SQL update statement
Update statement
Once there is some data in the table, it may be required to modify the data. To do so, the SQL UPDATE command can be used. It changes the records in tables.
The SQL UPDATE command changes the data which already exists in the table. Usually, it is needed to make a conditional UPDATE in order to specify which row(s) are going to be updated.
The WHERE clause is used to make the update restricted and the updating can happen only on the specified rows.
Without using any WHERE clause (or without making any restriction) the SQL UPDATE command can change all the records for the specific columns of a table.
Syntax:
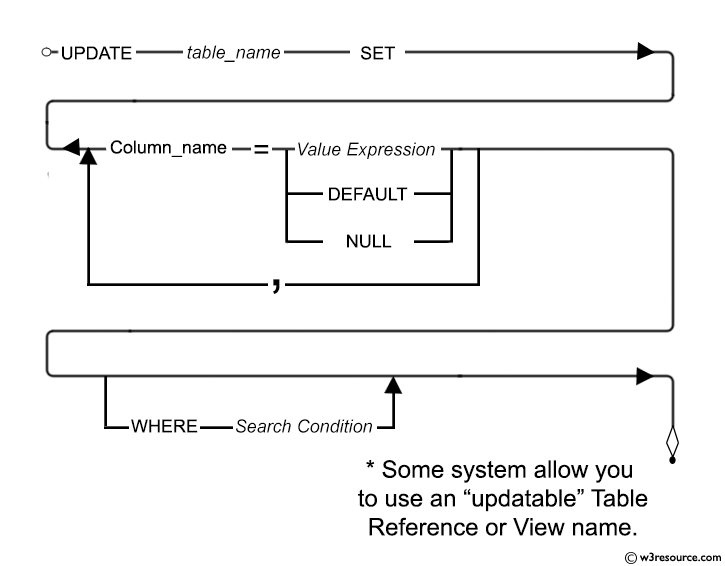
UPDATE < table name > SET<column1>=<value1>,<column2>=<value2>,..... WHERE <condition>;
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| table_name | Name of the table to be updated. |
| column1,column2 | Name of the columns of the table. |
| value1,value2 | New values. |
| condition | Condition(s) using various functions and operators. |
Syntax diagram - UPDATE STATEMENT
Some important questions regarding the SQL UPDATE command
What is the SQL UPDATE command used for?
What does the WHERE clause do in an UPDATE statement?
How can you update multiple columns using the UPDATE command?
What happens if you omit the WHERE clause in an UPDATE statement?
How can you update data in one table based on values from another table?
How can you verify that the update operation was successful?
SQL update for a specific column
Data for a specific column(s) can be changed with the SQL UPDATE statement.
Example:
Sample table: neworders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
..........
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
To change the value of 'ord_description' of 'neworder' table with 'ZOD', the following SQL statement can be used :
SQL Code:
-- This SQL code updates the 'ord_description' column in the 'neworder' table.
-- UPDATE statement begins
UPDATE neworder
-- Specifies the target table 'neworder' where the data will be updated
SET ord_description='ZOD';
-- Sets the value of the 'ord_description' column to 'ZOD' for all rows in the 'neworder' table
Explanation:
- This SQL code uses the UPDATE statement to modify existing records in the 'neworder' table.
- The UPDATE statement specifies the target table 'neworder' where the update operation will be performed.
- The SET clause assigns the new value 'ZOD' to the 'ord_description' column for all rows in the 'neworder' table.
- Since no WHERE clause is provided, the update operation will affect all rows in the table, setting the 'ord_description' column to 'ZOD' for each row.
Here is a new document which is a collection of questions with short and simple answers, useful for learning SQL as well as for interviews.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
PREV : Insert using nested subqueries with any operator
NEXT : Update with condition