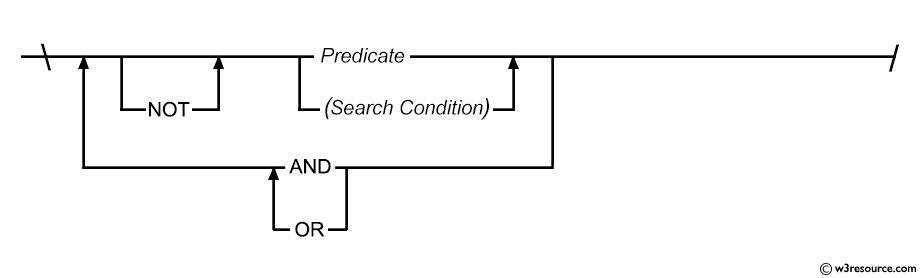
SQL WHERE clause
Where clause
The basic form of the SELECT statement is SELECT-FROM-WHERE block. In a SELECT statement, WHERE clause is optional. Using SELECT without a WHERE clause is useful for browsing data from tables.
In a WHERE clause, you can specify a search condition (logical expression) that has one or more conditions. When the condition (logical expression) evaluates to true the WHERE clause filter unwanted rows from the result.
Here is the syntax:
Syntax:
SELECT <column_list> FROM < table name > WHERE <condition>;
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| table_name | Name of the table. |
| column_list | Name of the columns of the table. |
| condition | Search condition. |
SQL: WHERE clause - Syntax diagram
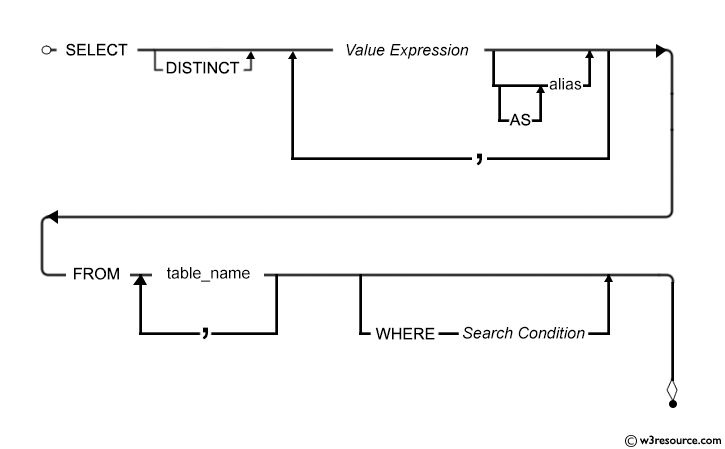
Contents:
- Types of conditions
- Example: Using the WHERE clause
- Example : WHERE clause using comparison conditions
- Example: WHERE clause using expression
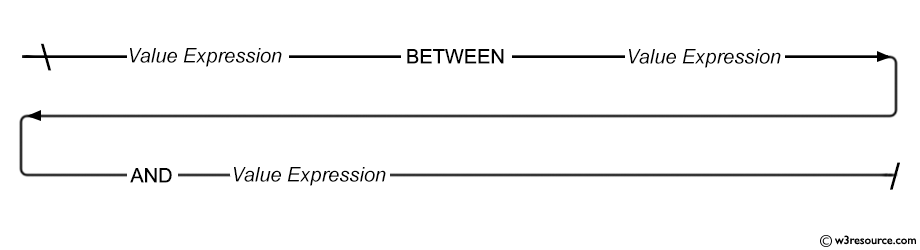
- Example: WHERE clause using BETWEEN condition
- Example: WHERE clause using IN condition
- Example: WHERE clause using LIKE condition
- Example: WHERE clause using NULL condition
- Example: WHERE clause using Logical Conditions
Types of conditions
| Condition | SQL Operators |
|---|---|
| Comparison | =, >, >=, <, <=, <> |
| Range filtering | BETWEEN |
| Match a character pattern | LIKE |
| List filtering [Match any of a list of values] | IN |
| Null testing | IS NULL |
A list of SQL Operators and Descriptions can be used in WHERE clause:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Tests for equality between two values. |
| <> | Tests for inequality between two values. |
| > | Tests if the left operand is greater than the right operand. |
| < | Tests if the left operand is less than the right operand. |
| >= | Tests if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand. |
| <= | Tests if the left operand is less than or equal to the right operand. |
| BETWEEN | Tests if a value lies within a specified range (inclusive). |
| IN | Tests if a value matches any value in a list of specified values. |
| LIKE | Tests if a value matches a specified pattern, using wildcards (%) to represent zero or more characters |
| and (_) to represent a single character. | |
| IS NULL | Tests if a value is NULL (has no value). |
| IS NOT NULL | Tests if a value is not NULL (has a value). |
SQL: Comparison condition - Syntax diagram
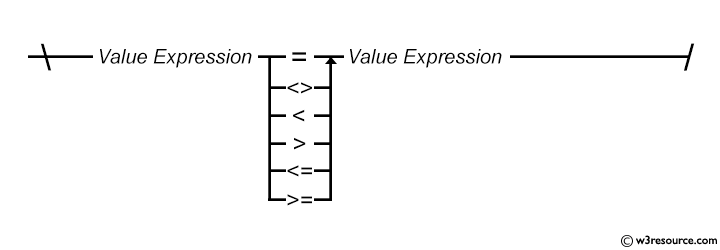
Example: Using the WHERE clause in SQL
The query selects the employee_id, first_name, last_name, and department_id columns from the employees table, filtering the results to include only rows where the department_id is equal to 100.
