NumPy: numpy.vander() function
numpy.vander() function
The numpy.vander() function returns a Vandermonde matrix of a given input array. The Vandermonde matrix is a matrix with the elements of an input vector raised to different powers, where the power is determined by the position of the element in the vector.
Syntax:
numpy.vander(x, N=None, increasing=False)
Parameters:
| Name | Discription | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| x | 1-D input array. | Required |
| N | Number of columns in the output. If N is not specified, a square array is returned (N = len(x)). | optional |
| increasing | Order of the powers of the columns. If True, the powers increase from left to right, if False (the default) they are reversed. |
optional |
Return value:
out : ndarray - Vandermonde matrix. If increasing is False, the first column is x^(N-1), the second x^(N-2) and so forth. If increasing is True, the columns are x^0, x^1, ..., x^(N-1).
Example: Generating a Vandermonde matrix using NumPy
>>> import numpy as np
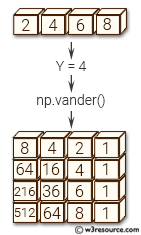
>>> a = np.array ([1,2,4,6])
>>> Y=4
>>> np.vander(a, Y)
array([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],
[ 8, 4, 2, 1],
[ 64, 16, 4, 1],
[216, 36, 6, 1]])
>>> np.column_stack([a**(Y-1-i) for i in range(Y)])
array([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],
[ 8, 4, 2, 1],
[ 64, 16, 4, 1],
[216, 36, 6, 1]])
In the above code, the np.vander function is used to create the Vandermonde matrix for the input array a and power Y. The resulting matrix has Y columns, with the first column consisting of ones, and subsequent columns consisting of powers of the input array a, raised to decreasing powers of Y-1.
The np.column_stack function is used to stack the individual arrays created using the list comprehension. This creates the same Vandermonde matrix as the one generated using np.vander.
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: Vandermonde Matrix Generation with Numpy
>>> import numpy as np
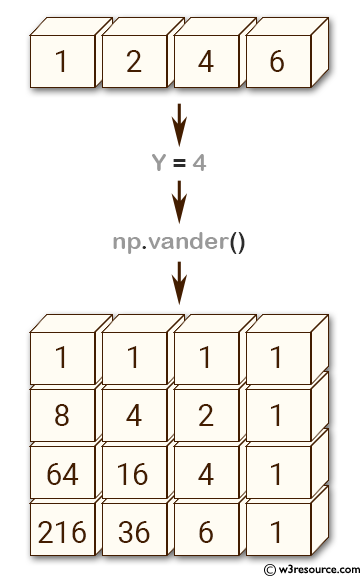
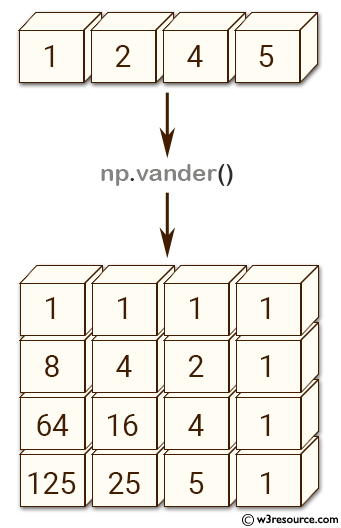
>>> a = np.array([1,2,4,5])
>>> np.vander(a)
array([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],
[ 8, 4, 2, 1],
[ 64, 16, 4, 1],in
[125, 25, 5, 1]])
>>> np.vander(a, increasing=True)
array([[ 1, 1, 1, 1],
[ 1, 2, 4, 8],
[ 1, 4, 16, 64],
[ 1, 5, 25, 125]])
In the above code, the first example generates a Vandermonde matrix of order n (where n is the length of a) with decreasing powers of elements. The resulting matrix has dimensions (n, n), with the i-th row consisting of the elements a**(n-1-i), where ** denotes exponentiation.
The second example generates a Vandermonde matrix with increasing powers of elements by passing the increasing=True parameter to np.vander(). The resulting matrix has the same dimensions as the first example, but the i-th row consists of the elements a**i.
Both examples demonstrate the versatility of np.vander() for generating Vandermonde matrices with varying order and power configurations.
Pictorial Presentation:
The determinant of a square Vandermonde matrix is the product of the differences between the values of the input vector:
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.array([1,2,4,5])
>>> np.linalg.det(np.vander(a))
72.000000000000071
>>> (5-4)*(5-2)*(5-1)*(4-2)*(4-1)*(2-1)
72
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: triu()
Next: The Matrix class mat()
