Python Syntax
Introduction
Python is designed to be a highly readable language with a straightforward syntax. The syntax defines the rules for writing a Python program. A Python parser reads the program and translates it into executable code.
Python Line Structure:
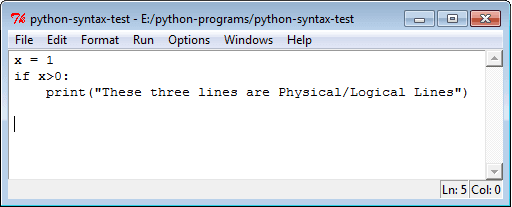
A Python program consists of logical lines. Every logical line is terminated by a NEWLINE token. A logical line may span one or more physical lines.
- A blank line contains only spaces, tabs, or comments. The Python interpreter ignores blank lines.
- A physical line is a sequence of characters terminated by an end-of-line sequence:
- On Windows: CR LF (carriage return followed by a line feed)
- On Unix/Linux: LF (line feed)
See the following example.
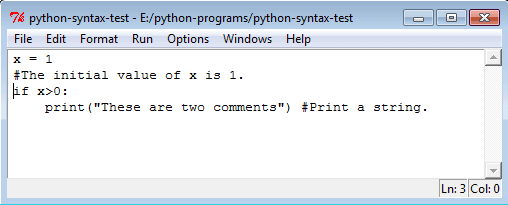
Comments in Python:
- A comment starts with the # symbol and continues until the end of the line.
- Comments are ignored by the Python interpreter and are not part of the program's output.
- Python does not have multi-line comment syntax like some other languages. If multiple lines are required for comments, each line should start with #.
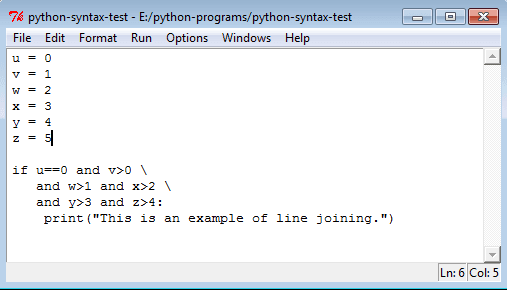
Joining two lines:
To write a long statement across multiple physical lines, use the backslash (\) at the end of the first line. This allows you to break the code logically without causing syntax errors.
Example:
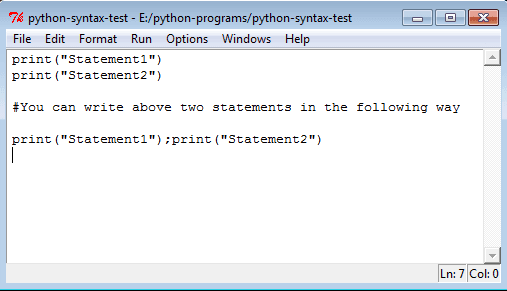
Multiple Statements on a Single Line:
You can write multiple statements on a single line using the semicolon (;) as a separator.
Indentation:
- Python uses whitespace (spaces or tabs) to define code blocks, unlike languages like C or Java that use curly braces {}.
- The amount of indentation is flexible, but all statements within a block must have the same level of indentation.
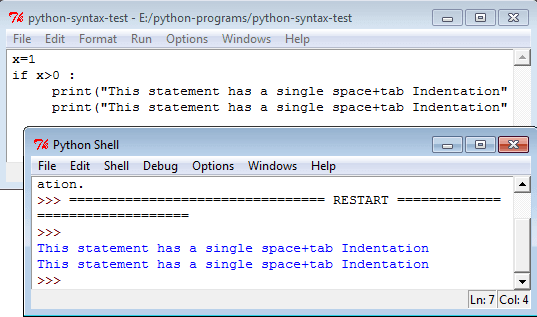
Incorrect example (no indentation):
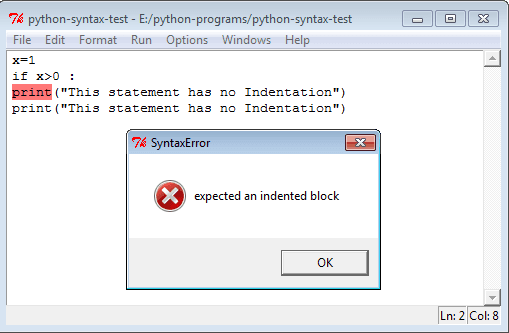
This is a program with single space indentation.
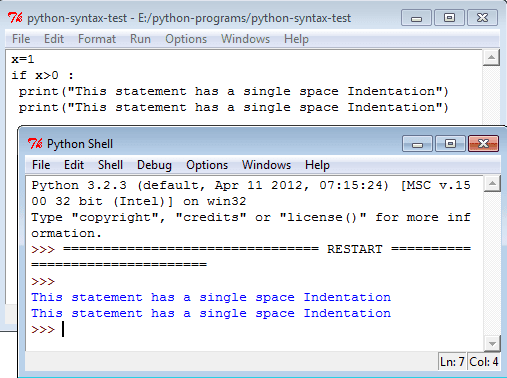
This is a program with single tab indentation.
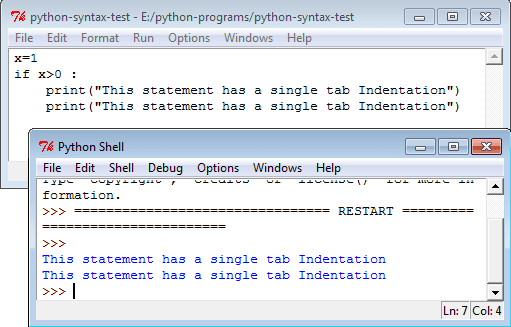
Here is an another program with an indentation of a single space + a single tab.
Python Coding Style (PEP 8)
- Indentation: Use 4 spaces per indentation level. Avoid tabs.
- Line Length: Limit lines to a maximum of 79 characters for better readability on small screens
- Blank Lines:
- Separate top-level functions and class definitions with two blank lines.
- Separate methods inside a class with one blank line.
- Inline Comments: Use inline comments sparingly, and make sure they are complete sentences.
- Whitespace: Add spaces around operators and after commas, to improve readability.
Python Reserve words:
The following are Python's reserved words. These cannot be used as variable names or identifiers in your program:
| False | class | finally | is | return |
| None | continue | for | lambda | try |
| True | def | from | nonlocal | while |
| and | del | global | not | with |
| as | el | if | or | yield |
| assert | else | import | pass | |
| break | except | in | raise |
Previous: CGI Programming
Next: Python Variable
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
