C++ Exercises: Move all negative elements of an array of integers to the end of the array without changing the order of positive element and negative element
18. Move Negative Elements to the End
Write a C++ program to move all negative elements of an array of integers to the end of the array. This is done without changing the order of the positive and negative elements of the array.
Sample Solution:
C++ Code :
#include <iostream> // Header file for input/output stream
#include <cstring> // Header file for C-style string operations
using namespace std; // Using the standard namespace
// Function to segregate positive and negative elements in an array
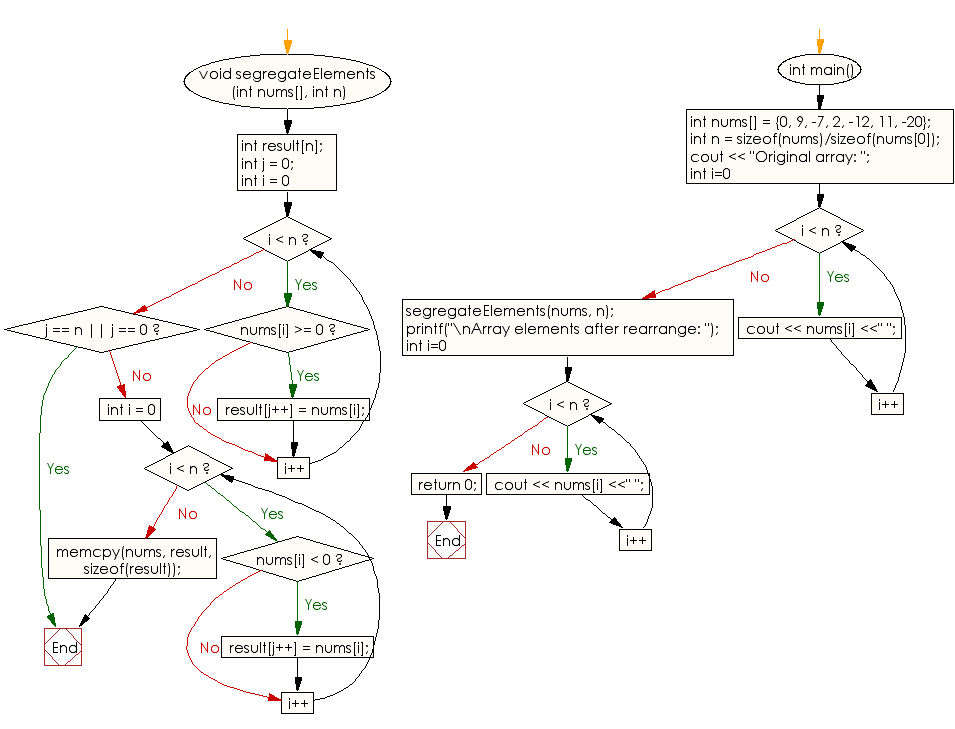
void segregateElements(int nums[], int n)
{
int result[n]; // Array to store the segregated elements
int j = 0; // Index to track positive elements in the result array
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] >= 0)
result[j++] = nums[i]; // Store positive elements at the beginning of 'result'
}
// If all elements are positive or all elements are negative, return without further processing
if (j == n || j == 0)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (nums[i] < 0)
result[j++] = nums[i]; // Store negative elements after positive elements in 'result'
}
// Copy the contents of 'result' back to 'nums'
memcpy(nums, result, sizeof(result));
}
// Main function
int main()
{
int nums[] = {0, 9, -7, 2, -12, 11, -20}; // Declaration and initialization of an integer array
int n = sizeof(nums) / sizeof(nums[0]); // Calculate the number of elements in the array
cout << "Original array: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << nums[i] << " "; // Output each element of the original array
segregateElements(nums, n); // Segregate positive and negative elements in the array
cout << "\nArray elements after rearrange: ";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << nums[i] << " "; // Output each element of the modified array after rearrangement
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Original array: 0 9 -7 2 -12 11 -20 Array elements after rearrange: 0 9 2 11 -7 -12 -20
Flowchart:
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a C++ program to move all negative numbers in an array to the end while preserving the order of positive numbers.
- Write a C++ program that reads an array and reorders it so that all negatives appear at the end using a two-pass algorithm.
- Write a C++ program to partition an array into positive and negative elements without disturbing their original order.
- Write a C++ program that creates a new array where all non-negative numbers are listed first, followed by negative numbers, maintaining their sequence.
Go to:
PREV : Descending Order Sorting by Absolute Difference.
NEXT : Find Element Occurring Odd Number of Times.
C++ Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