Sample table : employees
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id
-- From the 'employees' table
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'department_id' is equal to 100
-- From the 'employees' table
WHERE department_id = 100;
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', and 'department_id' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE department_id = 100: This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'department_id' column is equal to 100. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with a 'department_id' of 100 to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
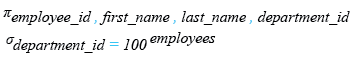
Relational Algebra Tree:
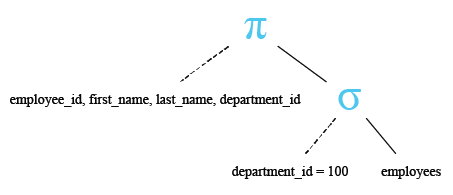
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- -------------
108 Nancy Greenberg 100
109 Daniel Faviet 100
110 John Chen 100
111 Ismael Sciarra 100
112 Jose Manuel Urman 100
113 Luis Popp 100
Visual presentation :
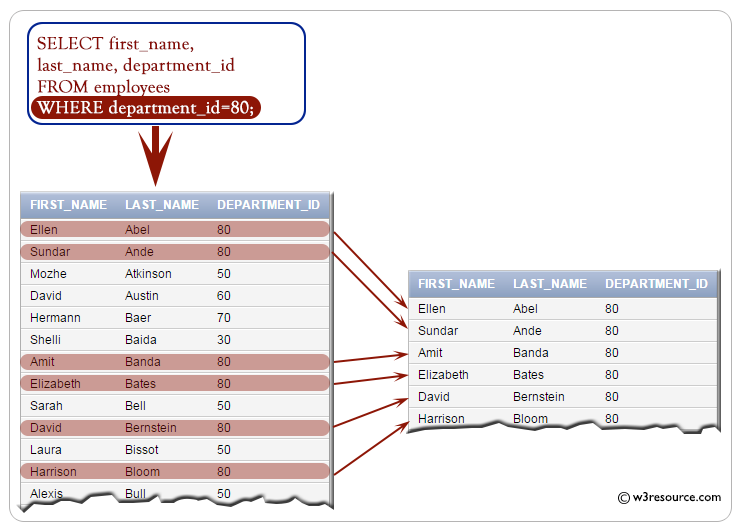
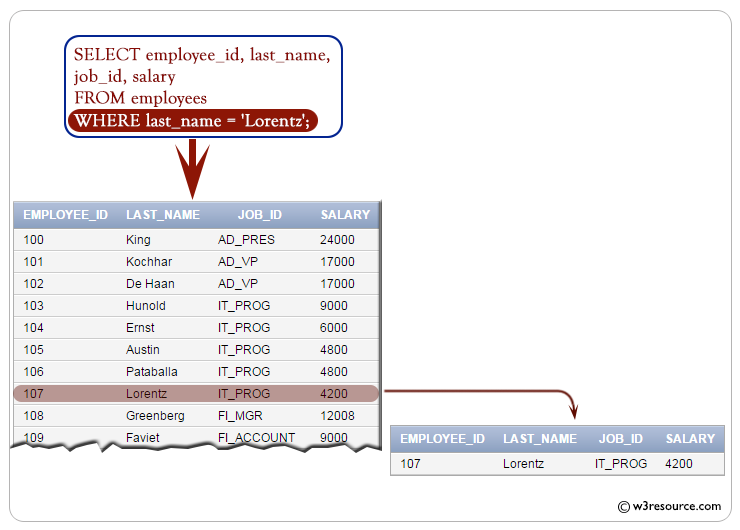
The provided SQL code retrieves the employee ID, job ID, and salary of employees with the last name 'Lorentz' from the employees table.
