NumPy: numpy.triu() function
numpy.triu() function
The numpy.triu() function is used to get a copy of a matrix with the elements below the k-th diagonal zeroed.
Syntax:
numpy.triu(m, k=0)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| m | Number of rows in the array. | |
| k | Diagonal above which to zero elements. k = 0 (the default) is the main diagonal, k < 0 is below it and k > 0 is above. | optional |
Return value:
Return a copy of a matrix with the elements below the k-th diagonal zeroed.
Example: Using the triu() function to extract the upper triangle of a matrix
import numpy as np
m = np.matrix([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
print("Sample matrix")
print(m)
print("\ntriu() function without any parameter:")
print(np.triu(m))
print("\nBelow 1st diagonal zeroed.")
print(np.triu(m,-1))
print("\nBelow 2nd diagonal zeroed.")
print(np.triu(m,-2))
Output:
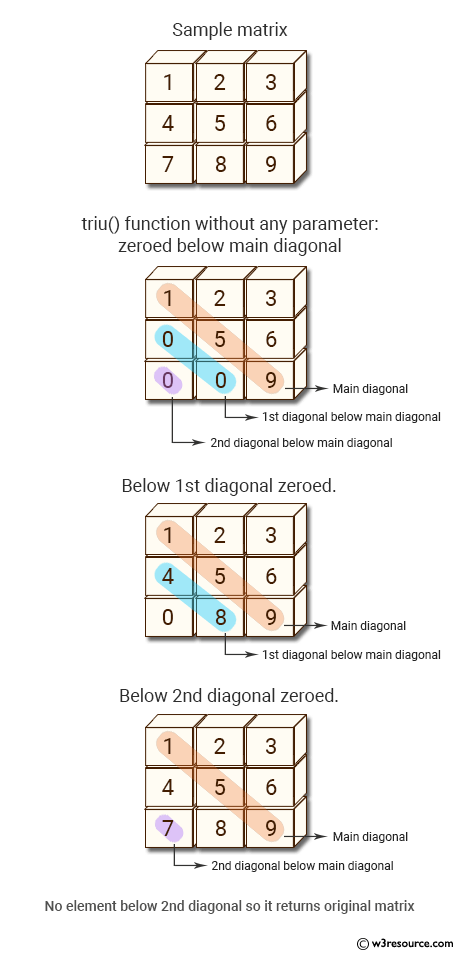
Sample matrix [[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]] triu() function without any parameter: [[1 2 3] [0 5 6] [0 0 9]] Below 1st diagonal zeroed. [[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [0 8 9]] Below 2nd diagonal zeroed. [[1 2 3] [4 5 6] [7 8 9]]
The above code demonstrates how to use the triu() function in NumPy to extract the upper triangle of a matrix. The input matrix is first defined as a 3x3 matrix using the np.matrix() function. The triu() function is then used to extract the upper triangle of the matrix, with the default parameter of 0. The output is printed using the print() function.
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
