Python Operators
Operators and Operands
In computer programming languages operators are special symbols which represent computations, conditional matching etc. The values the operator uses are called operands.
c = a + b Here a and b are called operands and '+' is an operator
Python supports following operators.
Contents:
Operator: Commands
Module of functions that provide the functionality of operators.
from operator import add, sub, mul, truediv, floordiv, mod, pow, neg, abs
from operator import eq, ne, lt, le, gt, ge
from operator import and_, or_, not_
from operator import itemgetter, attrgetter, methodcaller
import operator as op
sorted_by_second = sorted(<collection>, key=op.itemgetter(1))
sorted_by_both = sorted(<collection>, key=op.itemgetter(1, 0))
product_of_elems = functools.reduce(op.mul, <collection>)
LogicOp = enum.Enum('LogicOp', {'AND': op.and_, 'OR' : op.or_})
last_el = op.methodcaller('pop')(<list>)
Python Arithmetic Operators
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | x+y | Sum of x and y. |
| - | Subtraction | x-y | Difference of x and y. |
| * | Multiplication | x*y | Product of x and y. |
| / | Division | x/y | Quotient of x and y. |
| % | Modulus | x%y | Remainder of x divided by y. |
| ** | Exponent | x**y | x**y will give x to the power y |
| // | Floor Division | x/ y | The division of operands where the result is the quotient in which the digits after the decimal point are removed. |
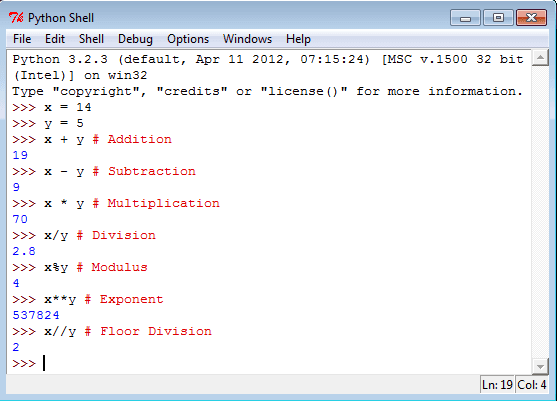
See the following statements in Python Shell.
Python Comparison Operators
| Operator | Name | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|---|
| == | Equal | x==y | True if x is exactly equal to y. |
| != | Not equal | x!=y | True if x is exactly not equal to y. |
| > | Greater than | x>y | True if x (left-hand argument) is greater than y (right-hand argument). |
| < | Less than | x<y | True if x (left-hand argument) is less than y (right-hand argument). |
| >= | Greater than or equal to | x>=y | True if x (left-hand argument) is greater than or equal to y (left-hand argument). |
| <= | Less than or equal to | x<=y | True if x (left-hand argument) is less than or equal to y (right-hand argument). |
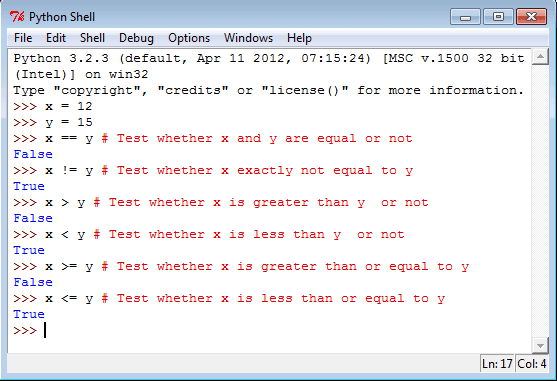
See the following statements in Python Shell.
Python Logical Operators
| Operator | Example | Result |
|---|---|---|
| and | (x and y) | is True if both x and y are true. |
| or | (x or y) | is True if either x or y is true. |
| not | (x not y) | If a condition is true then Logical not operator will make false. |
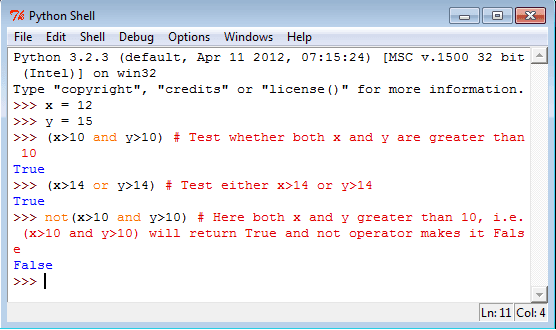
See the following statements in Python Shell.