Note : Character strings are enclosed in quotation marks. Character values are case-sensitive for some database.
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns: employee_id, job_id, salary
SELECT employee_id, job_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'last_name' is equal to 'Lorentz'
WHERE last_name = 'Lorentz';
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, job_id, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'job_id', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE last_name = 'Lorentz': This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'last_name' column is equal to 'Lorentz'. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with the last name 'Lorentz' to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
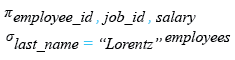
Relational Algebra Tree:
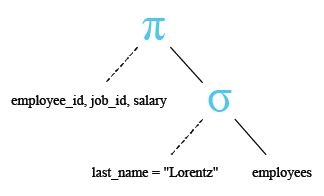
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID JOB_ID SALARY
----------- ---------- ----------
107 IT_PROG 4200
Visual presentation :
Example: WHERE clause using comparison conditions in SQL
The provided SQL query retrieves the employee ID, first name, last name, and salary of employees with a salary greater than or equal to 4000.
Sample table : employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'salary' is greater than or equal to 4000
FROM employees
WHERE salary >= 4000;
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE salary >= 4000: This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'salary' column is greater than or equal to 4000. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with a salary of 4000 or higher to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
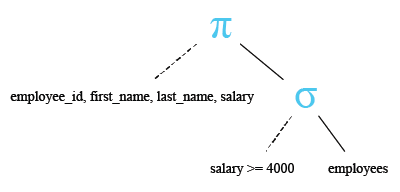
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ----------
100 Steven King 24000
101 Neena Kochhar 17000
102 Lex De Haan 17000
103 Alexander Hunold 9000
104 Bruce Ernst 6000
105 David Austin 4800
106 Valli Pataballa 4800
107 Diana Lorentz 4200
108 Nancy Greenberg 12008
109 Daniel Faviet 9000
110 John Chen 8200
111 Ismael Sciarra 7700
112 Jose Manuel Urman 7800
113 Luis Popp 6900
114 Den Raphaely 11000
.........................
.........................
Example: WHERE clause using expression in SQL
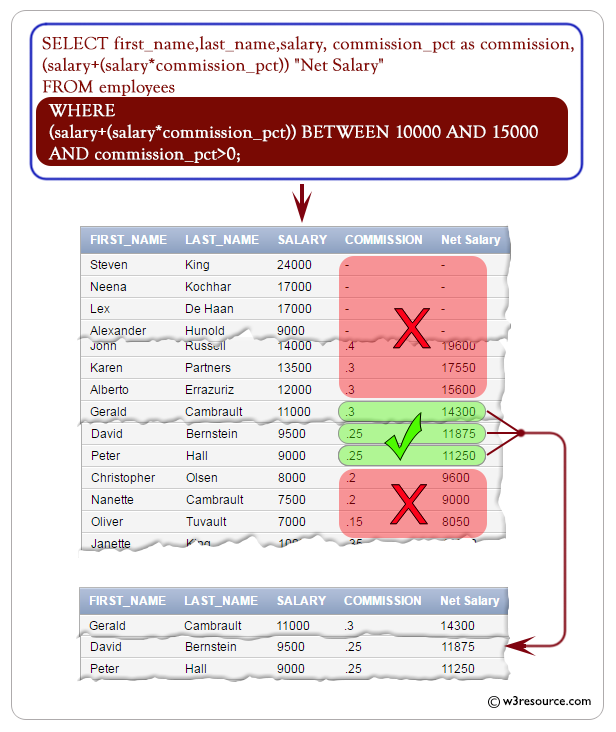
The given SQL query retrieves the first name, last name, salary, and net salary (calculated as salary plus the product of salary and commission percentage) of employees whose net salary falls within the range of 10000 to 15000 and who receive a commission percentage greater than zero.
Sample table: employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: first_name, last_name, salary
-- Calculating the "Net Salary" by adding the commission to the salary
SELECT first_name, last_name, salary, (salary + (salary * commission_pct)) "Net Salary"
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the "Net Salary" is between 10000 and 15000
-- and the commission_pct is greater than 0
WHERE (salary + (salary * commission_pct)) BETWEEN 10000 AND 15000 AND commission_pct > 0;
Explanation:
- SELECT first_name, last_name, salary, (salary + (salary * commission_pct)) "Net Salary": This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'first_name', 'last_name', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table. Additionally, it calculates the "Net Salary" by adding the commission percentage (commission_pct) to the salary. The result is aliased as "Net Salary".
