PHP: next() function
PHP: Advance the internal array pointer of an array
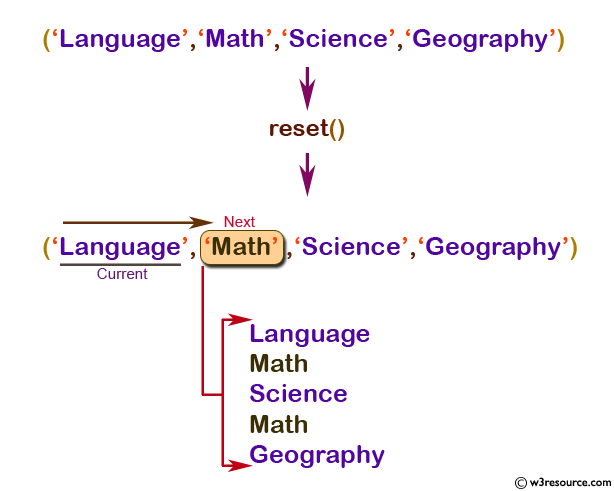
The next() function is used to advance the internal array pointer. next() behaves like current(), with one difference. It advances the internal array pointer one place forward before returning the element value.
Version:
(PHP 4 and above)
Syntax:
next(array_name)
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
Type |
| array_name | The input array. | Required | Array |
Return value:
The array value in the next place in the array pointed by internal array pointer, or FALSE if there are no more elements.
Value Type : Mixed*.
*Mixed: Mixed indicates multiple (but not necessarily all) types.
Example:
<?php
$val1 = array('Language', 'Math', 'Science', 'Geography');
$cval = current($val1);
echo "$cval <br />";
$cval = next($val1);
echo "$cval <br />";
$cval = next($val1);
echo "$cval <br />";
$cval= prev($val1);
echo "$cval <br />";
$cval= end($val1);
echo "$cval <br />";
?>
Output:
Language Math Science Math Geography
Pictorial Presentation:
View the example in the browser
Practice here online:
See also
