SQL LN() function
LN() function
SQL LN() function returns the natural logarithm of n, where n is greater than 0 and its base is a number equal to approximately 2.71828183.
Syntax:
LN(expression)
DB2, PostgreSQL, and Oracle
All of above platforms support the SQL syntax of LN().
MySQL and SQL Server
If you are using above two platforms, use LOG() instead.
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| expression | An expression which is a float or can be converted to a float. |
SQL LN() function: Visual presentation
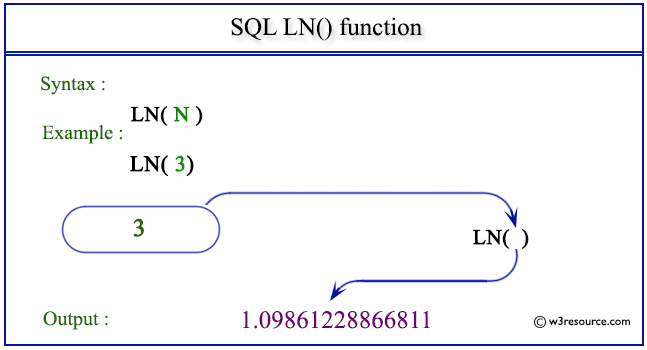
Example:
To get the natural logarithm of 65 from the DUAL table, the following SQL statement can be used:
-- This SQL statement calculates the natural logarithm of the number 65 and renames the result as 'natural_log of 65', selecting the result from the 'dual' table.
SELECT LN(65) "natural_log of 65"
-- SELECT statement retrieves data from the database
-- LN() function calculates the natural logarithm of the specified number
-- In this case, LN(65) calculates the natural logarithm of 65
FROM dual;
-- Specifies the 'dual' table, a special one-row, one-column table present in Oracle database
-- The 'dual' table is often used for performing calculations or returning single results in SQL queries
Explanation:
- This SQL query is straightforward, as it's only a single statement.
- The purpose of this query is to calculate the natural logarithm of the number 65.
- LN() is a mathematical function that calculates the natural logarithm of a given number.
- In this case, LN(65) will return the natural logarithm of 65, which is approximately 4.174387.
- The "natural_log of 65" is an alias provided to the result of the calculation, making it easier to identify in the query result.
- The 'dual' table is used here because it's a convenient way to execute single-row queries in Oracle SQL without needing to specify an actual table with data.
Output:
natural_log of 65
-----------------
4.17438727
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition.
Here is a slide presentation which covers the SQL arithmetic functions.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