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE (salary + (salary * commission_pct)) BETWEEN 10000 AND 15000 AND commission_pct > 0: This line specifies conditions for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the calculated "Net Salary" falls between 10000 and 15000, and where the commission percentage (commission_pct) is greater than 0. These conditions act as filters, allowing only rows that meet both criteria to be included in the result set.
Output:
FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME SALARY Net Salary -------------------- ------------------------- ---------- ---------- Gerald Cambrault 11000 14300 Eleni Zlotkey 10500 12600 Peter Tucker 10000 13000 David Bernstein 9500 11875 Peter Hall 9000 11250 Janette King 10000 13500 Patrick Sully 9500 12825 Allan McEwen 9000 12150 Lindsey Smith 8000 10400 Clara Vishney 10500 13125 Danielle Greene 9500 10925 Lisa Ozer 11500 14375 Harrison Bloom 10000 12000 Tayler Fox 9600 11520 Ellen Abel 11000 14300 Alyssa Hutton 8800 11000 Jonathon Taylor 8600 10320 Jack Livingston 8400 10080
Visual presentation :
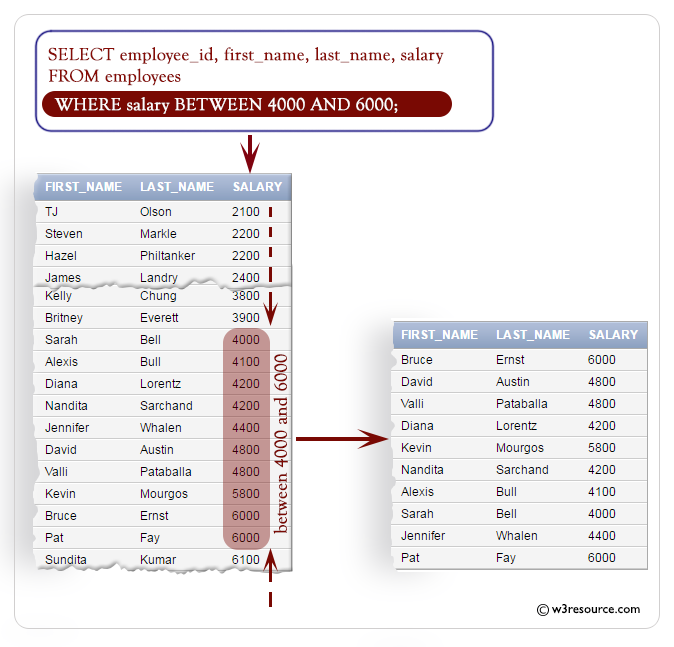
Example: WHERE clause using BETWEEN condition in SQL
The BETWEEN condition is used to test for values in a list.
SQL: BETWEEN condition - Syntax diagram
The given SQL query retrieves the employee ID, first name, last name, and salary of employees whose salary falls within the range of 4000 to 6000, inclusive.
Sample table : employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'salary' is between 4000 and 6000
WHERE salary BETWEEN 4000 AND 6000;
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE salary BETWEEN 4000 AND 6000: This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'salary' column falls within the range of 4000 to 6000 (inclusive). The BETWEEN keyword is used to specify a range condition.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
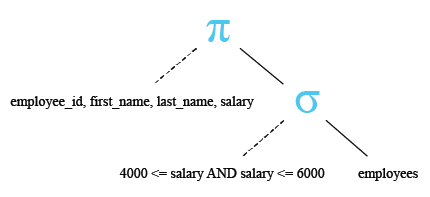
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ----------
104 Bruce Ernst 6000
105 David Austin 4800
106 Valli Pataballa 4800
107 Diana Lorentz 4200
124 Kevin Mourgos 5800
184 Nandita Sarchand 4200
185 Alexis Bull 4100
192 Sarah Bell 4000
200 Jennifer Whalen 4400
202 Pat Fay 6000
Visual presentation :
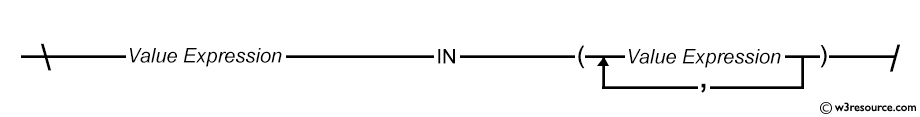
Example: WHERE clause using IN condition in SQL
The IN condition is used to test for values in a list.
