NumPy: numpy.fromiter() function
numpy.fromiter() function
The numpy.fromiter() function is used to create a new 1-dimensional array from an iterable object.
The fromiter() function is useful when we want to create a new numpy array from an iterable object without having to convert the iterable to a list or tuple first. It is also useful when we have a large dataset and we do not want to load it all into memory at once. Instead, we can read it in chunks using a generator and create a new numpy array from each chunk using fromiter().
Syntax:
numpy.fromiter(iterable, dtype, count=-1)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| iterable | An iterable object providing data for the array. | Required |
| dtype | The data-type of the returned array. | Required |
| count | The number of items to read from iterable. The default is -1, which means all data is read. | Optional |
Return value:
out : ndarray
The output array.
Example: Creating NumPy array from iterable using fromiter()
>>> import numpy as np
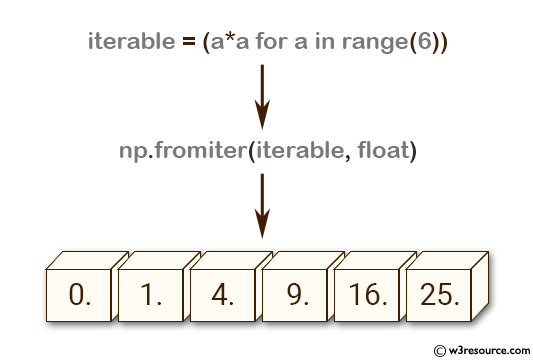
>>> iterable = (a*a for a in range(6))
>>> np.fromiter(iterable, float)
array([ 0., 1., 4., 9., 16., 25.])
In the above code, an iterable object is created using a generator expression that yields the squares of integers from 0 to 5.
The fromiter() function is then called with the iterable object and the data type of the resulting array as arguments. It returns a new one-dimensional NumPy array containing the values yielded by the iterable object, converted to the specified data type.
In this case, the resulting array is of type float and contains the first six perfect squares: 0.0, 1.0, 4.0, 9.0, 16.0, and 25.0.
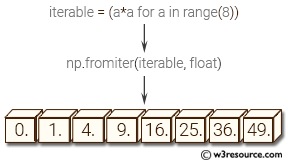
Visual Presentation:
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) - numpy. fromiter()
1. What is the purpose of numpy.fromiter()?
numpy.fromiter() is used to create a new one-dimensional array from an iterable.
2. When should we use numpy.fromiter()?
You should use numpy.fromiter() when you need to efficiently convert an iterable to a NumPy array, especially when the size of the iterable is not known beforehand.
3. How does numpy.fromiter() improve performance?
numpy.fromiter() can improve performance by avoiding the overhead of creating a list first and then converting it to an array, as it directly constructs the array from the iterable.
4. Can numpy.fromiter() handle all types of iterables?
numpy.fromiter() can handle any iterable that yields elements which can be converted to the specified data type of the array.
5. Is it necessary to know the length of the iterable when using numpy.fromiter()?
No, it is not necessary to know the length of the iterable beforehand. However, specifying the length can lead to further performance optimizations.
6. What data types can be specified with numpy.fromiter()?
numpy.fromiter() can create arrays of any specified NumPy data type.
7. Are there any limitations on the elements yielded by the iterable?
The elements yielded by the iterable must be compatible with the specified data type of the resulting array. If the elements are not compatible, an error will be raised.
8. How does numpy.fromiter() handle errors during the conversion process?
If an element of the iterable cannot be converted to the specified data type, numpy.fromiter() will raise a ValueError or TypeError.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: fromfunction()
Next: fromstring()
