JavaScript: HTML Form - restricting the length
Checking string length
Sometimes situation arises when a field in an html form accept a restricted number of characters. For example a userid (length between 6 to 10 character) or password (length between 8 to 14 characters). You can write a JavaScript form validation script where the required field(s) in the HTML form accepts the restricted number of characters.
Javascript function to restrict length of user input
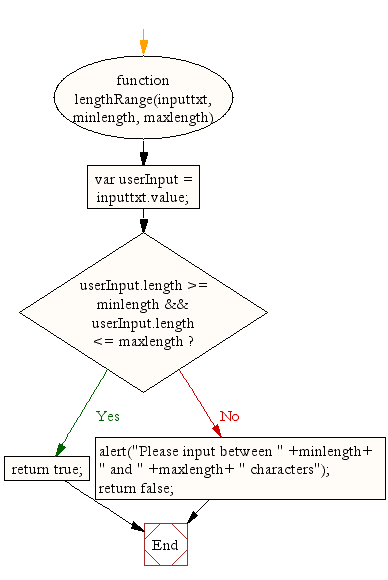
function lengthRange(inputtxt, minlength, maxlength)
{
var userInput = inputtxt.value;
if(userInput.length >= minlength && userInput.length <= maxlength)
{
return true;
}
else
{
alert("Please input between " +minlength+ " and " +maxlength+ " characters");
return false;
}
}
Flowchart:
Here's an example of the above function for a field that requires 6 to 8 characters to valid a usercode.
HTML Code
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>JavaScript form validation - checking non empty</title>
<link rel='stylesheet' href='form-style.css' type='text/css' />
</head>
<body onload='document.form1.text1.focus()'>
<div class="mail">
<p>Enter Userid [between 6 to 8 characters] and Submit</p>
<form name="form1" action="#">
<ul>
<li>Username:<input type='text' name='text1'/></li>
<li> </li>
<li class="submit"it"><input type="submit" name="submit" value="Submit" onclick="stringlength(document.form1.text1,6,8)"/></li>
<li> </li>
</form>
</ul>
</div>
<script src="string-lenght.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Javascript code
function stringlength(inputtxt, minlength, maxlength)
{
var field = inputtxt.value;
var mnlen = minlength;
var mxlen = maxlength;
if(field.length<mnlen || field.length> mxlen)
{
alert("Please input the userid between " +mnlen+ " and " +mxlen+ " characters");
return false;
}
else
{
alert('Your userid have accepted.');
return true;
}
}
CSS Code
li {list-style-type: none;
font-size: 16pt;
}
.mail {
margin: auto;
padding-top: 10px;
padding-bottom: 10px;
width: 400px;
background : #D8F1F8;
border: 1px soild silver;
}
.mail h2 {
margin-left: 38px;
}
input {
font-size: 20pt;
}
input:focus, textarea:focus{
background-color: lightyellow;
}
input submit {
font-size: 12pt;
}
.rq {
color: #FF0000;
font-size: 10pt;
}
View the example in the browser
Practice the example online
See the Pen string-length-1 by w3resource (@w3resource) on CodePen.
file_download Download the validation code from here.
Other JavaScript Validation:
- Checking for non-empty
- Checking for all letters
- Checking for all numbers
- Checking for floating numbers
- Checking for letters and numbers
- Checking string length
- Email Validation
- Date Validation
- A sample Registration Form
- Phone No. Validation
- Credit Card No. Validation
- Password Validation
- IP address Validation
Previous: JavaScript: HTML Form - checking for numbers and letters
Next: JavaScript: HTML Form - email validation
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