SQL: IN condition - Syntax diagram
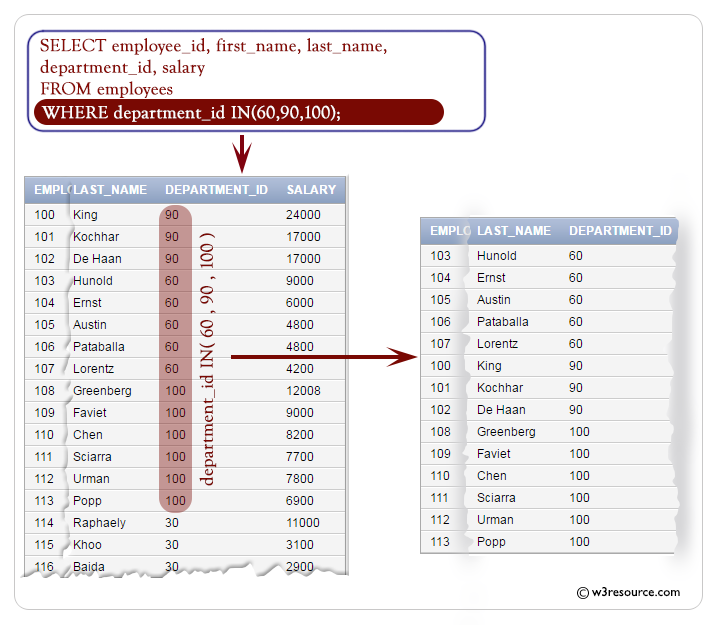
The following query displays the employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id and salary of employees whose department_id 60, 90 or 100.
Sample table : employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
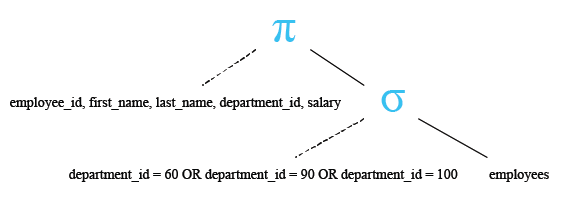
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'department_id' is in the list (60, 90, 100)
WHERE department_id IN (60, 90, 100);
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'department_id', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE department_id IN (60, 90, 100): This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'department_id' column is contained within the list (60, 90, 100). The IN keyword is used to check if the value of 'department_id' matches any value in the provided list.
Relational Algebra Expression:
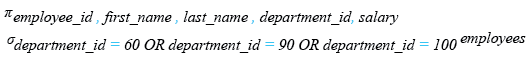
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output :
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ------------- ----------
103 Alexander Hunold 60 9000
104 Bruce Ernst 60 6000
105 David Austin 60 4800
106 Valli Pataballa 60 4800
107 Diana Lorentz 60 4200
100 Steven King 90 24000
101 Neena Kochhar 90 17000
102 Lex De Haan 90 17000
108 Nancy Greenberg 100 12008
109 Daniel Faviet 100 9000
110 John Chen 100 8200
111 Ismael Sciarra 100 7700
112 Jose Manuel Urman 100 7800
113 Luis Popp 100 6900
Visual presentation :
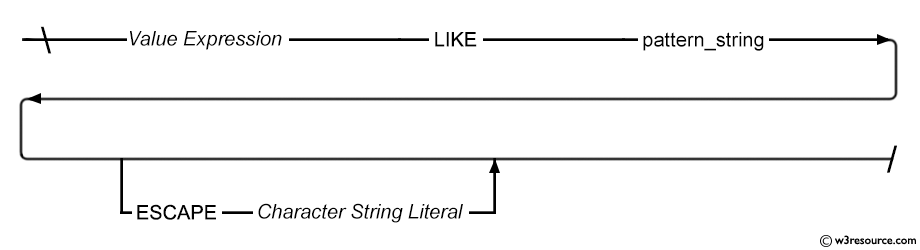
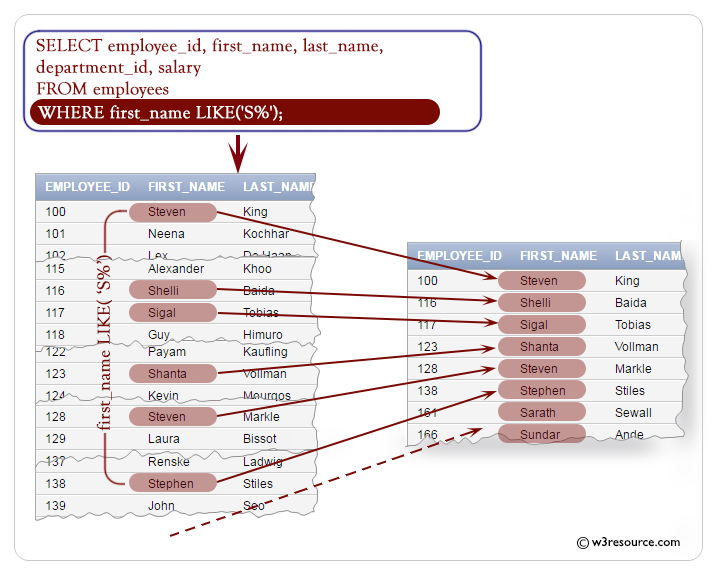
Example: WHERE clause using LIKE condition in SQL
The LIKE condition facilitates wildcard searches within string values. This condition allows for the inclusion of numbers or literal characters, where '_' represents a single character and '%' represents zero or multiple characters.
