NumPy: numpy.zeros_like() function
numpy.zeros_like() function
The numpy.zeros_like() function takes an array_like object as input and returns an array of the same shape, size, and dtype with all elements set to zero.
This function is useful when you want to create an array of zeros with the same shape and type as another array without explicitly specifying the shape and data type. It can also be used to initialize a new array with the same shape as an existing array but with all elements set to zero.
Syntax:
numpy.zeros_like(a, dtype=None, order=’K’, subok=True)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| a | The shape and data-type of a define these same attributes of the returned array. | Required |
| dtype | Overrides the data type of the result. New in version 1.6.0. | optional |
| order | Overrides the memory layout of the result. 'C' means C-order, 'F' means F-order, 'A' means 'F' if a is Fortran contiguous, 'C' otherwise. 'K' means match the layout of a as closely as possible. New in version 1.6.0. | optional |
| subok | If True, then the newly created array will use the sub-class type of 'a', otherwise it will be a base-class array. Defaults to True. | optional |
Return value:
[ndarray] Array of zeros with the same shape and type as a.
Example: Creating an array of zeros with the same shape and data type as a given array using numpy.zeros_like()
>>> import numpy as np
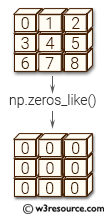
>>> a = np.arange(4)
>>> a = a.reshape((2, 2))
>>> a
array([[0, 1],
[2, 3]])
>>> np.zeros_like(a)
array([[0, 0],
[0, 0]])
In the above code an array a is created using np.arange(4) and is reshaped into a 2x2 array using .reshape((2,2)). Next, numpy.zeros_like(a) is called, which returns an array of zeros with the same shape and data type as a. This means that the returned array will also be a 2x2 array of integers filled with zeros.
Visual Presentation:
Example: Creating an array of zeros with the same shape and data type as an existing array
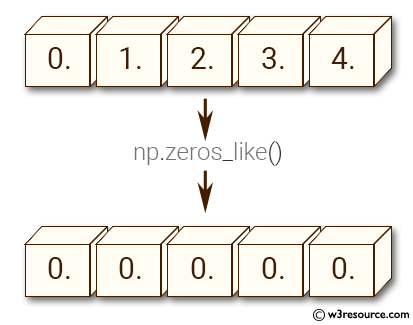
>>> import numpy as np
>>> b = np.arange(5, dtype=float)
>>> b
array([ 0., 1., 2., 3., 4.])
>>> np.zeros_like(b)
array([ 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
Here the code creates a one-dimensional NumPy array b containing float values from 0 to 4 using the arange() function. Then, the zeros_like() function creates a new NumPy array of zeros with the same shape and data type as b. Since b is a one-dimensional array of length 5, zeros_like(b) also creates a one-dimensional array of the same length, containing all zeros and having the same data type (float).
Visual Presentation:
Frequently asked questions (FAQ) - numpy. zeros_like ()
1. What is numpy.ones_like()?
numpy.ones_like() is a NumPy function that creates a new array of ones with the same shape and type as a given array.
2. When should we use numpy.ones_like()?
Use numpy.ones_like() when you need an array of ones that matches the shape and data type of an existing array. It is particularly useful for initializing arrays for computations that require a matching structure.
3. How does numpy.ones_like() differ from numpy.ones()?
numpy.ones_like() creates an array with the same shape and type as an existing array, whereas numpy.ones() creates an array of a specified shape and data type from scratch.
4. Can numpy.ones_like() handle different data types?
Yes, numpy.ones_like() can handle different data types and will match the data type of the input array unless specified otherwise.
5. Is numpy.ones_like() compatible with multi-dimensional arrays?
Yes, numpy.ones_like() works with arrays of any number of dimensions, creating a new array of ones that mirrors the dimensions of the input array.
6. What happens if the input array is empty?
If the input array is empty, numpy.ones_like() will return an empty array of ones with the same shape and type as the input.
7. Are there any performance considerations?
numpy.ones_like() is optimized for performance, but creating large arrays can still be memory-intensive. Ensure your system has sufficient memory for large array operations.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
