it matches the hashed password we want to attack. If a match is found, we print the password and exit the loop. If no match is found, we print a message indicating that the password was not available.
Note:
Possible passwords generated the said program.
password
password123
password1234
password12345
password123456
password!
password@
password#
password$
password%
password^
password&
password*
password(
password)
password-
password_
password+
password=
password/
password\
password|
password[
password]
password{
password}
password<
password>
password123
password123123
password1231234
password12312345
password123123456
password123!
password123@
password123#
password123$
password123%
password123^
password123&
password123*
password123(
password123)
password123-
password123_
password123+
password123=
password123/
password123\
password123|
password123[
password123]
password123{
password123}
password123<
password123>
letmein
letmein123
letmein1234
letmein12345
letmein123456
letmein!
letmein@
letmein#
letmein$
letmein%
letmein^
letmein&
letmein*
letmein(
letmein)
letmein-
letmein_
letmein+
letmein=
letmein/
letmein\
letmein|
letmein[
letmein]
letmein{
letmein}
letmein<
letmein>
qwerty
qwerty123
qwerty1234
qwerty12345
qwerty123456
qwerty!
qwerty@
qwerty#
qwerty$
qwerty%
qwerty^
qwerty&
qwerty*
qwerty(
qwerty)
qwerty-
qwerty_
qwerty+
qwerty=
qwerty/
qwerty\
qwerty|
qwerty[
qwerty]
qwerty{
qwerty}
qwerty<
qwerty>
123456
123456123
1234561234
12345612345
123456123456
123456!
123456@
123456#
123456$
123456%
123456^
123456&
123456*
123456(
123456)
123456-
123456_
123456+
123456=
123456/
123456\
123456|
123456[
123456]
123456{
123456}
123456<
123456>
abc123
abc123123
abc1231234
abc12312345
abc123123456
abc123!
abc123@
abc123#
abc123$
abc123%
abc123^
abc123&
abc123*
abc123(
abc123)
abc123-
abc123_
abc123+
abc123=
abc123/
abc123\
abc123|
abc123[
abc123]
abc123{
abc123}
abc123<
abc123>
admin
admin123
admin1234
admin12345
admin123456
admin!
admin@
admin#
admin$
admin%
admin^
admin&
admin*
admin(
admin)
admin-
admin_
admin+
admin=
admin/
admin\
admin|
admin[
admin]
admin{
admin}
admin<
admin>
welcome
welcome123
welcome1234
welcome12345
welcome123456
welcome!
welcome@
welcome#
welcome$
welcome%
welcome^
welcome&
welcome*
welcome(
welcome)
welcome-
welcome_
welcome+
welcome=
welcome/
welcome\
welcome|
welcome[
welcome]
welcome{
welcome}
welcome<
welcome>
monkey
monkey123
monkey1234
monkey12345
monkey123456
monkey!
monkey@
monkey#
monkey$
monkey%
monkey^
monkey&
monkey*
monkey(
monkey)
monkey-
monkey_
monkey+
monkey=
monkey/
monkey\
monkey|
monkey[
monkey]
monkey{
monkey}
monkey<
monkey>
sunshine
sunshine123
sunshine1234
sunshine12345
sunshine123456
sunshine!
sunshine@
sunshine#
sunshine$
sunshine%
sunshine^
sunshine&
sunshine*
sunshine(
sunshine)
sunshine-
sunshine_
sunshine+
sunshine=
sunshine/
sunshine\
sunshine|
sunshine[
sunshine]
sunshine{
sunshine}
sunshine<
sunshine>
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Python program to simulate a dictionary attack by trying a list of common passwords against a given hashed password, then print the matching password if found.
- Write a Python function that iterates over a list of common passwords and their common variations, comparing each to a target hash using SHA-256.
- Write a Python script to load a dictionary of common passwords, simulate a dictionary attack on a sample password hash, and output the number of attempts made.
- Write a Python program to implement a dictionary attack that includes timing information for each attempt and prints a summary of the attack performance.
Go to:
Previous: Generate password from a dictionary file.
Next: Program for a Brute-Force Attack on Passwords.
Python Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
