JavaScript setUTCMinutes() Method: Date Object
Description
The setUTCMinutes() method is used to set the minutes for a specified date according to Universal Coordinated Time (UTC).
Version
Implemented in JavaScript 1.3
Syntax
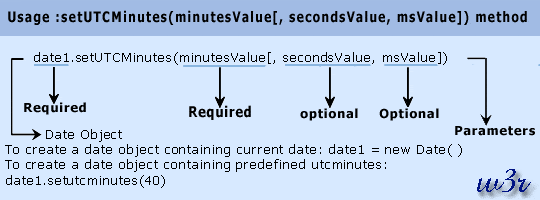
setUTCMinutes(minutesValue, secondsValue, msValue)
Parameter
minutesValue: An integer between 0 and 59, representing the minutes.
secondsValue: An integer between 0 and 59, representing the seconds. If you specify the secondsValue parameter, you must also specify the minutesValue.
msValue: A number between 0 and 999, representing the milliseconds. If you specify the msValue parameter, you must also specify the minutesValue and secondsValue.
Example:
In the following web document setUTCMinutes() method sets the minutes to 26.
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN"
"http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xml:lang="en" lang="en">
<head>
<meta http-equiv="content-type" content="text/html; charset=iso-8859-1" />
<title>JavaScript date object - setUTCMinutes() method example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 style="color: red">JavaScript date object : setUTCMinutes() method</h1>
<hr />
<script type="text/javascript">
//This is done to make the following JavaScript code compatible to XHTML. <![CDATA[
user_date = new Date()
document.write("Initial Minutes : "+user_date+"<br />")
user_date.setUTCMinutes(26)
document.write("After changing the current Minutes to 26 : "+user_date+"<br />")
//]]>
</script>
</body>
</html>
View the example in the browser
Supported Browser
| Internet Explorer 7 | Firefox 3.6 | Google Chrome 7 | Safari 5.0.1 | Opera 10 |
| Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
See also:
JavaScript Core objects, methods, properties.
Previous: JavaScript setUTCMilliseconds() Method: Date Object
Next: JavaScript setUTCmonth() Method: Date Object
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
