Pandas Series: plot.density() function
Series-plot.density() function
In statistics, kernel density estimation (KDE) is a non-parametric way to estimate the probability density function (PDF) of a random variable. This function uses Gaussian kernels and includes automatic bandwidth determination.
The plot.density() function generates Kernel Density Estimate plot using Gaussian kernels.
Syntax:
Series.plot.density(self, bw_method=None, ind=None, **kwargs)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Type/Default Value | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|---|
| bw_method | The method used to calculate the estimator bandwidth. This can be 'scott', 'silverman', a scalar constant or a callable. If None (default), 'scott' is used. See scipy.stats.gaussian_kde for more information. | str, scalar or callable | Optional |
| ind | Evaluation points for the estimated PDF. If None (default), 1000 equally spaced points are used. If ind is a NumPy array, the KDE is evaluated at the points passed. If ind is an integer, ind number of equally spaced points are used. | NumPy array or integer | Optional |
| **kwds | Additional keyword arguments are documented in pandas.%(this-datatype)s.plot(). | Optional |
Returns: matplotlib.axes.Axes or numpy.ndarray of them.
Example - Given a Series of points randomly sampled from an unknown distribution, estimate its PDF using KDE with automatic bandwidth determination and plot the results, evaluating them at 1000 equally spaced points (default):
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
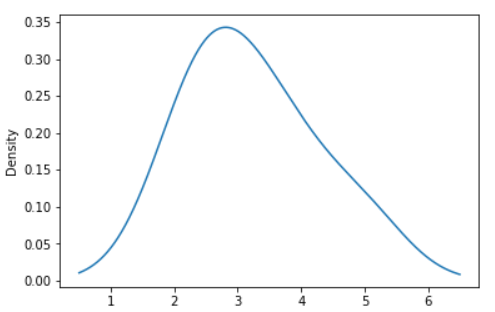
s = pd.Series([2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5])
ax = s.plot.kde()
Output:
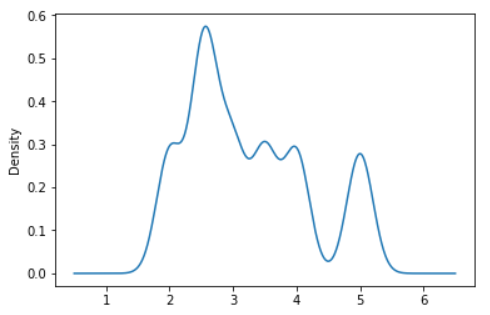
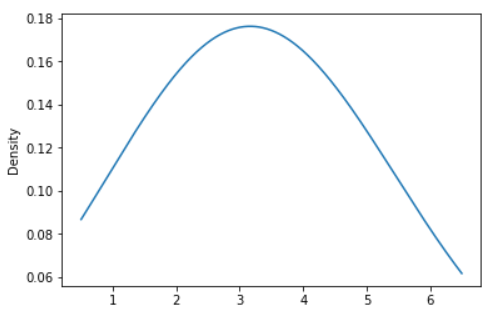
Example - A scalar bandwidth can be specified. Using a small bandwidth value can lead to over-fitting, while using a large bandwidth value may result in under-fitting:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5])
ax = s.plot.kde(bw_method=0.2)
Output:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5])
ax = s.plot.kde(bw_method=2)
Output:
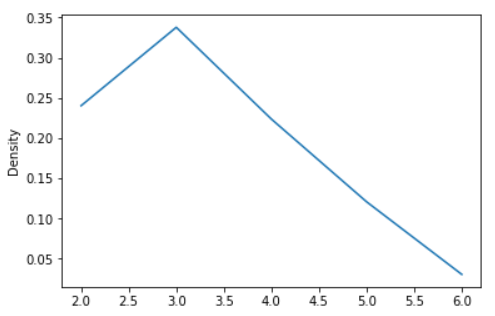
Example - Finally, the ind parameter determines the evaluation points for the plot of the estimated PDF:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
s = pd.Series([2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5])
ax = s.plot.kde(ind=[2, 3, 4, 5, 6])
Output:
Example - For DataFrame, it works in the same way:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'x': [2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5],
'y': [4, 3, 4.5, 4, 5, 5.5, 6],
})
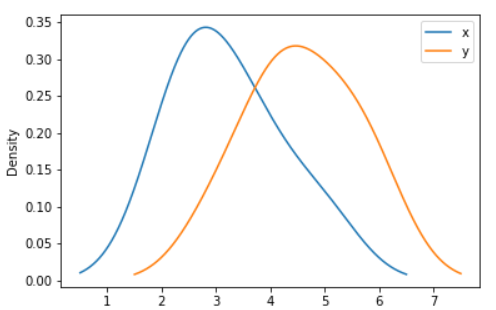
ax = df.plot.kde()
Output:
Example - A scalar bandwidth can be specified. Using a small bandwidth value can lead to over-fitting, while using a large bandwidth value may result in under-fitting:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'x': [2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5],
'y': [4, 3, 4.5, 4, 5, 5.5, 6],
})
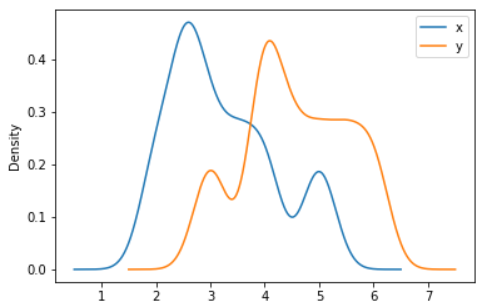
ax = df.plot.kde(bw_method=0.3)
Output:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'x': [2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5],
'y': [4, 3, 4.5, 4, 5, 5.5, 6],
})
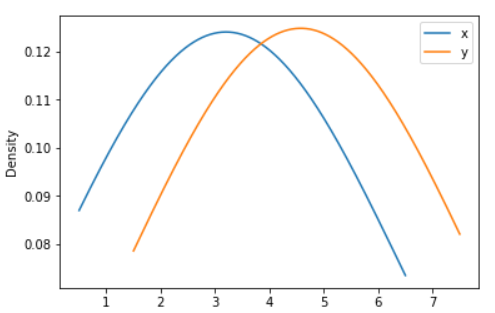
ax = df.plot.kde(bw_method=3)
Output:
Example - Finally, the ind parameter determines the evaluation points for the plot of the estimated PDF:
Python-Pandas Code:
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({
'x': [2, 3, 2.6, 3.5, 2.5, 4, 5],
'y': [4, 3, 4.5, 4, 5, 5.5, 6],
})
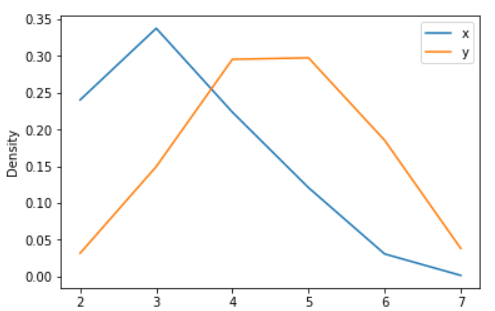
ax = df.plot.kde(ind=[2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
Output:
Previous: Series-plot.box() function
Next: Series-plot.hist() function