SQL: LIKE condition - Syntax diagram
The following query displays the employee_id, first_name, last_name and salary of employees whose first_name starting with 'S'.
Sample table : employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
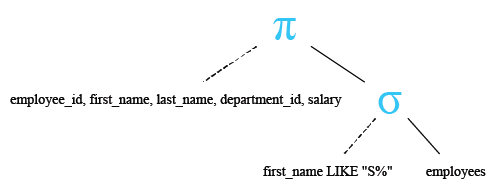
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'first_name' starts with the letter 'S'
WHERE first_name LIKE ('S%');
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'department_id', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE first_name LIKE ('S%'): This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'first_name' column starts with the letter 'S'. The LIKE keyword is used for pattern matching, where 'S%' represents any string that starts with 'S' followed by zero or more characters.
Relational Algebra Expression:
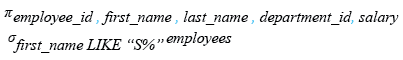
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ------------- ----------
166 Sundar Ande 80 6400
116 Shelli Baida 30 2900
192 Sarah Bell 50 4000
205 Shelley Higgins 110 12008
100 Steven King 90 24000
173 Sundita Kumar 80 6100
128 Steven Markle 50 2200
203 Susan Mavris 40 6500
194 Samuel McCain 50 3200
161 Sarath Sewall 80 7000
138 Stephen Stiles 50 3200
117 Sigal Tobias 30 2800
123 Shanta Vollman 50 6500
Visual presentation :
Example : WHERE clause using NULL condition in SQL
IS NULL operator is used to test for nulls.
SQL: NULL condition - Syntax diagram
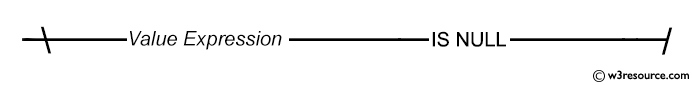
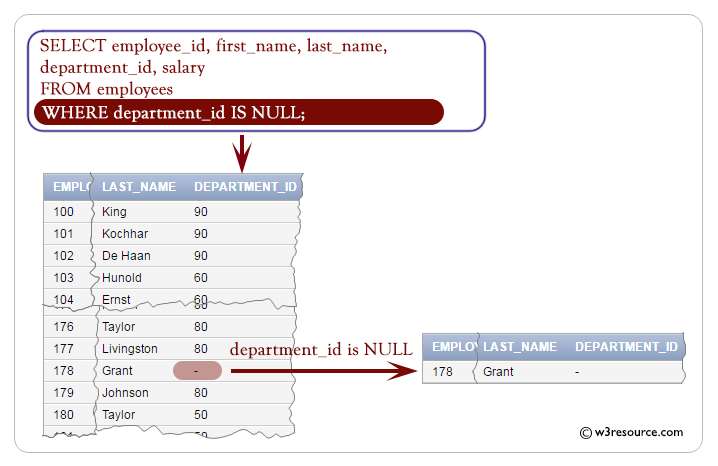
The following query displays the employee_id, first_name, last_name and salary of employees whose department_id is null.
Sample table : employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'department_id' is NULL
WHERE department_id IS NULL;
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'department_id', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE department_id IS NULL: This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'department_id' column is NULL. The IS NULL condition is used to check for NULL values in the 'department_id' column.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ------------- ----------
178 Kimberely Grant 7000
Visual presentation :
Example : WHERE clause using Logical Conditions in SQL
Logical Conditions
| Operators | Description |
|---|---|
| AND | Returns TRUE if both conditions are true. |
| OR | Returns TRUE if either condition is true. |
| NOT | Returns TRUE if the following condition is false. |
SQL: Logical condition - Syntax diagram
Example : WHERE clause using the AND operator in SQL
The following query displays the employee_id, first_name, last_name and salary of employees whose first_name starting with 'S' and salary greater than or equal to 4000.
