NumPy Tutorial
What is NumPy?
NumPy is the fundamental package for scientific computing in Python. It is a Python library that provides a multidimensional array object, various derived objects (such as masked arrays and matrices), and an assortment of routines for fast operations on arrays, including mathematical, logical, shape manipulation, sorting, selecting, I/O, discrete Fourier transforms, basic linear algebra, basic statistical operations, random simulation and much more.
NumPy Basics
import numpy as np
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| np.array([1,2,3]) | 1d array |
| np.array([(1,2,3),(4,5,6)]) | 2d array |
| np.arange(start,stop,step) | range array |
Placeholders
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| np.linspace(0,2,9) | Add evenly spaced values btw interval to array of length |
| np.zeros((1,2)) | Create and array filled with zeros |
| np.ones((1,2)) | Creates an array filled with ones |
| np.random.random((5,5)) | Creates random array |
| np.empty((2,2)) | Creates an empty array |
Array
| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| array.shape | Dimensions (Rows,Columns) |
| len(array) | Length of Array |
| array.ndim | Number of Array Dimensions |
| array.dtype | Data Type |
| array.astype(type) | Converts to Data Type |
| type(array) | Type of Array |
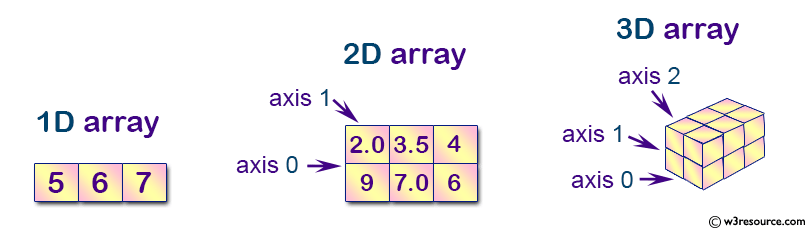
Copying/Sorting
| Operators | Description |
|---|---|
| np.copy(array) | Creates copy of array |
| other = array.copy() | Creates deep copy of array |
| array.sort() | Sorts an array |
| array.sort(axis=0) | Sorts axis of array |
Array Manipulation
Adding or Removing Elements
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| np.append(a,b) | Append items to array |
| np.insert(array, 1, 2, axis) | Insert items into array at axis 0 or 1 |
| np.resize((2,4)) | Resize array to shape(2,4) |
| np.delete(array,1,axis) | Deletes items from array |
Combining Arrays
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| np.concatenate((a,b),axis=0) | Concatenates 2 arrays, adds to end |
| np.vstack((a,b)) | Stack array row-wise |
| np.hstack((a,b)) | Stack array column wise |
Splitting Arrays
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| numpy.split() | Split an array into multiple sub-arrays. |
| np.array_split(array, 3) | Split an array in sub-arrays of (nearly) identical size |
| numpy.hsplit(array, 3) | Split the array horizontally at 3rd index |
More
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| other = ndarray.flatten() | Flattens a 2d array to 1d |
| array = np.transpose(other) array.T |
Transpose array |
| inverse = np.linalg.inv(matrix) | Inverse of a given matrix |
Mathematics
Operations
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| np.add(x,y) x + y |
Addition |
| np.substract(x,y) x - y |
Subtraction |
| np.divide(x,y) x / y |
Division |
| np.multiply(x,y) x @ y |
Multiplication |
| np.sqrt(x) | Square Root |
| np.sin(x) | Element-wise sine |
| np.cos(x) | Element-wise cosine |
| np.log(x) | Element-wise natural log |
| np.dot(x,y) | Dot product |
| np.roots([1,0,-4]) | Roots of a given polynomial coefficients |
Comparison
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| == | Equal |
| != | Not equal |
| < | Smaller than |
| > | Greater than |
| <= | Smaller than or equal |
| >= | Greater than or equal |
| np.array_equal(x,y) | Array-wise comparison |
Basic Statistics
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| np.mean(array) | Mean |
| np.median(array) | Median |
| array.corrcoef() | Correlation Coefficient |
| np.std(array) | Standard Deviation |
More
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| array.sum() | Array-wise sum |
| array.min() | Array-wise minimum value |
| array.max(axis=0) | Maximum value of specified axis |
| array.cumsum(axis=0) | Cumulative sum of specified axis |
Slicing and Subsetting
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| array[i] | 1d array at index i |
| array[i,j] | 2d array at index[i][j] |
| array[i<4] | Boolean Indexing, see Tricks |
| array[0:3] | Select items of index 0, 1 and 2 |
| array[0:2,1] | Select items of rows 0 and 1 at column 1 |
| array[:1] | Select items of row 0 (equals array[0:1, :]) |
| array[1:2, :] | Select items of row 1 |
| [comment]: <> ( | array[1,...] |
| array[ : :-1] | Reverses array |
Importing/exporting
| Syntax | Description |
|---|---|
| np.loadtxt('file.txt') | From a text file. |
| np.genfromtxt('file.csv',delimiter=',') | From a csv file. |
| np.savetxt('file.txt',arr,delimiter=' ') | Writes to a text file. |
| np.savetxt('file.csv',arr,delimiter=',') | Writes to a CSV file. |
Next: NumPy Installation
