MySQL ABS() function
ABS() function
MySQL ABS() returns the absolute (positive) value of a number.
This function is useful in -
- It allows you to disregard the sign (positive or negative) of a number and work only with its magnitude.
- ABS() ensures that you're always working with positive values, reducing the likelihood of errors that can occur due to unexpected negative values.
- In applications like GIS (Geographic Information Systems), physics simulations, or navigation systems, ABS() is used to calculate distances between points regardless of their direction.
- ABS() is a fundamental function for calculating absolute deviations.
- In statistics, absolute deviation is used to quantify the variability or spread of a dataset.
- In scenarios where only positive results are meaningful, ABS() is applied to ensure that the output is always positive, regardless of the input.
Syntax:
ABS(N);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | A number whose absolute value is to be retrieved. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial presentation of MySQL ABS() function
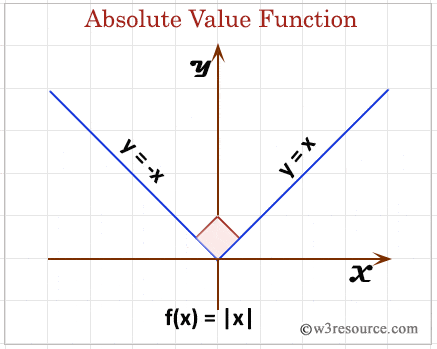
Example:
The following MySQL statement will return the absolute value of a positive number specified in the argument.
Code:
SELECT ABS(5);
Output:
mysql> SELECT ABS(5); +--------+ | ABS(5) | +--------+ | 5 | +--------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Example : ABS() function using negative value
The following MySQL statement will return the absolute value of a negative number defined in the argument.
Code:
SELECT ABS(-5);
Output:
mysql> SELECT ABS(-5); +---------+ | ABS(-5) | +---------+ | 5 | +---------+ 1 row in set (0.01 sec)