Sample table : employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'first_name' starts with the letter 'S'
-- and the 'salary' is greater than or equal to 4000
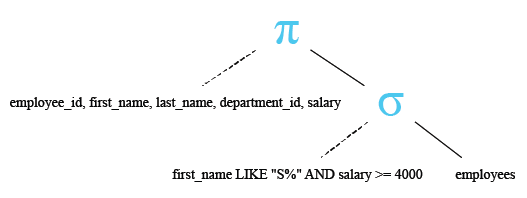
WHERE first_name LIKE ('S%') AND salary >= 4000;
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'department_id', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE first_name LIKE ('S%') AND salary >= 4000: This line specifies conditions for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where:
- The value in the 'first_name' column starts with the letter 'S' (using the LIKE keyword for pattern matching).
- The value in the 'salary' column is greater than or equal to 4000.
- The AND keyword is used to combine these conditions, ensuring that both conditions must be true for a row to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
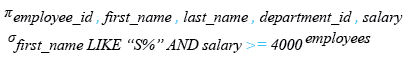
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ------------- ----------
166 Sundar Ande 80 6400
192 Sarah Bell 50 4000
205 Shelley Higgins 110 12008
100 Steven King 90 24000
173 Sundita Kumar 80 6100
203 Susan Mavris 40 6500
161 Sarath Sewall 80 7000
123 Shanta Vollman 50 6500
Example: WHERE clause using the OR operator in SQL
The following query displays the employee_id, first_name, last_name and salary of employees whose first_name starting with 'S' or 'A'.
Sample table: employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'first_name' starts with the letter 'S'
-- OR the 'first_name' starts with the letter 'A'
WHERE first_name LIKE ('S%') OR first_name LIKE ('A%');
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'department_id', and 'salary' from the 'employees' table.
- FROM employees: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'employees' table.
- WHERE first_name LIKE ('S%') OR first_name LIKE ('A%'): This line specifies conditions for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where:
- The value in the 'first_name' column starts with the letter 'S' (using the LIKE keyword for pattern matching), OR
- The value in the 'first_name' column starts with the letter 'A'.
- The OR keyword is used to combine these conditions, ensuring that a row will be included in the result set if either condition is true.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
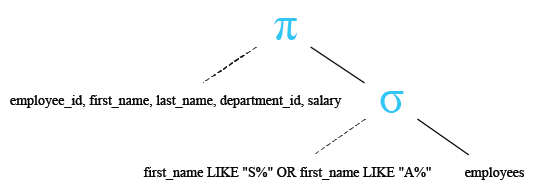
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ------------- ----------
100 Steven King 90 24000
103 Alexander Hunold 60 9000
115 Alexander Khoo 30 3100
116 Shelli Baida 30 2900
117 Sigal Tobias 30 2800
121 Adam Fripp 50 8200
123 Shanta Vollman 50 6500
128 Steven Markle 50 2200
138 Stephen Stiles 50 3200
147 Alberto Errazuriz 80 12000
158 Allan McEwen 80 9000
161 Sarath Sewall 80 7000
166 Sundar Ande 80 6400
167 Amit Banda 80 6200
173 Sundita Kumar 80 6100
175 Alyssa Hutton 80 8800
185 Alexis Bull 50 4100
187 Anthony Cabrio 50 3000
192 Sarah Bell 50 4000
194 Samuel McCain 50 3200
196 Alana Walsh 50 3100
203 Susan Mavris 40 6500
205 Shelley Higgins 110 12008
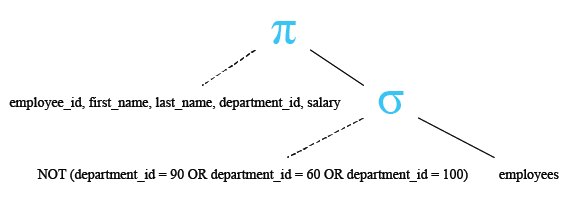
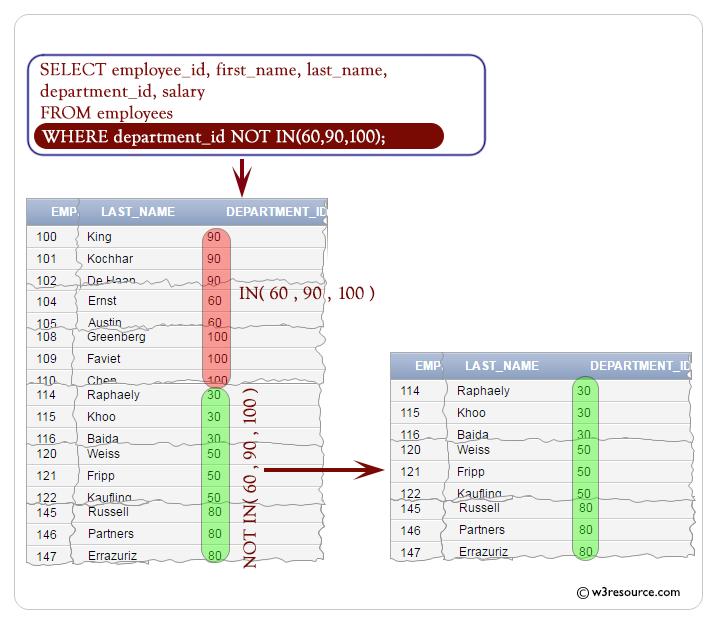
