NumPy: numpy.ones() function
numpy.ones() function
The numpy.ones() function is used to create a new array of given shape and type, filled with ones. The ones() function is useful in situations where we need to create an array of ones with a specific shape and data type, for example in matrix operations or in initializing an array with default values.
Syntax:
numpy.ones(shape, dtype=None, order='C')
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| shape | Shape of the new array, e.g., (2, 3) or 2. | Required |
| dtype | The desired data-type for the array, e.g., numpy.int8. Default is numpy.float64. | optional |
| order | Whether to store multi-dimensional data in row-major (C-style) or column-major (Fortran-style) order in memory | optional |
Return value:
[ndarray] Array of ones with the given shape, dtype, and order.
Example-1: Create arrays of ones with NumPy's ones() function
>>> import numpy as np
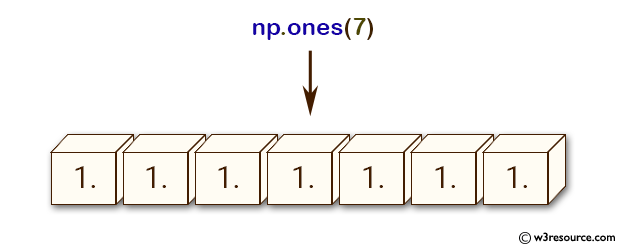
>>> np.ones(7)
array([ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
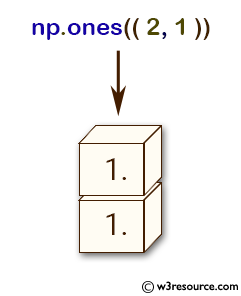
>>> np.ones((2, 1))
array([[ 1.],
[ 1.]])
>>> np.ones(7,)
array([ 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
>>> x = (2, 3)
>>> np.ones(x)
array([[ 1., 1., 1.],
[ 1., 1., 1.]])
>>>
In the above code:
np.ones(7): This creates a 1-dimensional array of length 7 with all elements set to 1.
np.ones((2, 1)): This creates a 2-dimensional array with 2 rows and 1 column, with all elements set to 1.
np.ones(7,): This is equivalent to np.ones(7) and creates a 1-dimensional array of length 7 with all elements set to 1.
x = (2, 3) and np.ones(x): This creates a 2-dimensional array with 2 rows and 3 columns, with all elements set to 1.
Visual Presentation:
Example: Createng a 3D array with ones along a specified axis
Code:
import numpy as np
# Create a 3D array with ones along the second axis
arr = np.ones((2, 3, 4), dtype=int)
arr[:, 1, :] = 2
print(arr)
Output:
[[[1 1 1 1] [2 2 2 2] [1 1 1 1]] [[1 1 1 1] [2 2 2 2] [1 1 1 1]]]
In the above example, we create a 3D array with dimensions (2, 3, 4) using np.ones() function. We then set the values of the second axis to 2, resulting in a 3D array with ones along the first and third axis and 2's along the second axis.
Example: Create a 2D array with a custom data type and byte order
Code:
import numpy as np
# Create a 2D array of unsigned 16-bit integers with little-endian byte order
nums = np.ones((2, 3), dtype=np.dtype('<u2'))
print(nums)
Output:
[[1 1 1] [1 1 1]]
In the above example, we create a 2D array with dimensions (2, 3) using np.ones() function. We specify the data type using np.dtype() function, which represents unsigned 16-bit integers with little-endian byte order. The resulting array has values of 1 and the specified data type and byte order.
Advanced Use Cases
Use Case 1: Initializing Weight Matrices in Machine Learning
# Initialize a weight matrix for a neural network layer
weights = np.ones((10, 5)) # 10 neurons, 5 inputs per neuron
print("Weight Matrix:\n", weights)
Use Case 2: Creating Masks for Image Processing
# Create a mask for image processing (e.g., 100x100 image)
mask = np.ones((100, 100), dtype=bool)
print("Mask:\n", mask)
Performance Considerations
Memory Efficiency
- numpy.ones() efficiently allocates memory for the array and initializes all elements to one.
- For large arrays, specifying the dtype can significantly reduce memory usage.
Comparison with Other Functions
- numpy.zeros(): Similar to numpy.ones(), but initializes arrays with zeros.
- numpy.full(): Creates arrays filled with a specified value.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) - numpy. ones()
1. What is the numpy.ones() function?
The numpy.ones() function in NumPy creates a new array of a specified shape, filled with ones.
2. What are the common use cases for numpy.ones()?
- Initializing arrays for mathematical operations.
- Creating arrays with default values for further modification.
- Setting up identity matrices or masks in data processing.
3. What types of arrays can numpy.ones() create?
numpy.ones() can create arrays of any shape and dimension specified by the user, including multi-dimensional arrays.
4. What data types can be used with numpy.ones()?
You can specify the data type of the array elements using the dtype parameter, supporting all standard NumPy data types.
5. How does numpy.ones() handle memory allocation?
numpy.ones() efficiently allocates memory for the array and initializes all elements to one, which can be important for performance in large arrays.
6. Can the shape of the array created by numpy.ones() be changed after creation?
While you can't change the shape of an array directly, you can use methods like reshape() to create a new array with the desired shape from the existing one.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: identity()
Next: ones_like()