PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function
SPLIT_PART() function
The PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function is used to split a string into multiple parts based on a delimiter and return a specific part of the split result. It takes three arguments: the input string, the delimiter, and the position of the desired part, start from the left of the string.
Uses of SPLIT_PART() Function
- Extract Specific Substrings: Retrieve specific parts of a string by specifying a delimiter and position.
- Data Parsing: Break down complex strings into meaningful components.
- Email Processing: Extract domain names or usernames from email addresses.
- Name Splitting: Separate first names, last names, or middle names from full names.
- ID and Code Extraction: Extract specific segments from IDs or codes based on consistent delimiters.
- Log File Analysis: Parse log entries that use delimiters to separate fields.
Syntax:
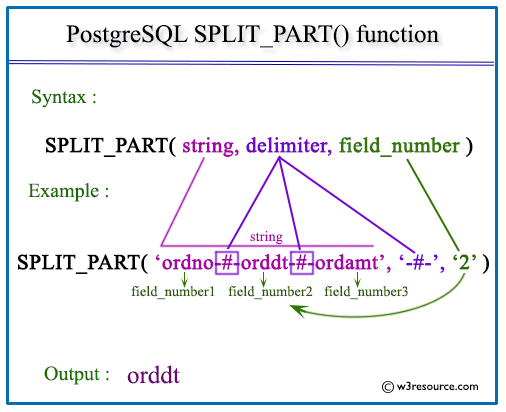
split_part(<string>,<delimiter>, <field_number>)
PostgreSQL Version: 9.3
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function
Example: PostgreSQL SPLIT_PART() function :
In the example below, the delimiter of the defined string is '-#-' and specified field number is 2. So the split_part function splits the second field from the specified string.
SQL Code:
SELECT split_part('ordno-#-orddt-#-ordamt', '-#-', 2);
Output:
split_part ------------ orddt (1 row)
Example:
Table : test
p_name |p_id |p_email | -----------+--------------+-----------------------+ Peter Mont |PEMO-7894-OMEP|[email protected] | Derak Powel|DEPO-8529-OPED|[email protected]|
If we want to extract the first part of the p_name column the following code can be used:
SQL Code:
SELECT SPLIT_PART(p_name, ' ', 1) AS first_name
FROM test;
Output:
first_name| ----------+ Peter | Derak |
In this example, we use a space (' ') as the delimiter to split the p_name column. The 1 as the third argument indicates that we want to retrieve the first part after splitting, which represents the first name. The result will be a list of first names extracted from the p_name column.
Example:
Table : test
p_name |p_id |p_email | -----------+--------------+-----------------------+ Peter Mont |PEMO-7894-OMEP|[email protected] | Derak Powel|DEPO-8529-OPED|[email protected]|
If we want to extract the middle part of the p_id column, which represents the numeric code the following code can be used:
SQL Code:
SELECT SPLIT_PART(p_id, '-', 2) AS numeric_p_id
FROM test;
Output:
numeric_p_id| ------------+ 7894 | 8529 |
In this example, we use a hyphen ('-') as the delimiter to split the p_id column. The 2 as the third argument indicates that we want to retrieve the second part after splitting, which corresponds to the numeric code. The result will be a list of numeric codes extracted from the product_code column.
Example:
Table : test
p_name |p_id |p_email | -----------+--------------+-----------------------+ Peter Mont |PEMO-7894-OMEP|[email protected] | Derak Powel|DEPO-8529-OPED|[email protected]|
If we want to extract the domain name from the p_email column the following code can be used:
SQL Code:
SELECT SPLIT_PART(p_email, '@', 2) AS domain_name
FROM test;
Output:
domain_name| -----------+ xyzmail.kom| xyzmail.kom|
In this example, we use the at symbol ('@') as the delimiter to split the p_email column. The 2 as the third argument indicates that we want to retrieve the second part after splitting, which represents the domain name. The result will be a list of domain names extracted from the p_email column.
Previous: RTRIM function
Next: STRPOS function