SQL Exercise: Employees who earn more than 100 as daily salary
[An editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.]
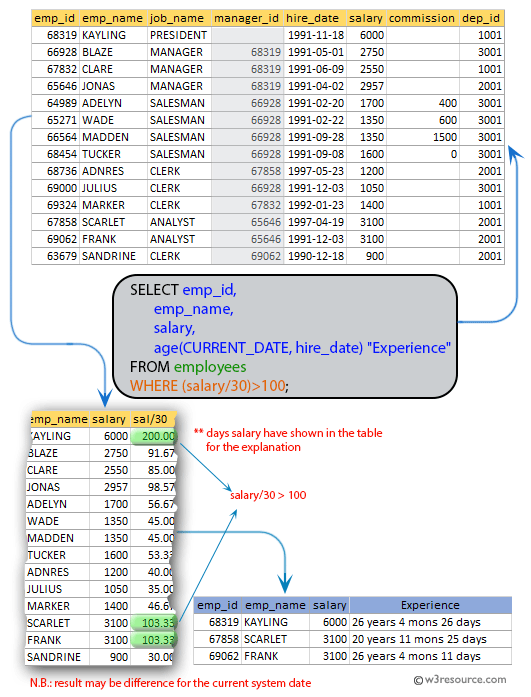
29. From the following table, write a SQL query to find out which employees earn more than 100 per day as a salary. Return employee ID, employee name, salary, and experience.
Sample table: employees
+-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | EMPLOYEE_ID | FIRST_NAME | LAST_NAME | EMAIL | PHONE_NUMBER | HIRE_DATE | JOB_ID | SALARY | COMMISSION_PCT | MANAGER_ID | DEPARTMENT_ID | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+ | 100 | Steven | King | SKING | 515.123.4567 | 2003-06-17 | AD_PRES | 24000.00 | 0.00 | 0 | 90 | | 101 | Neena | Kochhar | NKOCHHAR | 515.123.4568 | 2005-09-21 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 102 | Lex | De Haan | LDEHAAN | 515.123.4569 | 2001-01-13 | AD_VP | 17000.00 | 0.00 | 100 | 90 | | 103 | Alexander | Hunold | AHUNOLD | 590.423.4567 | 2006-01-03 | IT_PROG | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 102 | 60 | | 104 | Bruce | Ernst | BERNST | 590.423.4568 | 2007-05-21 | IT_PROG | 6000.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 105 | David | Austin | DAUSTIN | 590.423.4569 | 2005-06-25 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 106 | Valli | Pataballa | VPATABAL | 590.423.4560 | 2006-02-05 | IT_PROG | 4800.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 107 | Diana | Lorentz | DLORENTZ | 590.423.5567 | 2007-02-07 | IT_PROG | 4200.00 | 0.00 | 103 | 60 | | 108 | Nancy | Greenberg | NGREENBE | 515.124.4569 | 2002-08-17 | FI_MGR | 12008.00 | 0.00 | 101 | 100 | | 109 | Daniel | Faviet | DFAVIET | 515.124.4169 | 2002-08-16 | FI_ACCOUNT | 9000.00 | 0.00 | 108 | 100 | ......... | 206 | William | Gietz | WGIETZ | 515.123.8181 | 2002-06-07 | AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 | 0.00 | 205 | 110 | +-------------+-------------+-------------+----------+--------------------+------------+------------+----------+----------------+------------+---------------+
Pictorial Presentation:
Sample Solution:
SELECT emp_id,
emp_name,
salary,
age(CURRENT_DATE, hire_date) "Experience"
FROM employees
WHERE (salary/30)>100;
Sample Output:
emp_id | emp_name | salary | Experience --------+----------+---------+------------------------- 68319 | KAYLING | 6000.00 | 26 years 2 mons 12 days 67858 | SCARLET | 3100.00 | 20 years 9 mons 11 days 69062 | FRANK | 3100.00 | 26 years 1 mon 27 days (3 rows)
Explanation:
The said query in SQL that selects the "emp_id", "emp_name", "salary", and experience (in years and months) from the 'employees' table and filters the results based on a calculation using the "salary" column.
The experience of the employee in years and months, calculated using the "age" function applied to the "hire_date" column.
The WHERE clause filters the results to include only those employees whose daily salary (calculated by dividing the monthly salary by 30) is greater than 100.
Go to:
PREV : Experiences of all employees working with Manger 68319.
NEXT : Employees retiring after 31-Dec-99 after 8 years.
Practice Online
Sample Database: employees
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.