MySQL SIGN() function
SIGN() function
MySQL SIGN() returns the sign of the argument.
The function returns 1 when the value of the argument is positive, returns -1 when the value of the argument is negative and return 0 when the value of the argument is 0.
This function is useful in -
- SIGN() provides a clear indication of the direction or polarity of a numeric value, helping users quickly understand if a value is positive, negative, or zero.
- In scenarios where you need to sort or rank values based on their sign, SIGN() provides a straightforward way to achieve this.
- In certain computations, especially those involving financial or scientific data, it's crucial to identify situations where a value might be negative or zero.
- SIGN() can be employed when performing statistical analysis to categorize data points into positive, negative, or zero groups, enabling more specific calculations.
- When performing operations like multiplication or division, the sign of the result depends on the signs of the operands.
Syntax:
SIGN(X);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| X | A number whose sign is to be retrieved. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial presentation of MySQL SIGN() function
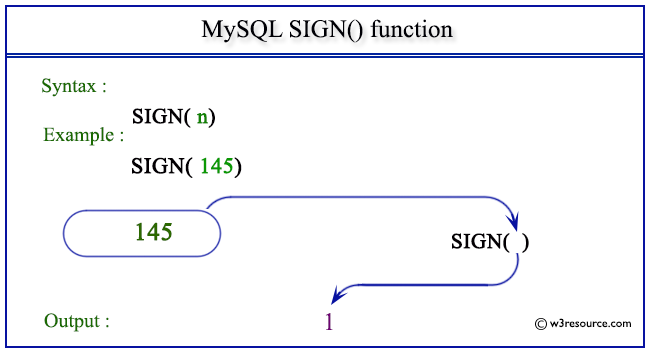
Example of MySQL SIGN() function
Code:
SELECT SIGN(-145), SIGN(0), SIGN(145);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will return the sign of given numbers -145, 0 and 145.
Output:
mysql> SELECT SIGN(-145), SIGN(0), SIGN(145); +------------+---------+-----------+ | SIGN(-145) | SIGN(0) | SIGN(145) | +------------+---------+-----------+ | -1 | 0 | 1 | +------------+---------+-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
