SQL HAVING clause
Having Clause
SQL HAVING clause specifies a search condition for a group or an aggregate. HAVING is usually used in a GROUP BY clause, but even if you are not using GROUP BY clause, you can use HAVING to function like a WHERE clause. You must use HAVING with SQL SELECT.
Syntax:
SELECT <column_list> FROM < table name >
WHERE <search_condition]>
GROUP BY <columns>
[HAVING] <search_condition]>
[ORDER BY {order_expression [ASC | DESC]}[, ...]];
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| table_name | Name of the table. |
| column_list | Name of the columns of the table. |
| columns | Name of the columns which will participate in grouping. |
How a HAVING clause works IN SQL?
- The select clause specifies the columns.
- The from clause supplies a set of potential rows for the result.
- The where clause gives a filter for these potential rows.
- The group by clause divide the rows in a table into smaller groups.
- The having clause gives a filter for these group rows.
Some important questions related to the SQL HAVING clause:
What is the purpose of the HAVING clause in SQL?
What happens if you use a column alias defined in the SELECT statement in the HAVING clause?
Can you use the HAVING clause without the GROUP BY clause?
Can you use aggregate functions in the HAVING clause?
Can you use subqueries in the HAVING clause?
In which order are the clauses executed in a SQL query with the HAVING clause?
Can you use logical operators such as AND, OR, and NOT in the HAVING clause?
What is the difference between the WHERE and HAVING clauses?
How do you filter groups based on aggregate values using the HAVING clause?
What are some common use cases for the HAVING clause?
Example: SQL HAVING clause
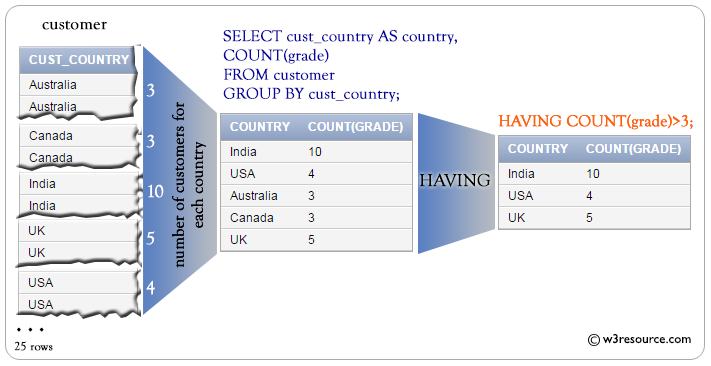
The following query display cust_country and number of customers for the same grade for each cust_country, with the following condition -
1. number of customer for a same 'grade' must be more than 2,
Sample table: customer
SQL Code:
-- This SQL query counts the number of customers in each country who have a grade assigned to them,
-- and displays the country along with the count, but only for countries where the count of grades is greater than 2.
-- SELECT statement begins
SELECT
cust_country, -- Selects the 'cust_country' column
COUNT(grade) -- Counts the number of grades for each country
FROM
customer -- Specifies the 'customer' table to retrieve data from
GROUP BY
cust_country -- Groups the result set by the 'cust_country' column
HAVING
COUNT(grade) > 2; -- Filters the grouped results to include only countries where the count of grades is greater than 2
Explanation:
- This SQL code is a SELECT statement that retrieves data from the 'customer' table.
- It counts the number of customers in each country who have a grade assigned to them and displays the country along with the count.
- The SELECT clause selects the 'cust_country' column from the 'customer' table.
- The COUNT(grade) function counts the number of grades for each country. It is applied within the HAVING clause to filter groups based on this count.
- The GROUP BY clause groups the result set by the 'cust_country' column, ensuring that calculations are performed for each unique country.
- The HAVING clause filters the grouped results to include only countries where the count of grades is greater than 2.
- The query retrieves the country and the count of grades for each country from the 'customer' table, but only for countries where the count of grades is greater than 2.
Relational Algebra Expression:
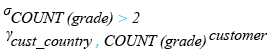
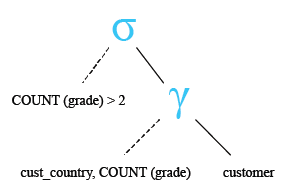
Relational Algebra Tree:
Sample Output:
CUST_COUNTRY COUNT(GRADE) -------------------- ------------ USA 4 India 10 Australia 3 Canada 3 UK 5
Pictorial presentation:
SQL HAVING using where
In the following example, the SQL WHERE clause along with the HAVING clause have used to make a select statement.