Example: WHERE clause using the NOT operator in SQL
The following query displays the employee_id, first_name, last_name and salary of employees except the department_id 90, 60 or 100 :
Sample table: employees
employee_id first_name last_name email phone_number hire_date job_id salary commission_pct manager_id department_id ----------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ------------ ---------- ---------- ---------- -------------- ---------- ------------- 100 Steven King SKING 515.123.4567 6/17/1987 AD_PRES 24000 90 101 Neena Kochhar NKOCHHAR 515.123.4568 6/18/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 102 Lex De Haan LDEHAAN 515.123.4569 6/19/1987 AD_VP 17000 100 90 103 Alexander Hunold AHUNOLD 590.423.4567 6/20/1987 IT_PROG 9000 102 60 104 Bruce Ernst BERNST 590.423.4568 6/21/1987 IT_PROG 6000 103 60 105 David Austin DAUSTIN 590.423.4569 6/22/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 106 Valli Pataballa VPATABAL 590.423.4560 6/23/1987 IT_PROG 4800 103 60 107 Diana Lorentz DLORENTZ 590.423.5567 6/24/1987 IT_PROG 4200 103 60 108 Nancy Greenberg NGREENBE 515.124.4569 6/25/1987 FI_MGR 12000 101 100 109 Daniel Faviet DFAVIET 515.124.4169 6/26/1987 FI_ACCOUNT 9000 108 100 ........... 206 William Gietz WGIETZ 515.123.8181 10/1/1987 AC_ACCOUNT 8300 205 110
SQL Code:
-- Selecting specific columns from the 'employees' table: employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary
-- From the 'employees' table
FROM employees
-- Filtering the results to include only rows where the 'department_id' is NOT IN (90, 60, 100)
WHERE department_id NOT IN (90, 60, 100);
Explanation:
- SELECT employee_id, first_name, last_name, department_id, salary: This line selects specific columns from the 'employees' table, namely 'employee_id', 'first_name', 'last_name', 'department_id', and 'salary'.
- FROM employees: This specifies that the data is being retrieved from the 'employees' table.
- WHERE department_id NOT IN (90, 60, 100): This condition filters the rows to only include those where the 'department_id' is not equal to 90, 60, or 100. The NOT IN operator negates the list of values provided within the parentheses.
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME DEPARTMENT_ID SALARY
----------- -------------------- ------------------------- ------------- ----------
114 Den Raphaely 30 11000
115 Alexander Khoo 30 3100
116 Shelli Baida 30 2900
117 Sigal Tobias 30 2800
118 Guy Himuro 30 2600
119 Karen Colmenares 30 2500
120 Matthew Weiss 50 8000
121 Adam Fripp 50 8200
122 Payam Kaufling 50 7900
123 Shanta Vollman 50 6500
124 Kevin Mourgos 50 5800
125 Julia Nayer 50 3200
126 Irene Mikkilineni 50 2700
127 James Landry 50 2400
128 Steven Markle 50 2200
129 Laura Bissot 50 3300
130 Mozhe Atkinson 50 2800
131 James Marlow 50 2500
132 TJ Olson 50 2100
133 Jason Mallin 50 3300
134 Michael Rogers 50 2900
135 Ki Gee 50 2400
136 Hazel Philtanker 50 2200
137 Renske Ladwig 50 3600
................
................
Visual presentation :
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
PREV :SQL SELECT statement
NEXT : SQL ORDER BY clause
