Python Redirect Handling and final URL example
Write a Python program to handle redirects and print the final response URL.
Sample Solution:
Python Code :
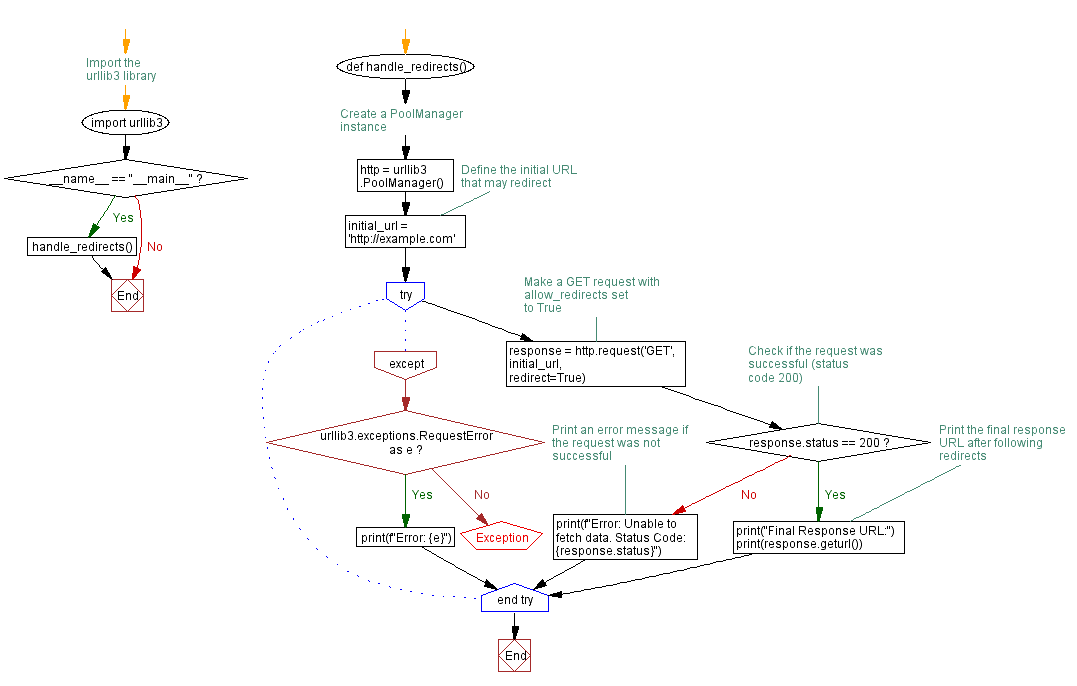
# Import the urllib3 library
import urllib3
def handle_redirects():
# Create a PoolManager instance
http = urllib3.PoolManager()
# Define the initial URL that may redirect
initial_url = 'http://example.com'
try:
# Make a GET request with allow_redirects set to True
response = http.request('GET', initial_url, redirect=True)
# Check if the request was successful (status code 200)
if response.status == 200:
# Print the final response URL after following redirects
print("Final Response URL:")
print(response.geturl())
else:
# Print an error message if the request was not successful
print(f"Error: Unable to fetch data. Status Code: {response.status}")
except urllib3.exceptions.RequestError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
handle_redirects()
Sample Output:
Final Response URL: http://example.com/
Explanation:
Here's a brief explanation of the above Python urllib3 library code:
- Import Library:
- urllib3: Used for handling HTTP requests.
- Define Function handle_redirects:
- Encapsulates the logic for a GET request with redirection handling.
- Create a PoolManager Instance:
- Initializes a urllib3.PoolManager() instance ('http') to manage HTTP connections.
- Define Initial URL:
- Specifies the initial URL ('initial_url') that may undergo redirects.
- Make a GET Request with Redirects:
- Uses http.request() to make a GET request to the initial URL with redirect=True to enable automatic following of redirects.
- Check Response and Print Results:
- Checks the HTTP status code of the response.
- If the status code is 200, print the final response URL using response.geturl().
- If not, print an error message with the status code.
- Handle Exceptions:
- Uses a try-except block to catch potential "urllib3" request-related exceptions.
- Prints an error message if exceptions occur.
- Run the Function:
- Calls the handle_redirects() function when the script is executed.
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor :
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Python Multiple Requests with Connection Pooling Example.
Next: Python HTTPS Requests with and without SSL/TLS verification example.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