Example:
Sample table: customer+-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ |CUST_CODE | CUST_NAME | CUST_CITY | WORKING_AREA | CUST_COUNTRY | GRADE | OPENING_AMT | RECEIVE_AMT | PAYMENT_AMT |OUTSTANDING_AMT| PHONE_NO | AGENT_CODE | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ | C00013 | Holmes | London | London | UK | 2 | 6000.00 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | BBBBBBB | A003 | | C00001 | Micheal | New York | New York | USA | 2 | 3000.00 | 5000.00 | 2000.00 | 6000.00 | CCCCCCC | A008 | | C00020 | Albert | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 6000.00 | BBBBSBB | A008 | | C00025 | Ravindran | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | 8000.00 | AVAVAVA | A011 | | C00024 | Cook | London | London | UK | 2 | 4000.00 | 9000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | FSDDSDF | A006 | | C00015 | Stuart | London | London | UK | 1 | 6000.00 | 8000.00 | 3000.00 | 11000.00 | GFSGERS | A003 | | C00002 | Bolt | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | DDNRDRH | A008 | | C00018 | Fleming | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 2 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | NHBGVFC | A005 | | C00021 | Jacks | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | WERTGDF | A005 | | C00019 | Yearannaidu | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | ZZZZBFV | A010 | | C00005 | Sasikant | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 147-25896312 | A002 | | C00007 | Ramanathan | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | GHRDWSD | A010 | | C00022 | Avinash | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 2 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | 113-12345678 | A002 | | C00004 | Winston | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 5000.00 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | AAAAAAA | A005 | | C00023 | Karl | London | London | UK | 0 | 4000.00 | 6000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | AAAABAA | A006 | | C00006 | Shilton | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 10000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 11000.00 | DDDDDDD | A004 | | C00010 | Charles | Hampshair | Hampshair | UK | 3 | 6000.00 | 4000.00 | 5000.00 | 5000.00 | MMMMMMM | A009 | | C00017 | Srinivas | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 4000.00 | 3000.00 | 9000.00 | AAAAAAB | A007 | | C00012 | Steven | San Jose | San Jose | USA | 1 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | KRFYGJK | A012 | | C00008 | Karolina | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | HJKORED | A004 | | C00003 | Martin | Torento | Torento | Canada | 2 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | MJYURFD | A004 | | C00009 | Ramesh | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 3 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | 12000.00 | Phone No | A002 | | C00014 | Rangarappa | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | AAAATGF | A001 | | C00016 | Venkatpati | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | JRTVFDD | A007 | | C00011 | Sundariya | Chennai | Chennai | India | 3 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | PPHGRTS | A010 | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+
To get list of cust_city, sum of opening_amt, average of receive_amt and maximum payment_amt from customer table with following conditions-
1. grade of customer table must be 2,
2. average of receive_amt for each group of cust_city must be more than 500,
then, the following SQL statement can be used:
SQL Code:
-- This SQL query calculates various financial metrics for customers in each city who have a grade of 2,
-- and displays the city along with the sum of opening amounts, average receive amount, and maximum payment amount.
-- Additionally, it filters the results to include only cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500.
-- SELECT statement begins
SELECT
cust_city, -- Selects the 'cust_city' column
SUM(opening_amt), -- Calculates the sum of opening amounts for each city
AVG(receive_amt), -- Calculates the average receive amount for each city
MAX(payment_amt) -- Finds the maximum payment amount for each city
FROM
customer -- Specifies the 'customer' table to retrieve data from
WHERE
grade = 2 -- Filters the rows where the grade is equal to 2
GROUP BY
cust_city -- Groups the result set by the 'cust_city' column
HAVING
AVG(receive_amt) > 500; -- Filters the grouped results to include only cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500
Explanation:
- This SQL code is a SELECT statement that retrieves data from the 'customer' table.
- It calculates various financial metrics for customers in each city who have a grade of 2 and displays the city along with the sum of opening amounts, average receive amount, and maximum payment amount.
- The SELECT clause selects the 'cust_city' column from the 'customer' table.
- SUM(opening_amt) calculates the sum of opening amounts for each city, AVG(receive_amt) calculates the average receive amount, and MAX(payment_amt) finds the maximum payment amount for each city.
- The WHERE clause filters the rows where the grade is equal to 2, ensuring that only customers with a grade of 2 are considered.
- The GROUP BY clause groups the result set by the 'cust_city' column, ensuring that calculations are performed for each unique city.
- The HAVING clause filters the grouped results to include only cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500.
- The query retrieves the city along with the financial metrics for each city from the 'customer' table, but only for cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500 and the customers have a grade of 2.
Sample Output:
CUST_CITY SUM(OPENING_AMT) AVG(RECEIVE_AMT) MAX(PAYMENT_AMT) ----------------------------------- ---------------- ---------------- ---------------- Bangalore 29000 8250 7000 Brisban 7000 7000 9000 London 10000 7000 7000 Mumbai 7000 11000 9000 New York 3000 5000 2000 Torento 8000 7000 7000
SQL HAVING with order by
In the following example, the SQL WHERE clause along with the HAVING clause is used to make a query. An ORDER BY clause arranges the final result in the specific order. The default order is ascending.