Python Assignment Operators
| Operator | Shorthand | Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| += | x+=y | x = x + y | Adds 2 numbers and assigns the result to left operand. |
| -= | x-= y | x = x -y | Subtracts 2 numbers and assigns the result to left operand. |
| *= | x*= y | x = x*y | Multiplies 2 numbers and assigns the result to left operand. |
| /= | x/= y | x = x/y | Divides 2 numbers and assigns the result to left operand. |
| %= | x%= y | x = x%y | Computes the modulus of 2 numbers and assigns the result to left operand. |
| **= | x**=y | x = x**y | Performs exponential (power) calculation on operators and assign value to the equivalent to left operand. |
| //= | x//=y | x = x//y | Performs floor division on operators and assign value to the left operand. |
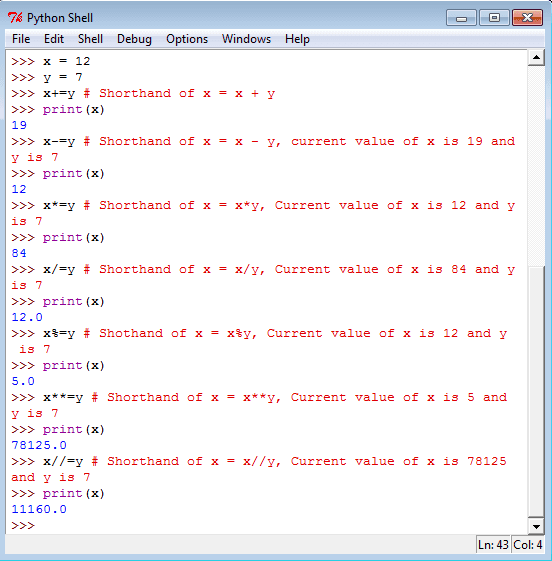
See the following statements in Python Shell.
Python Bitwise Operators
| Operator | Shorthand | Expression | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| & | And | x & y | Bits that are set in both x and y are set. |
| | | Or | x | y | Bits that are set in either x or y are set. |
| ^ | Xor | x ^ y | Bits that are set in x or y but not both are set. |
| ~ | Not | ~x | Bits that are set in x are not set, and vice versa. |
| << | Shift left | x <<y | Shift the bits of x, y steps to the left |
| >> | Shift right | x >>y | Shift the bits of x, y steps to the right. |
# Each step means 'multiply by two'
* Each step means 'divide by two'
Conditional Operators
Conditional expressions or ternary operator have the lowest priority of all Python operations. The expression x if C else y first evaluates the condition, C (not x); if C is true, x is evaluated and its value is returned; otherwise, y is evaluated and its value is returned.
Operator precedence
Operator precedence determines how operators are parsed concerning each other. The following table summarizes the operator precedence in Python, from lowest precedence (least binding) to highest precedence (most binding). Operators in the same box have the same precedence. Unless the syntax is explicitly given, operators are binary. Operators in the same box group left to right (except for exponentiation, which groups from right to left).
Note: Comparisons, membership tests, and identity tests, all have the same precedence and have a left-to-right chaining feature as described in the Comparisons section.
| Operator Name | Description |
|---|---|
| := | Assignment expression |
| lambda | Lambda expression |
| if – else | Conditional expression |
| or | Boolean OR |
| and | Boolean AND |
| not x | Boolean NOT |
| in, not in, is, is not, <, <=, >, >=, !=, == | Comparisons, including membership tests and identity tests |
| | | Bitwise OR |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR |
| & | Bitwise AND |
| <<, >> | Shifts |
| +, - | Addition and subtraction |
| *, @, /, //, % | Multiplication, matrix multiplication, division, floor division, remainder |
| +x, -x, ~x | Positive, negative, bitwise NOT |
| ** | Exponentiation |
| await x | Await expression |
| x[index], x[index:index], x(arguments...), x.attribute | Subscription, slicing, call, attribute reference |
| (expressions...),[expressions...], {key: value...}, {expressions...} | Binding or parenthesized expression, list display, dictionary display, set display |
Previous: Python Data Type
Next: Python If elif else
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