Example:
Sample table: customer+-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ |CUST_CODE | CUST_NAME | CUST_CITY | WORKING_AREA | CUST_COUNTRY | GRADE | OPENING_AMT | RECEIVE_AMT | PAYMENT_AMT |OUTSTANDING_AMT| PHONE_NO | AGENT_CODE | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ | C00013 | Holmes | London | London | UK | 2 | 6000.00 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | BBBBBBB | A003 | | C00001 | Micheal | New York | New York | USA | 2 | 3000.00 | 5000.00 | 2000.00 | 6000.00 | CCCCCCC | A008 | | C00020 | Albert | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 6000.00 | BBBBSBB | A008 | | C00025 | Ravindran | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | 8000.00 | AVAVAVA | A011 | | C00024 | Cook | London | London | UK | 2 | 4000.00 | 9000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | FSDDSDF | A006 | | C00015 | Stuart | London | London | UK | 1 | 6000.00 | 8000.00 | 3000.00 | 11000.00 | GFSGERS | A003 | | C00002 | Bolt | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | DDNRDRH | A008 | | C00018 | Fleming | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 2 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | NHBGVFC | A005 | | C00021 | Jacks | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | WERTGDF | A005 | | C00019 | Yearannaidu | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | ZZZZBFV | A010 | | C00005 | Sasikant | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 147-25896312 | A002 | | C00007 | Ramanathan | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | GHRDWSD | A010 | | C00022 | Avinash | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 2 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | 113-12345678 | A002 | | C00004 | Winston | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 5000.00 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | AAAAAAA | A005 | | C00023 | Karl | London | London | UK | 0 | 4000.00 | 6000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | AAAABAA | A006 | | C00006 | Shilton | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 10000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 11000.00 | DDDDDDD | A004 | | C00010 | Charles | Hampshair | Hampshair | UK | 3 | 6000.00 | 4000.00 | 5000.00 | 5000.00 | MMMMMMM | A009 | | C00017 | Srinivas | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 4000.00 | 3000.00 | 9000.00 | AAAAAAB | A007 | | C00012 | Steven | San Jose | San Jose | USA | 1 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | KRFYGJK | A012 | | C00008 | Karolina | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | HJKORED | A004 | | C00003 | Martin | Torento | Torento | Canada | 2 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | MJYURFD | A004 | | C00009 | Ramesh | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 3 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | 12000.00 | Phone No | A002 | | C00014 | Rangarappa | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | AAAATGF | A001 | | C00016 | Venkatpati | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | JRTVFDD | A007 | | C00011 | Sundariya | Chennai | Chennai | India | 3 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | PPHGRTS | A010 | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+
To get list of cust_city, sum of opening_amt, average of receive_amt and maximum payment_amt from customer table with following conditions-
1. grade of customer table must be 2,
2. average of receive_amt for each group of cust_city must be more than 500,
3. the output should be arranged in the ascending order of SUM(opening_amt),
then, the following SQL statement can be used:
SQL Code:
-- This SQL query calculates various financial metrics for customers in each city who have a grade of 2,
-- and displays the city along with the sum of opening amounts, average receive amount, and maximum payment amount.
-- Additionally, it filters the results to include only cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500,
-- and orders the result set by the sum of opening amounts in ascending order.
-- SELECT statement begins
SELECT
cust_city, -- Selects the 'cust_city' column
SUM(opening_amt), -- Calculates the sum of opening amounts for each city
AVG(receive_amt), -- Calculates the average receive amount for each city
MAX(payment_amt) -- Finds the maximum payment amount for each city
FROM
customer -- Specifies the 'customer' table to retrieve data from
WHERE
grade = 2 -- Filters the rows where the grade is equal to 2
GROUP BY
cust_city -- Groups the result set by the 'cust_city' column
HAVING
AVG(receive_amt) > 500 -- Filters the grouped results to include only cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500
ORDER BY
SUM(opening_amt); -- Orders the result set by the sum of opening amounts in ascending order
Explanation:
- This SQL code is a SELECT statement that retrieves data from the 'customer' table.
- It calculates various financial metrics for customers in each city who have a grade of 2 and displays the city along with the sum of opening amounts, average receive amount, and maximum payment amount.
- The SELECT clause selects the 'cust_city' column from the 'customer' table.
- SUM(opening_amt) calculates the sum of opening amounts for each city, AVG(receive_amt) calculates the average receive amount, and MAX(payment_amt) finds the maximum payment amount for each city.
- The WHERE clause filters the rows where the grade is equal to 2, ensuring that only customers with a grade of 2 are considered.
- The GROUP BY clause groups the result set by the 'cust_city' column, ensuring that calculations are performed for each unique city.
- The HAVING clause filters the grouped results to include only cities where the average receive amount is greater than 500.
- The ORDER BY clause orders the result set by the sum of opening amounts in ascending order.
Sample Output:
CUST_CITY SUM(OPENING_AMT) AVG(RECEIVE_AMT) MAX(PAYMENT_AMT) ----------------------------------- ---------------- ---------------- ---------------- New York 3000 5000 2000 Brisban 7000 7000 9000 Mumbai 7000 11000 9000 Torento 8000 7000 7000 London 10000 7000 7000 Bangalore 29000 8250 7000
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: Group By
Next: SELECT with DISTINCT
